Abstract
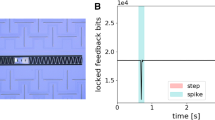
Once that the focal plane of the HFI instrument of the Planck mission (launched in May 2009) has reached operational temperature, we have observed the thermal effect of cosmic ray interaction with the Planck satellite, located at Lagrangian point L2. When a particle hits a component of the bolometers (e.g.: thermometer, grid or wafer) composing the focal plane of HFI, a thermal spike (called glitch), due to deposited energy, is observed. Processing these data revealed another effect due to high energy cosmic ray particle showers: High Coincidence Events (HCE), composed of glitches occurring coincidentally in many detectors and with a temperature increase from nK to \(\upmu \)K after the shower. A flux of about 100 HCE per hour has been calculated. Two types of HCE have been detected: fast and slow. For the first type, the untouched bolometers reach the same temperature as the touched ones in a few seconds which can be explained by a storage of the deposited energy in the stainless steel focal plane. The second type of HCE is not fully understood yet. These effects might be explained by extra conduction from the helium released from cryogenic surfaces, creating a temporary thermal link between the different stages of the HFI.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Planck Collaboration, Planck 2013 results I, Submitted to A & A (2013).
W.A. Holmes, J.J. Bock, B.P. Crill, T.C. Koch, W.C. Jones, A.E. Lange, C.G. Paine, Appl. Opt. 47, 32 (2008)
B. Collaudin, T. Passvogel, Cryogenics 39, 157–165 (1999)
Planck Collaboration, Planck 2013 results X, Submitted to A & A (2013).
P. Meyer, Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 33, 323–81 (1983)
R.C. Reedy, J.R. Arnold, D. Lal, Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 33, 505–37 (1983)
A. Mohammadzadeh, B. Nickson, R. Harboe Sorensen, ESA, Dedicated instruments to monitor the space radiation environment, (1998)
M. Piat, University Paris Sud, PhD Thesis, (2000).
A. Cruciani, L.J. Swenson, A. Monfardini, N. Boudou, M. Calvo, M. Roesch, J. Low. Temp. Phys. 167, 311–317 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miniussi, A., Puget, JL., Holmes, W. et al. Study of Cosmic Ray Impact on Planck/HFI Low Temperature Detectors. J Low Temp Phys 176, 815–821 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-014-1104-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-014-1104-x