Abstract
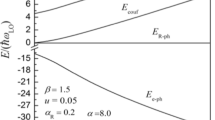
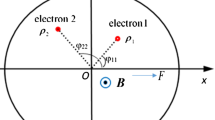
The influence of the Rashba effect on the ground-state properties of the Fröhlich bipolaron in a quantum dot is first studied using the variational method of Pekar type based on the Lee–Low–Pines unitary transformation. The results indicate that, under the condition of strong electron–phonon coupling (coupling strength \(\alpha >6\)), the condition of forming bipolaron in a quantum dot (binding energy \(E_{\mathrm{b}>0} )\) is naturally met; the bipolaron binding energy \(E_\mathrm{b} \) increases with increasing confinement strength of the quantum dot \(\omega _0 \), dielectric constant ratio of medium \(\omega _0\) and electron–phonon coupling strength \(\alpha \) and increases or decreases linearly with increasing Rashba spin–orbit coupling strength \(\alpha _\mathrm{R} \). The bipolaron in quantum dot is in a bound state, and the contribution of the Rashba effect to the ground-state energy consists of \(E(\uparrow \uparrow )\), \(E(\downarrow \downarrow )\) and \(E(\uparrow \downarrow )\), corresponding to three spin states of two electrons as follows, spin-parallel and antiparallel; the absolute value of the ground-state energy increases with increasing \(\eta \) and \(\alpha \) and increases or decreases linearly with increasing \(\alpha _\mathrm{R} \); in the interaction energy \(E_\mathrm{int} \) of the ground-state bipolaron, the electron–phonon coupling energy \(E_{\mathrm{e}-\mathrm{ph}}\) obviously takes a larger ratio than the Rashba spin–orbit coupling energy \(E_{\mathrm{SO}} \), but the electron–phonon coupling and the Rashba spin–orbit coupling influence and infiltrate each other.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
X.M. Dou, X.Y. Chang, B.Q. Sun et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 221903 (2009)
Z. Yu, Y. Guo, J. Zheng, F. Chi, Chin. Phys. B 22, 117303 (2013)
Y.F. Huang, Z.W. Yan, Phys. E 40, 2982 (2008)
H.Z. Tang, L.X. Zhai, J.J. Liu, Chin. Phys. B 21, 120303 (2012)
F. Chi, L.L. Sun, Y. Guo, J. Appl. Phys. 116, 164305 (2014)
A.X. Li, S.Q. Duan, Chin. Phys. B 21, 117201 (2012)
A.V. Moroz, C.H.W. Barnes, Phys. Rev. B 60, 14272 (1999)
Q.F. Sun, X.X. Xie, J. Wang, Phys. Rev. B 77, 035327 (2008)
S. Bandyopadhyay, Phys. Rev. B 61, 13813 (2000)
E. Tsitsishvili, G.S. Lozano, A.O. Gogolin, Phys. Rev. B 70, 115316 (2004)
M.S. Kushwaha, J. Appl. Phys. 104, 083714 (2008)
J.L. Li, Y.X. Li, Chin. Phys. Lett. 27, 057202 (2010)
H. Hassanabadi, H. Rahimov, S. Zarrinkamar, Few-Body Syst. 52, 87 (2012)
L.C. Fai, V. Teboul, A. Montei et al., Condens. Matter. Phys. 8, 639 (2005)
J.W. Yin, W.P. Li, Y.F. Yu et al., J. Low Temp. Phys. 163, 53 (2011)
S.P. Shan, S.H. Chen, J.L. Xiao, J. Low Temp. Phys. 176, 93 (2014)
X.Q. Zhang, Y.S. Wang, Z. Xu et al., Acta Phys. Sin. 48, 180 (1999). (in Chinese)
J.S. Pan, Phys. Stat. Sol(b) 127, 307 (1985)
Eerdunchaolu, W. Xin, Phys. B 406, 358 (2011)
P.M. Krishna, S. Mukhopadhyay, A. Chatterjee, Phys. Lett. A. 360, 655 (2007)
T.D. Lee, F.M. Low, D. Pines, Phys. Rev. 90, 297 (1953)
T. Yildirim, A. Ercelebi, J. Phys. Conden. Matt. 3, 1271 (1999)
J. Adamowski, Phys. Rev. B 39, 3649 (1989)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National Nature Science Foundation of Hebei Province, China (No. E2013407119), and by the Items of Institution of Higher Education Scientific Research of Hebei Province, China (Nos. ZD20131008, Z2015149 and Z2015219).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wuyunqimuge, Zhang, Y., Yin, HW. et al. Influence of the Rashba Effect on the Ground-State Properties of the Fröhlich Bipolaron in a Quantum Dot. J Low Temp Phys 187, 221–231 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-016-1663-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-016-1663-0