Abstract
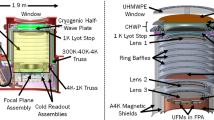
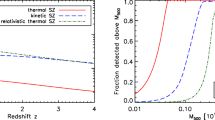
The B-mode Foreground Experiment (BFORE) is a proposed NASA balloon project designed to make optimal use of the sub-orbital platform by concentrating on three dust foreground bands (270, 350, and 600 GHz) that complement ground-based cosmic microwave background (CMB) programs. BFORE will survey \(\sim \)1/4 of the sky with 1.7–3.7 arcminute resolution, enabling precise characterization of the Galactic dust that now limits constraints on inflation from CMB B-mode polarization measurements. In addition, BFORE’s combination of frequency coverage, large survey area, and angular resolution enables science far beyond the critical goal of measuring foregrounds. BFORE will constrain the velocities of thousands of galaxy clusters, provide a new window on the cosmic infrared background, and probe magnetic fields in the interstellar medium. We review the BFORE science case, timeline, and instrument design, which is based on a compact off-axis telescope coupled to \({>}10,000\) superconducting detectors.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Baumann et al., AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 1141 (2009), p. 10 . doi:10.1063/1.3160885
C.L. Bennet et al., Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 208, 674 (2013). doi:10.1088/0067-0049/208/2/20
Planck Collaboration XXX, accepted in Astronomy and Astrophysics (2015). arXiv:1409.5738
B.T. Draine, A.A. Fraisse, Astrophys. J. 696, 1 (2009). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/696/1/1
Planck Collaboration I, accepted in Astronomy and Astrophysics (2015). arXiv:1502.01582
P.A.R. Ade et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 241101 (2014). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.241101
BICEP2/Keck and Planck Collaborations, Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 101301 (2015). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.114.101301
E.D. Kovetz, M. Kamionkowski, Phys. Rev. D 91, 081303 (2015). doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.91.081303
B. Reichborn-Kjennerud et al., Proc. SPIE 7741, 77411C (2014). doi:10.1117/12.857138
J.P. Filippini et al., Proc. SPIE 7741, 74111N (2010). doi:10.1117/12.857720
J. Lazear et al., Proc. SPIE 9153, 91531L (2014). doi:10.1117/12.2056806
Z. Staniszewski et al., J. Low Temp. Phys. 167, 827 (2012). doi:10.1007/s10909-012-0510-1
S. W. Henderson et al., J. Low Temp. Phys. This Special Issue (2015)
K. Arnold et al., Proc. SPIE 9153, 91531F (2014). doi:10.1117/12.2057332
B.A. Benson et al., Proc. SPIE 9153, 91531P (2014). doi:10.1117/12.2057305
C. Armitage-Caplan et al., Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 418, 1498 (2011). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.19307
P. Predehl et al., Proc. SPIE 9144, 91441T (2014). doi:10.1117/12.2055426
Z. Staniszewski et al., Astrophys. J. 701, 32 (2009). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/701/1/32
F. Menanteau et al., Astrophys. J. 723, 1523 (2010). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/722/2/1148
Planck Collaboration VIII, Astron. Astrophys. 28, A28 (2011). doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201116459
N. Hand et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 041101 (2012). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.109.041101
B.A. Benson et al., Astrophys. J. 592, 674 (2003). doi:10.1086/375864
S. Bhattacharya, A. Kosowsky, Phys. Rev. D 77, 083004 (2008). doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.77.083004
E.-M. Mueller, F. de Bernardis, R. Bean, M.D. Niemack, Phys. Rev. D 92, 063501 (2015). doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.92.063501
L. Knox, G. Holder, S. Church, Astrophys. J. 612(1), 96 (2004). doi:10.1086/422447
P. Hennebelle, E. Falgarone, Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 20, 1 (2012). doi:10.1007/s00159-012-0055-y
G. Pisano et al., Proc. SPIE 9153, 915317 (2014). doi:10.1117/12.2056380
R. Datta et al., J. Low Temp. Phys. 176(5), 670 (2014). doi:10.1007/s10909-014-1134-4
M.D. Niemack et al., J. Low Temp. Phys. 167(5), 917 (2014). doi:10.1007/s10909-012-0554-2
J. Hubmayr et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 106, 073505 (2015). doi:10.1063/1.4913418
R. Duan et al., Proc. SPIE 7741, 77411V (2010). doi:10.1117/12.856832
O. Noroozian et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 103(20), 202602 (2013). doi:10.1063/1.4829156
S. Dicker et al., Proc. SPIE 9153, 91530J (2014). doi:10.1117/12.2056455
Acknowledgments
The development of multichroic detectors and lenses was supported by NASA Grants NNX13AE56G and NNX14AB58G.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niemack, M.D., Ade, P., de Bernardis, F. et al. BFORE: The B-mode Foreground Experiment. J Low Temp Phys 184, 746–753 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-015-1395-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-015-1395-6