Abstract
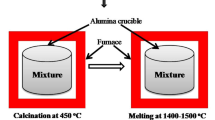
Lanthanides (Ce, Pr, Nd and Gd) 1, 3, 5 and 10 wt% of each were loaded into a pristine sodium aluminium phosphate glass matrix in order to simulate the immobilization of minor actinides (Am, Np, Cm) produced from spent nuclear fuel reprocessing. The optical parameters pertaining to these glasses were derived from the diffuse reflectance spectra. The systematic dependence of the physical and structural properties of these glasses on the dopants and the concentration of the latter was studied by XRD and Raman spectroscopy. The results on Rare Earth (RE) doped sodium aluminium phosphate are being reported for the first time. The physical parameters such as density, molar volume and oxygen packing density were evaluated. The XRD patterns showed the absence of any crystalline phase in these glasses. The relative % areas of (PO3)−2(Q2) bonds increase, whereas Q0 and Q1 tend to decrease with the addition of lanthanide oxides as compared to the pristine glass. The addition of different lanthanide oxides was found to depolymerize the network by forming more Q2 short chains. The results showed that the band gap energy (Eg) depends strongly on the cation field strength (CFS) of the lanthanides. The band gap energy decreases with an increase in the lanthanide concentration in the glass matrix. Praseodymium-doped glasses showed the highest Eg values (5.28–5.23 eV). The photoluminescence spectra confirm the characteristic excitation and emission peaks for the cations Ce+3, Pr+3 and Gd+3 and their variation with concentration was analysed.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Lee, M. Ojovan, M. Stennett, N. Hyatt, Immobilisation of radioactive waste in glasses, glass composite materials and ceramics. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 105(1), 3 (2006)
M.I. Ojovan, W.E. Lee, An introduction to nuclear waste immobilisation, 2nd edn. (Elsevier Science, City, 2013), pp. 245–282
W.J. Weber, A. Navrotsky, S. Stefanovsky, E.R. Vance, E. Vernaz, Materials science of high-level nuclear waste immobilization. MRS bulletin 34(1), 46 (2009)
P. Sengupta, A review on immobilization of phosphate containing high level nuclear wastes within glass matrix–present status and future challenges. J. Hazard. Mater. 235, 17 (2012)
A. Bohre, K. Avasthi, V.I. Pet’kov, Vitreous and crystalline phosphate high level waste matrices: present status and future challenges. J. Indus. Eng. Chem. 50, 1 (2017)
X. Wang, Y. Teng, Y. Huang, L. Wu, P. Zeng, Synthesis and structure of Ce1− xEuxPO4 solid solutions for minor actinides immobilization. J. Nuclear Mater. 451(1–3), 147 (2014)
Y. Zhang, Z. Zhang, T. Wei, L. Kong, Y.J. Kim, D.J. Gregg, Pyrochlore glass-ceramics fabricated via both sintering and hot isostatic pressing for minor actinide immobilization. J. American Ceram. Soc. 103(10), 5470 (2020)
H. Yang, Y. Teng, X. Ren, L. Wu, H. Liu, S. Wang, L. Xu, Synthesis and crystalline phase of monazite-type Ce1− xGdxPO4 solid solutions for immobilization of minor actinide curium. J. nuclear mater. 444(1–3), 39 (2014)
X. Gao, Y. Huang, Y. Teng, M. Yan, H. Zhang, X. Tuo, S. Peng, Fabrication and chemical durability of hot-pressed Na-bearing fluorapatite-type Ca8Sm1Na1 (PO4) 6F2 ceramic for immobilization of trivalent minor actinide. J. Nuclear Mater. 507, 297 (2018)
L.R. Blackburn, L.T. Townsend, S.M. Lawson, A.R. Mason, M.C. Stennett, S.-K. Sun, L.J. Gardner, E.R. Maddrell, C.L. Corkhill, N.C. Hyatt, Phase evolution in the CaZrTi2O7–Dy2Ti2O7 system: a potential host phase for minor actinide immobilization. Inorg. chem. 61(15), 5744 (2022)
R.T. Shannon, C. Prewitt, Revised values of effective ionic radii. Acta Crystallograph. Sect. B: Struct. Crystallograph. Cryst. Chem. 26(7), 1046 (1970)
Y. Jiang, L. Wang, W. Zhang, L. Teng, F. Hu, H. Guo, Dual-valence Ce doped UV-shielding glasses with high transparency and stability. Ceram. Int. 46(10), 16032 (2020)
M. Abdel Maksoud, E. Abou Hussein, S.M. Kassem, R.A. Fahim, A. Awed, Effect of CeO2 addition on structural, optical, and radiation shielding properties of B2O3–Na2O–SrO glass system. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32(14), 18931 (2021)
D. Yılmaz, B. Aktaş, Ş Yalçın, M. Albaşkara, Erbium oxide and Cerium oxide-doped borosilicate glasses as radiation shielding material. Radiat. Effects Defects Solids 175(5–6), 458 (2020)
L. Teng, Y. Jiang, W. Zhang, R. Wei, H. Guo, Highly transparent cerium doped glasses with full-band UV-shielding capacity. J. American Ceram. Soc. 103(5), 3249 (2020)
J. Rajagukguk, R. Situmorang, M. Djamal, R. Rajaramakrishna, J. Kaewkhao, P.H. Minh, Structural, spectroscopic and optical gain of Nd3+ doped fluorophosphate glasses for solid state laser application. J. Lumin. 216, 116738 (2019)
K. Brahmachary, D. Rajesh, Y. Ratnakaram, Radiative properties and luminescence spectra of Sm3+ ion in zinc–aluminum–sodium-phosphate (ZANP) glasses. J. Lumin. 161, 202 (2015)
T. Suhasini, J.S. Kumar, T. Sasikala, K. Jang, H.S. Lee, M. Jayasimhadri, J.H. Jeong, S.S. Yi, L.R. Moorthy, Absorption and fluorescence properties of Sm3+ ions in fluoride containing phosphate glasses. Opt. Mater. 31(8), 1167 (2009)
H. Lin, D. Yang, G. Liu, T. Ma, B. Zhai, Q. An, J. Yu, X. Wang, X. Liu, E.Y.-B. Pun, Optical absorption and photoluminescence in Sm3+-and Eu3+-doped rare-earth borate glasses. J. Lumin. 113(1–2), 121 (2005)
V.M. Martins, D.N. Messias, N.O. Dantas, A.M. Neto, Concentration dependent fluorescence quantum efficiency of neodymium doped phosphate glass matrix. J. lumin. 130(12), 2491 (2010)
K. Mahmoud, Spectroscopic and radiative properties study of Nd3+ doped cadmium-phosphate glasses. Phys. B: Condensed Matter. 405(23), 4746 (2010)
P. Kaur, D. Singh, T. Singh, Optical, photoluminescence and physical properties of Sm3+ doped lead alumino phosphate glasses. J. Non-Crystall. Solids 452, 87 (2016)
M.B. Volf, in Chemical Approach to Glass, Vol 7, (Elsevier Science, City, 1984), pp. 118–133
J. Marchi, D. Morais, J. Schneider, J. Bressiani, A. Bressiani, Characterization of rare earth aluminosilicate glasses. J. non-crystall. solids 351(10–11), 863 (2005)
R.D. Shannon, Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta crystallography. Sect. A 32(5), 751 (1976)
P. Loiseau, D. Caurant, N. Baffier, L. Mazerolles, C. Fillet, Glass–ceramic nuclear waste forms obtained from SiO2–Al2O3–CaO–ZrO2–TiO2 glasses containing lanthanides (Ce, Nd, Eu, Gd, Yb) and actinides (Th): study of internal crystallization. J. Nuclear Mater. 335(1), 14 (2004)
Y. Deng, Q. Liao, F. Wang, H. Zhu, Synthesis and characterization of cerium containing iron phosphate based glass-ceramics. J. Nuclear Mater. 499, 410 (2018)
Y. He, Y. Lü, Q. Zhang, Characterization of monazite glass–ceramics as wasteform for simulated α-HLLW. J. of nuclear mater. 376(2), 201 (2008)
A. Kishioka, M. Hayashi, M. Kinoshita, Glass formation and crystallization in ternary phosphate systems containing Al2O3. Bulletin Chem. Soc. Japan 49(11), 3032 (1976)
A. Kishioka, The structural role of the aluminum ion in alkali aluminophosphate glass containing less than 50 mol% of P2O5. Bulletin Chem. Soc. Japan 50(8), 2088 (1977)
S.K. Barik, A. Senapati, S. Balakrishnan, K. Ananthasivan, Synthesis and characterization of rare-earth doped aluminium phosphate glasses. Prog. Nucl. Energ. 152, 104372 (2022)
N. Sawangboon, A. Nizamutdinova, T. Uesbeck, R. Limbach, E. Meechoowas, K. Tapasa, D. Möncke, L. Wondraczek, E.I. Kamitsos, L. van Wüllen, Modification of silicophosphate glass composition, structure, and properties via crucible material and melting conditions. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 11(1), 46 (2020)
B. Bhatia, S. Meena, V. Parihar, M. Poonia, Optical basicity and polarizability of Nd 3+-doped bismuth borate glasses. New J. Glass Ceram. 5(03), 44 (2015)
G. Srinivas, B. Ramesh, J. Siva Kumar, M. Shareefuddin, M. Chary, R. Sayanna, Mixed alkali effect in the physical and optical properties of x K2O-(25–x) Na2O-12.5 MgO-12.5 BaO-50B2O3 glasses. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 10(3), 442 (2016)
A. Senapati, S.K. Barik, R. Venkata Krishnan, S. Chakraborty, H. Jena, Studies on synthesis, structural and thermal properties of sodium niobium phosphate glasses for nuclear waste immobilization applications. J. Thermal Analysis Calorim. 148(2), 355–369 (2022)
J. Tauc, Absorption edge and internal electric fields in amorphous semiconductors. Mater. Res. Bullet. 5(8), 721 (1970)
V. Dimitrov, S. Sakka, Linear and nonlinear optical properties of simple oxides. II J. Appl. Phys. 79(3), 1741 (1996)
V. Bhatia, D. Kumar, A. Kumar, V. Mehta, S. Chopra, A. Vij, S. Rao, S.P. Singh, Mixed transition and rare earth ion doped borate glass: structural, optical and thermoluminescence study. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30(1), 677 (2019)
P. Pawar, S. Munishwar, R. Gedam, Physical and optical properties of Dy3+/Pr3+ Co-doped lithium borate glasses for W-LED. J. Alloys Comp. 660, 347 (2016)
K. Annapoorani, C. Basavapoornima, N.S. Murthy, K. Marimuthu, Investigations on structural and luminescence behavior of Er3+ doped Lithium Zinc borate glasses for lasers and optical amplifier applications. J. Non-Crystall. Solids 447, 273 (2016)
K. Herzfeld, On atomic properties which make an element a metal. Phys. Rev. 29(5), 701 (1927)
J. Duffy, M.D. Ingram, An interpretation of glass chemistry in terms of the optical basicity concept. J. Non-Crystall. Solids 21(3), 373 (1976)
R.K. Brow, Nature of alumina in phosphate glass: I, properties of sodium aluminophosphate glass. J. American Ceram. Soc. 76(4), 913 (1993)
R.K. Brow, R.J. Kirkpatrick, G.L. Turner, Nature of alumina in phosphate glass: II, structure of sodium alurninophosphate glass. J. American Ceram. Soc. 76(4), 919 (1993)
P. Stoch, P. Goj, M. Ciecińska, P. Jeleń, A. Błachowski, A. Stoch, I. Krakowiak, Influence of aluminum on structural properties of iron-polyphosphate glasses. Ceram Int. 46(11), 19146 (2020)
P. Stoch, P. Goj, A. Wajda, A. Stoch, Alternative insight into aluminium-phosphate glass network from ab initio molecular dynamics simulations. Ceram. Int. 47(2), 1891 (2021)
P. Stoch, A. Stoch, M. Ciecinska, I. Krakowiak, M. Sitarz, Structure of phosphate and iron-phosphate glasses by DFT calculations and FTIR/Raman spectroscopy. J. Non-Crystall. Solids 450, 48 (2016)
M. Elisa, B. Sava, I. Vasiliu, R. Monteiro, J. Veiga, L. Ghervase, I. Feraru, R. Iordanescu, Optical and structural characterization of samarium and europium-doped phosphate glasses. J. non-crystall. solids 369, 55 (2013)
O. Cozar, D. Magdas, L. Nasdala, I. Ardelean, G. Damian, Raman spectroscopic study of some lead phosphate glasses with tungsten ions. J. non-crystall. solids 352(28–29), 3121 (2006)
A.K. Yadav, P. Singh, A review of the structures of oxide glasses by Raman spectroscopy. RSC adv. 5(83), 67583 (2015)
A. Moguš-Milanković, A. Gajović, A. Šantić, D. Day, Structure of sodium phosphate glasses containing Al2O3 and/or Fe2O3. Part I J. non-crystall. solids 289(1–3), 204 (2001)
S. Stefanovsky, O. Stefanovsky, M. Kadyko, FTIR and Raman spectroscopic study of sodium aluminophosphate and sodium aluminum-iron phosphate glasses containing uranium oxides. J. Non-crystall. Solids 443, 192 (2016)
R.K. Brow, D.R. Tallant, S.T. Myers, C.C. Phifer, The short-range structure of zinc polyphosphate glass. J. Non-Crystall. Solids 191(1–2), 45 (1995)
H. Yu, R. Xin, X. Zhang, H. Liu, K. Zheng, J. Zhao, L. Zhan, C. Xu, W. Wan, Y. Zhu, Crystallization behavior, quantitation of Ce3+/Ce4+ and chemical stability analysis of multiple alkaline earths borosilicate glasses for immobilizing simulated tetravalent actinides. J. Non-Crystall. Solids 558, 120642 (2021)
V. Nicolini, E. Gambuzzi, G. Malavasi, L. Menabue, M.C. Menziani, G. Lusvardi, A. Pedone, F. Benedetti, P. Luches, S. D’Addato, Evidence of catalase mimetic activity in Ce3+/Ce4+ doped bioactive glasses. J. Phys. Chem. B. 119(10), 4009 (2015)
J.-H. Maeng, S.-C. Choi, The effect of cerium reduction on light emission in cerium-containing 20Y 2 O 3–25Al 2 O 3–55SiO 2 glass. J. Opt. Soci. Korea 16(4), 414 (2012)
D. Pugliese, F.S. Gobber, I. Forno, D. Milanese, M. Actis Grande, Design and manufacturing of a Nd-doped phosphate glass-based jewel. Materials 13(10), 2321 (2020)
V. Rai, B.R. Sekhar, P. Tiwari, R. Kshirsagar, S. Deb, Spectroscopic studies of gamma irradiated Nd doped phosphate glasses. J. non-crystall. solids 357(22–23), 3757 (2011)
A. Novais, N. Dantas, I. Guedes, M. Vermelho, Spectroscopic properties of highly Nd-doped lead phosphate glass. J. Alloys Compounds 648, 338 (2015)
S. Babu, P. Rajput, Y. Ratnakaram, Compositional-dependent properties of Pr 3+-doped multicomponent fluoro-phosphate glasses for visible applications: a photoluminescence study. J. Mater. Sci. 51, 8037 (2016)
V. Singh, S. Borkotoky, A. Murali, J. Rao, T.G. Rao, S. Dhoble, Electron paramagnetic resonance and photoluminescence investigation on ultraviolet-emitting gadolinium-ion-doped CaAl12O19 phosphors. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectr. 139, 1 (2015)
C. Basavapoornima, C. Kesavulu, T. Maheswari, W. Pecharapa, S.R. Depuru, C. Jayasankar, Spectral characteristics of Pr3+-doped lead based phosphate glasses for optical display device applications. J. Lumin. 228, 117585 (2020)
S. Mitra, S. Jana, Intense orange emission in Pr3+ doped lead phosphate glass. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 85, 245 (2015)
G. Chen, S. Baccaro, M. Nikl, A. Cecilia, Y.Y. Du, E. Mihokova, The red-shift of ultraviolet spectra and the relation to optical basicity of Ce-doped alkali rare-earth phosphate glasses. J. American Ceram. Soc. 87(7), 1378 (2004)
S. Poort, J. Van Krevel, R. Stomphorst, A. Vink, G. Blasse, Luminescence of Eu2+ in host lattices with three alkaline earth ions in a row. J. Solid State Chem. 122(2), 432 (1996)
R. Reisfeld, Spectra and energy transfer of rare earths in inorganic glasses, in Rare Earths (Springer, City, 1973), p.53
G.S. Rao, B. Sudhakar, H. Prasanna, V. Devasahayam, N. Chand, Infrared spectral study of the structure of oxyfluoroborate glasses. Mater. lett. 65(2), 378 (2011)
J.E. Shelby, Introduction to Glass Science and Technology, 2nd edn. (Royal Society of Chemistry, City, 2015), pp. 72–79
M. Gaafar, S. Marzouk, Mechanical and structural studies on sodium borosilicate glasses doped with Er2O3 using ultrasonic velocity and FTIR spectroscopy. Phys. B: Condensed Matter. 388(1–2), 294 (2007)
Y. Elbashar, M.I. Ali, H. Elshaikh, A.G.E.-D. Mostafa, Influence of CuO and Al2O3 addition on the optical properties of sodium zinc phosphate glass absorption filters. Optik 127(18), 7041 (2016)
X. Liang, H. Li, C. Wang, H. Yu, Z. Li, S. Yang, Physical and structural properties of calcium iron phosphate glass doped with rare earth. J. Non-Crystall. Solids. 402, 135 (2014)
G. Blinkova, S.A. Vakhidov, A.K. Islamov, I. Nuritdinov, K.A. Khaidarova, On the nature of yellow coloring in cerium-containing silica glasses. Glass Phys. Chem. 20, 3 (1994)
B. Karthikeyan, R. Vettumperumal, Structural and optical characterization of Mg2SiO4 and Mg2SiO4-Pr6O11 nanocomposite for optical devices. Opt. Mater. 123, 111878 (2022)
J.A. Duffy, The refractivity and optical basicity of glass. J. non-crystall. solids 86(1–2), 149 (1986)
J.A. Duffy, Polarisability and polarising power of rare earth ions in glass: an optical basicity assessment. Phys. Chemi. glass. 46(1), 1 (2005)
J. Duffy, M. Ingram, Optical basicity—IV: influence of electronegativity on the Lewis basicity and solvent properties of molten oxyanion salts and glasses. J. Inorg. Nuclear Chem. 37(5), 1203 (1975)
J.A. Duffy, A review of optical basicity and its applications to oxidic systems. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 57(16), 3961 (1993)
A. Novatski, A. Steimacher, A. Medina, A. Bento, M. Baesso, L. Andrade, S. Lima, Y. Guyot, G. Boulon, Relations among nonbridging oxygen, optical properties, optical basicity, and color center formation in CaO–MgO aluminosilicate glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 104(9), 094910 (2008)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Dr Satendra Kumar for his help in recording UV-Vis spectra. The authors also acknowledge Dr Sitakanta Panda for his assistance in recording PL spectra. This work was supported by Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research (IGCAR), Kalpakkam, Department of Atomic Energy, Government of India.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SKB: sample preparation, experimental work, conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, interpretation of results and writing—original draft. AS: Sample preparation, experimental work, data collection and formal analysis. SC: raman data collection and data interpretation. KA: supervision, review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors hereby declare that they have no known competing financial interests and the work reported in this article is original and has not been published elsewhere.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. The data will be made available on reasonable request.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Barik, S.K., Senapati, A., Chakraborty, S. et al. Structure and Optical Properties of Sodium Aluminium Phosphate Glass Matrix Containing Lanthanide Oxides (Ce, Pr, Nd and Gd). J Inorg Organomet Polym 33, 2093–2110 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02645-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02645-5