Abstract
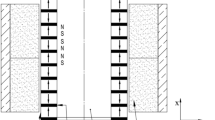
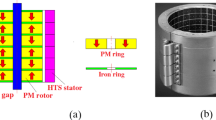
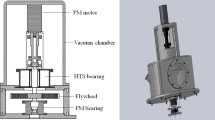
The magnetic bearing is considered as one of the most prospective applications of high temperature superconductors (HTSs) which can realize stable levitation in a magnetic field generated by permanent magnet devices or coils. The exploration of this kind of HTS bearing through numerical investigation is usually made by assuming the induced current circulates only within the ab-plane and thus simplifying the actual three-dimensional problem to a two-dimensional one. In this paper, on the basis of the three-dimensional model of the HTS bulk established before, we further introduce the developed finite-element software to calculate the magnetic field generated by a magnetic rotor which is composed of permanent magnet (PM) rings and ferromagnet (FM) shims, and in this way, we can investigate the magnetic forces (radial force and axial force) of a simplified HTS bearing model, i.e., two symmetric HTS bulks and a magnetic rotor, at a three-dimensional level. The investigations performed in this paper lead to the observations: the favorable configuration to construct the HTS bearing is that the axial height of each HTS element should be equivalent to the axial heights of PM ring plus FM shim; the increase of the radial thickness of PM ring will improve both the radial force and the axial force considerably, but its margin decreases; the enhancement of critical current density of HTSs due to the decrease of operating temperature can result in a higher increase of both the radial and axial force with a lower nominal gap between the HTSs and the magnetic rotor.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.R. Hull, Supercond. Sci. Technol. 13, R1 (2000)
P. Kummeth, W. Nick, H.W. Neumueller, Physica C 426–431, 739 (2005)
Z. Deng, Q. Lin, J. Wang, J. Zheng, G. Ma, Y. Zhang, S. Wang, Cryogenics 49, 259 (2009)
B.J. Park, Y.H. Han, S.Y. Jung, C.H. Kim, S.C. Han, J.P. Lee, B.C. Park, T.H. Sung, Physica C 470, 1772 (2010)
Q.X. Lin, D.H. Jiang, G.T. Ma, J.S. Wang, Z.G. Deng, J. Zheng, S.Y. Wang, C.Y. Yuan, IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 22, 5201604 (2012)
K. Demachi, A. Miura, T. Uchimoto, K. Miya, H. Higawa, R. Takahata, H. Kameno, Physica C 357–360, 882 (2001)
K. Demachi, K. Matsunaga, Physica C 412–414, 789 (2004)
Y. Luo, T. Takagi, K. Miya, Cryogenics 39, 331 (1999)
R. Shiraishi, K. Demachi, M. Uesaka, Physica C 392–396, 734 (2003)
I. Masaie, K. Demachi, T. Ichihara, M. Uesaka, IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 15, 2257 (2005)
I. Masaie, K. Demachi, T. Ichihara, M. Uesaka, IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 16, 1807 (2006)
N. Koshizuka, Physica C 445–448, 1103 (2006)
M. Strasik, J.R. Hull, J.A. Mittleider, J.F. Gonder, P.E. Johnson, K.E. McCrary, C.R. McIver, Supercond. Sci. Technol. 23, 034021 (2010)
F.N. Werfel, U. Floegel-Delor, T. Riedel, R. Rothfeld, D. Wippich, B. Goebel, G. Reiner, N. Wehlau, IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 20, 2272 (2010)
F.N. Werfel, U. Floegel-Delor, R. Rothfeld, T. Riedel, B. Goebel, D. Wippich, P. Schirrmeister, Supercond. Sci. Technol. 25, 014007 (2012)
G.T. Ma, J.S. Wang, S.Y. Wang, IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 20, 2219 (2010)
G.T. Ma, H.F. Liu, J.S. Wang, S.Y. Wang, X.C. Lin, J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 22, 841 (2009)
R. Pecher, M.D. McCulloch, S.J. Chapman, L. Prigozhin, C.M. Elliot, in EUCAS 2003, Sorrento, Italy, Sep. 14–18, 2003
M. Murakami, T. Oyama, H. Fujimoto, S. Gotoh, K. Yamaguchi, Y. Shiohara, N. Koshizuaka, S. Tanaka, IEEE Trans. Magn. 27, 1479 (1991)
G.T. Ma, J.S. Wang, S.Y. Wang, IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 20, 2228 (2010)
T. Matsushita, Flux Pinning in Superconductors (Springer, Berlin, 2007)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (50906093, 51007076), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant SWJTU11ZT34, and the Cultivation Foundation for Excellent Doctoral Dissertation of Southwest Jiaotong University. Our great thanks should go to the anonymous reviewers whose suggestions improve the quality of this paper considerably.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, G., Lin, Q., Jiang, D. et al. Numerical Studies of Axial and Radial Magnetic Forces Between High Temperature Superconductors and a Magnetic Rotor. J Low Temp Phys 172, 299–309 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-013-0872-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-013-0872-z