Abstract
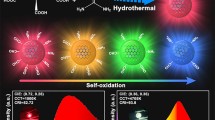
Carbon dots (CDs) have garnered significant attention owing to their fluorescence properties and biocompatibility, especially red fluorescent CDs for bio-imaging and optoelectronics. However, existing red fluorescent carbon dots exhibit limitations regarding shorter red wavelengths, lower fluorescence intensities, and complex preparation procedures. This paper employed the microwave method to synthesize four water-soluble red fluorescent carbon dots, utilizing p-phenylenediamine and urea as precursors. By doping with manganese and adjusting the precursor concentration, we enhanced the intensity and the wavelength of red fluorescence under 365 nm UV light. The manganese-decorated carbon dots (Mn-CDs) showed a 32 nm redshift compared to the original carbon dots (O-CDs). The manganese-decorated/precursor concentration changed carbon dots (Mn/P-CDs) had four times higher intensity and 677 nm wavelength. The enhancement was mainly due to the increased nitrogen content from manganese addition and the decreased precursor concentration. We also synthesized composite polyfluorescent films with four CDs as pigments, exhibiting excellent transparency, flexibility, and luminescence in various media. Importantly, we demonstrated that their luminescent properties remained intact across multiple media. This study provides a valuable method for high-quality red CDs synthesis and a novel perspective for their applications.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Xu, R. Ray, Y. Gu, H.J. Ploehn, L. Gearheart, K. Raker, W.A. Scrivens, Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126(40), 12736–12737 (2004)
L. Wang, B. Wang, E. Liu, Y. Zhao, B. He, C. Wang, G. Xing, Z. Tang, Y. Zhou, S. Qu, Polyetherimide functionalized carbon dots with enhanced red emission in aqueous solution for bioimaging. Chin. Chem. Lett. 33(8), 4111–4115 (2022)
A.A. Oladipo, Cu0-doped graphitic carbon quantum dots for rapid electrochemical sensing of glyphosate herbicide in environmental samples. Microchem. J. 200, 110294 (2024)
Q. Fu, C. Long, L. Qin, Z. Jiang, T. Qing, P. Zhang, B. Feng, Fluorescent and colorimetric dual-mode detection of tetracycline in wastewater based on heteroatoms-doped reduced state carbon dots. Environ. Pollut. 283, 117109 (2021)
M.L. Desai, H. Basu, S. Saha, R.K. Singhal, S.K. Kailasa, Fluorescence enhancement of bovine serum albumin gold nanoclusters from La3+ ion: Detection of four divalent metal ions (Hg2+, Cu2+, Pb2+ and Cd2+). J. Mol. Liq. 336, 116239 (2021)
A.A. Oladipo, S.D. Oskouei, M. Gazi, Metal-organic framework-based nanomaterials as opto-electrochemical sensors for the detection of antibiotics and hormones: A review. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 14, 631–673 (2023)
Y. Han, L. Liccardo, E. Moretti, H.G. Zhao, A. Vomiero, Synthesis, optical properties and applications of red/near-infrared carbon dots. J. Mater. Chem. C 10(33), 11827–11847 (2022)
E.A. Stepanidenko, A.A. Vedernikova, M.D. Miruschenko, D.R. Dadadzhanov, D. Feferman, B. Zhang, S. Qu, E.V. Ushakova, Red-Emissive Center Formation within Carbon Dots Based on Citric Acid and Formamide. J. Physical Chem. Lett. 14(50), 11522–11528 (2023)
H. Wang, X.U. Jing, Y.Q. Huang, H.L. Zhou, J.H. Yang, Red Emissive Carbon Dots: Photoluminescence Mechanism, Modulation and Application Research. Chinese J. Luminescence 41(12), 1579–1597 (2020)
L. Cui, X. Ren, J. Wang, M. Sun, Synthesis of homogeneous carbon quantum dots by ultrafast dual-beam pulsed laser ablation for bioimaging. Materials Today Nano 12, 100091 (2020)
H. Ding, J.S. Wei, P. Zhang, Z.Y. Zhou, Q.Y. Gao, H.M. Xiong, Solvent-Controlled Synthesis of Highly Luminescent Carbon Dots with a Wide Color Gamut and Narrowed Emission Peak Widths. Small 14(22), 1800612 (2018)
K. Jiang, Y.H. Wang, X.L. Gao, C.Z. Cai, H.W. Lin, Facile, Quick, and Gram-Scale Synthesis of Ultralong-Lifetime Room-Temperature-Phosphorescent Carbon Dots by Microwave Irradiation. Angewandte Chemie-Int. Edition 57(21), 6216–6220 (2018)
H.R. Jia, Z.B. Wang, T. Yuan, F.L. Yuan, X.H. Li, Y.C. Li, Z.A. Tan, L.Z. Fan, S.H. Yang, Electroluminescent Warm White Light-Emitting Diodes Based on Passivation Enabled Bright Red Bandgap Emission Carbon Quantum Dots. Adv. Sci. 6(13), 00397 (2019)
J. Li, G. Xu, Y. Lu, X. Xia, W. Song, Q. Wang, C. Liu, One-Pot Synthesis of Trichromatic Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Printing and Imaging. Acs Applied Nano Mater. 6, 10618–10625 (2023)
Z. Gan, Y. Di, S. Huang, J. Shen, L. Yang, X. Zhang, Modulating the fluorescent color of carbon nanodots via photon reabsorption and carbonization degree. Appl. Phys. Lett. 111(24), 5008454 (2017)
J. Yu, X. Yong, Z. Tang, B. Yang, S. Lu, Theoretical Understanding of Structure-Property Relationships in Luminescence of Carbon Dots. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 12(32), 7671–7687 (2021)
D. Zhang, D. Chao, C. Yu, Q. Zhu, S. Zhou, L. Tian, L. Zhou, One-Step Green Solvothermal Synthesis of Full-Color Carbon Quantum Dots Based on a Doping Strategy. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 12(37), 8939–8946 (2021)
V.M. Naik, S.V. Bhosale, G.B. Kolekar, A brief review on the synthesis, characterisation and analytical applications of nitrogen doped carbon dots. Anal. Methods 14(9), 877–891 (2022)
S.A.R. Pakkath, S.S. Chetty, P. Selvarasu, A.V. Murugan, Y. Kumar, L. Periyasamy, M. Santhakumar, S.R. Sadras, K. Santhakumar, Transition Metal Ion (Mn2+, Fe2+, Co2+, and Ni2+)-Doped Carbon Dots Synthesized via Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis: A Potential Nanoprobe for Magneto-fluorescent Dual-Modality Bioimaging. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 4(7), 2582–2596 (2018)
Liu, Y.; Chao, D.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; Deng, R.; Zhang, H. Yellow emissive carbon dots with quantum yield up to 68.6% from manganese ions. Carbon 2018, 135, 253–259
S. Sun, Q. Guan, Y. Liu, B. Wei, Y. Yang, Z. Yu, Highly luminescence manganese doped carbon dots. Chin. Chem. Lett. 30(5), 1051–1054 (2019)
H. Zhang, S. Yang, X. Zhou, Mn-doped carbon dots as a visible-light-driven catalyst for degradation of acid fuchsin and malachite green. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 33(7), 4170–4183 (2022)
T.-Y. Wang, C.-Y. Chen, C.-M. Wang, Y.Z. Tan, W.-S. Liao, Multicolor Functional Carbon Dots via One-Step Refluxing Synthesis. ACS Sensors 2(3), 354–363 (2017)
F.Y. Yan, Z.H. Sun, H. Zhang, X.D. Sun, Y.X. Jiang, Z.J. Bai, The fluorescence mechanismof carbon dots, and methods for tuning their emission color: a review. Microchim. Acta 186(8), 1–37 (2019)
B. Wang, J. Yu, L. Sui, S. Zhu, Z. Tang, B. Yang, S. Lu, Rational design of multi-color-emissive carbon dots in a single reaction system by hydrothermal. Adv. Sci. 8(1), 2001453 (2021)
X. Fu, G. Li, S. Cai, H. Yang, K. Lin, M. He, J. Wen, H. Li, Y. Xiong, D. Chen, Color-switchable hybrid dots/hydroxyethyl cellulose ink for anti-counterfeiting applications. Carbohyd. Polym. 251, 117084 (2021)
S. Sun, L. Zhao, D. Wu, H. Zhang, H. Lian, X. Zhao, A. Wu, L. Zeng, Manganese-Doped Carbon Dots with Redshifted Orange Emission for Enhanced Fluorescence and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 4(2), 1969–1975 (2021)
Susu, Z.; Li, Y.; Guozheng, L.; Aijuan, G (2022) Preparation of multicolor-emissive carbon dots with high quantum yields and their epoxy composites for fluorescence anti-counterfeiting and light-emitting devices. J Mater Chem, C Materials for optical and electronic devices. 10(21):8441–8458
W.U. Khan, D. Wang, W. Zhang, Z. Tang, Y. Wang, High Quantum Yield Green-Emitting Carbon Dots for Fe(III) Detection, Biocompatible Fluorescent Ink and Cellular Imaging. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 14866 (2017)
W.L. Li, J. Tang, Y.Z. Li, H. Bai, W.Z. Zhang, J. Zhang, Y.M. Xiao, W. Xu, Preparation and Fluorescent Wavelength Control of Multi-Color Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nano-Dots. Nanomaterials 11(12), 11123190 (2021)
W. Kwon, S. Do, J.H. Kim, M.S. Jeong, S.W. Rhee, Control of Photoluminescence of Carbon Nanodots via Surface Functionalization using Para-substituted Anilines. Sci. Rep. 5, 12604 (2015)
L. Ai, Z.Q. Song, M.J. Nie, J.K. Yu, F.K. Liu, H.Q. Song, B. Zhang, G.I.N. Waterhouse, S.Y. Lu, Solid-state Fluorescence from Carbon Dots Widely Tunable from Blue to Deep Red through Surface Ligand Modulation. Angewandte Chemie-Int. Edition. 62, 17822 (2023)
D. Gu, S. Shang, Q. Yu, J. Shen, Green synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon dots from lotus root for Hg(II) ions detection and cell imaging. Appl. Surf. Sci. 390, 38–42 (2016)
Y. Wang, T. Wang, X. Chen, Y. Xu, H. Li, Mn(II)-coordinated Fluorescent Carbon Dots: Preparation and Discrimination of Organic Solvents. Opt. Mater. 78, 118–125 (2018)
X. Chu, G. Ning, Z.Q. Zhou, Y. Liu, Q. Xiao, S. Huang, Bright Mn-doped carbon dots for the determination of permanganate and L-ascorbic acid by a fluorescence on-off-on strategy. Microchim. Acta 187(12), 11 (2020)
H. Nie, M.J. Li, Q.S. Li, S.J. Liang, Y.Y. Tan, L. Sheng, W. Shi, S.X.A. Zhang, Carbon Dots with Continuously Tunable Full-Color Emission and Their Application in Ratiometric pH Sensing. Chem. Mater. 26(10), 3104–3112 (2014)
H. Ding, S.-B. Yu, J.-S. Wei, H.-M. Xiong, Full-Color Light-Emitting Carbon Dots with a Surface-State-Controlled Luminescence Mechanism. ACS Nano 10(1), 484–491 (2016)
W. Lu, X. Qin, S. Liu, G. Chang, Y. Zhang, Y. Luo, A.M. Asiri, A.O. Al-Youbi, X. Sun, Economical, Green Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Nanoparticles and Their Use as Probes for Sensitive and Selective Detection of Mercury(II) Ions. Anal. Chem. 84(12), 5351–5357 (2012)
C. Wang, Y. Wang, H. Shi, Y. Yan, E. Liu, X. Hu, J. Fan, A strong blue fluorescent nanoprobe for highly sensitive and selective detection of mercury(II) based on sulfur doped carbon quantum dots. Mater. Chem. Phys. 232, 145–151 (2019)
M. Zhou, Z. Zhou, A. Gong, Y. Zhang, Q. Li, Synthesis of highly photoluminescent carbon dots via citric acid and Tris for iron(III) ions sensors and bioimaging. Talanta 143, 107–113 (2015)
Z. Sun, F. Yan, J. Xu, H. Zhang, L. Chen, Solvent-controlled synthesis strategy of multicolor emission carbon dots and its applications in sensing and light-emitting devices. Nano Res. 15(1), 414–422 (2022)
L. Cao, M. Zan, F. Chen, X. Kou, Y. Liu, P. Wang, Q. Mei, Z. Hou, W.-F. Dong, L. Li, Formation mechanism of carbon dots: From chemical structures to fluorescent behaviors. Carbon 194, 42–51 (2022)
P. Li, S. Xue, L. Sun, X. Zong, L. An, D. Qu, X. Wang, Z. Sun, Formation and fluorescent mechanism of red emissive carbon dots from o-phenylenediamine and catechol system. Light-Science & Applications 11(1), 5 (2022)
K. Luo, Y. Wen, X. Kang, Halogen-Doped Carbon Dots: Synthesis, Application, and Prospects. Molecules 27(14), 27144620 (2022)
L. Bao, Z.-L. Zhang, Z.-Q. Tian, L. Zhang, C. Liu, Y. Lin, B. Qi, D.-W. Pang, Electrochemical Tuning of Luminescent Carbon Nanodots: From Preparation to Luminescence Mechanism. Adv. Mater. 23(48), 5801–5806 (2011)
R. Atchudan, T.N.J.I. Edison, Y.R. Lee, Nitrogen-doped carbon dots originating from unripe peach for fluorescent bioimaging and electrocatalytic oxygen reduction reaction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 482, 8 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22208161) and the Students Practice Innovation and Training Program of Nanjing Forestry University(2022NFUSPITP0342).
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Q.W conceptualized this study. GZ.L. conducted the trials with assistance from T.L, Z.L, and ZJ.L. GZ.L get experimental data with assistance from Z.L. GZ.L and T.L performed the data analysis with advice from C.L. GZ.L and ZJ.L wrote the manuscript and drew figures. All authors revised the manuscript
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, G., Li, T., Li, Z. et al. Enhancing the Red Fluorescence of Carbon Dots: The Role of Mn Doping and Precursor Concentration Control. J Inorg Organomet Polym (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-024-03141-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-024-03141-0