Abstract
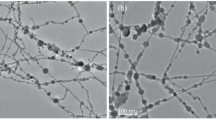
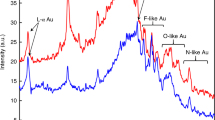
The coagulation of impurities in superfluid helium, in contrast to that in all other liquids where spherical colloid particles are usually produced, led to producing thin and long nanowires with regular internal structure. This is due to the presence in HeII of quasi one-dimensional quantized vortices serving as condensation nuclei and providing a catalyzing effect on the process of any impurities coagulation. The metal was introduced into superfluid helium by laser ablation of targets made of gold, copper, nickel, permalloy, indium, lead, tin and bismuth immersed in liquid HeII. For all of these metals, the formation of thin (about 8 nm in diameter), long high-quality nanowires was observed after laser ablation. The structure of nanowires as well as of micron-sized metallic spheres, appeared as products at high laser pulse energy, providing evidence that they were formed via molten state. The spheres are metastable, and under damage of their surface, thousands of nanoballs emerge from their interior. The hollow shells left after this event are similar to those found as the products of laser ablation in normal fluids. The metal ablation into HeII bulk from thin film was found much less effective then that from thick foils.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Sasaki, N. Takada, Liquid-phase laser ablation. Pure Appl. Chem. 82, 1317–1327 (2010)
F. Mafune, J. Kohno, Y. Takeda, T. Kondow, Formation of stable platinum nanoparticles by laser ablation in water. J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 4218–4223 (2003)
E.B. Gordon, A.V. Karabulin, V.I. Matyushenko, V.D. Sizov, I.I. Khodos, The role of vortices in the process of impurity nanoparticles coalescence in liquid helium. Chem. Phys. Lett. 519–520, 64 (2012)
P. Moroshkin, V. Lebedev, B. Grobety, C. Neururer, E.B. Gordon, A. Weis, Nanowire formation by gold nano-fragment coalescence on quantized vortices in He II. Europhys. Lett. 90, 34002 (2010)
V. Lebedev, P. Moroshkin, B. Groberty, E. Gordon, A. Weis, Formation of metallic nanowires by laser ablation in liquid helium. J. Low Temp. Phys. 165, 166 (2011)
E.B. Gordon, A.V. Karabulin, V.I. Matyushenko, V.D. Sizov, I.I. Khodos, Structure of metallic nanowires and nanoclusters formed in superfluid helium. JETP Lett. 112, 1061 (2011)
E.B. Gordon, A.V. Karabulin, V.I. Matyushenko, V.D. Sizov, I.I. Khodos, Electric properties of metallic nanowires obtained in quantum vortices of superfluid helium. Low Temp. Phys. 36, 590 (2010)
E.B. Gordon, A.V. Karabulin, V.I. Matyushenko, V.D. Sizov, I.I. Khodos, The electrical conductivity of bundles of superconducting nanowires produced by laser ablation of metals in superfluid helium. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 052605 (2012)
E.B. Gordon, R. Nishida, R. Nomura, Y. Okuda, The filament formation by impurities embedding into superfluid helium. JETP Lett. 85, 581 (2007)
R.J. Donnelly, Quantized Vortices in Helium II (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1991)
D. Jin, H.J. Maris, A study of the motion of particles in superfluid helium-4 and interactions with vortices. J. Low Temp. Phys. 162, 329–339 (2011)
D.D. Awschalom, K.W. Schwarz, Observation of a remanent vortex-line density in superfluid helium. Phys. Rev. Lett. 52, 49–52 (1984)
A. Golov, Private communication
F. Mafune, J. Kohno, Y. Takeda, T. Kondow, Formation of gold nanonetworks and small gold nanoparticles by irradiation of intense pulsed laser onto gold nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 12589 (2003)
S.W. Van Sciver, Transient heat transport in He II. Cryogenics 19, 385 (1979)
G.P. Bewley, Using frozen hydrogen particles to observe rotating and quantized flows in liquid helium. PhD dissertation, Yale University (2006)
M.S. Paoletti, R.B. Fiorito, K.R. Sreenivasan, D.P. Lathrop, Visualization of superfluid helium flow. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 77, 111007 (2008)
E.B. Gordon, Y. Okuda, Catalysis of impurities coalescence by quantized vortices in superfluid helium with nanofilament formation. Low Temp. Phys. 35, 209 (2009)
M.E. Povarnitsyn, T.E. Itina, K.V. Khishchenko, P.R. Levashov, Suppression of ablation in femtosecond double-pulse experiments. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 195002 (2009)
H.Q. Wang, M. Miyauchi, Y. Ishikawa, A. Pyatenko, N. Koshizaki, Y. Li, L. Li, X.Y. Li, Y. Bando, D. Golberg, Single-crystalline rutile TiO2 hollow spheres: room-temperature synthesis, tailored visible-light-extinction, and effective scattering layer for quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 19102 (2011)
S. Chandrasekar, M.M. Chaudhri, The explosive disintegration of Prince Rupert’s drops. Philos. Mag., B 70, 1195–1218 (1994)
R. Honeycombe, The Plastic Deformation of Metals (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1968)
Z. Yan, R. Bao, R.N. Wright, D.B. Chrisey, Hollow nanoparticle generation on laser-induced cavitation bubbles via bubble interface pinning. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 124106 (2010)
G. Viau, V. Colliere, L.-M. Lacroix, G.A. Shafeev, Internal structure of Al hollow nanoparticles generated by laser ablation in liquid ethanol. Chem. Phys. Lett. 501, 419–422 (2011)
S. Grebenev, J.P. Toennies, A.F. Vilesov, Superfluidity within a small helium-4 cluster: the microscopic Andronikashvili experiment. Science 279, 2083 (1998)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to V.T. Volkov for producing the permalloy film target. This work was partially supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, projects #10-03-00562 and #11-02-12048.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gordon, E.B., Karabulin, A.V., Matyushenko, V.I. et al. The Nanostructures Produced by Laser Ablation of Metals in Superfluid Helium. J Low Temp Phys 172, 94–112 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-012-0849-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-012-0849-3