Abstract
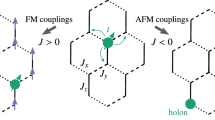
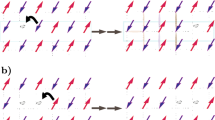
We have introduced the hole-induced magnetic soliton by using the gauge-invariant Lagrangian density and the path-integral method. The percolation-like dynamics of hole-induced magnetic solitons and the colossal magnetoresistance mechanism in doped manganites have been proposed from the standpoint of the random resistor network and percolation-scaling method. The long-relaxation behaviour of the spin has been discussed by using the effective Hamiltonian and the frustration-limited domain model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Tokura, Phys. Today 56, 50 (2003)
Y. Tokura, Rep. Prog. Phys. 68, 797 (2006)
K.H. Kim et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 1877 (1996)
A. Machida, Y. Morimoto, A. Nakamura, Phys. Rev. B 58, R4281 (1998)
P.G. Radaelli et al., Phys. Rev. B 55, 3015 (1997)
M. Mayr et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 135 (2001)
I. Kanazawa, Physica E 29, 647 (2005)
I. Kanazawa, Phys. Lett. A 355, 460 (2006)
I. Kanazawa, Phys. Status Solidi C 5, 318 (2008)
I. Kanazawa, Phys. Status Solidi B 247, 644 (2010)
M. Kleman, T.F. Sadoc, J. Phys. 40, L567 (1979)
S. Sachdev, D.R. Nelson, Phys. Rev. Lett. 53, 1947 (1984)
I. Kanazawa, Prog. Theor. Phys. Suppl. 126, 393 (1997)
C. Becchi, A. Rouet, R. Stora, Commun. Math. Phys. 42, 127 (1975)
T. Kugo, I. Ojima, Prog. Theor. Phys. Suppl. 66, 1 (1979)
I. Kanazawa, Physica E 21, 961 (2004)
K.B. Efetov, Adv. Phys. 32, 53 (1983)
K.B. Efetov, O. Viehweger, Phys. Rev. B 45, 11546 (1992)
D. Stauffer, A. Aharony, Introduction to Percolation Theory (Taylor & Francis, London, 1994)
L. Chayes, V.J. Emery, S.A. Kivelson, Z. Nussinov, G. Tarjus, Physica A 225, 129 (1996)
S.A. Kivelson, X.L. Zhao, D. Kivelson, C.M. Knobler, T. Fischer, J. Chem. Phys. 101, 2391 (1994)
D. Kivelson, G. Tarjus, S.A. Kivelson, Prog. Theor. Phys. Suppl. 126, 289 (1997)
L.D. Faddeev, A.A. Slavnov, Gauge Fields: An Introduction to Quantum Theory (Addison-Wesley, Reading, 1991)
A. Coniglio, W. Klein, J. Phys. A 13, 2775 (1980)
T.C. Lubensky, in Ill-Condensed Matter, ed. by R. Balian, R. Maynard, G. Thoulouse (North-Holland/World Scientific, Singapore, 1983), p. 408
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanazawa, I. Hole-Induced Magnetic Solitons and Colossal Magnetoresistance Phenomena in Doped Manganites. J Low Temp Phys 172, 177–183 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-013-0861-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-013-0861-2