Abstract
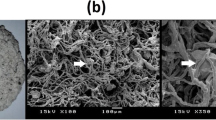
The phase inversion technique was used to successfully immobilize a submerged aquatic plant called Myriophyllum spicatum L. onto hybrid polymeric beads of Polyacrylonitrile/Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PAN/PVP). The surface morphology of the fabricated beads exhibited a porous structure with a homogeneous morphology. While their thermogram demonstrated a positive impact of PVP incorporation. In this study, the fabricated hybrid beads were tested against Safranin O as a dye adsorption model. Thus, the various parameters affecting Safranin O dye uptake onto the synthesized beads, such as time of contact, initial Safranin O concentration, adsorbent dose, and pH have been investigated and optimized using statistical response surface methodology (RSM). The results revealed that within 4 h, the fabricated PAN/PVP-M. spicatum beads showed a maximum adsorption capacity towards Safranin O dye of up to 217 mg g−1 using 0.3 g of the fabricated beads. The adsorption isotherm results were also fit to the Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin models, with the Langmuir model performing the best. The kinetic studies, on the other hand, obeyed the pseudo-second-order, and the fabricated PAN/PVP-M. spicatum beads showed appropriate reusability in the uptake of Safranin O dye from wastewater. Finally, the newly developed fabricated (PAN/PVP-M. spicatum) hybrid beads pave the way for the use of low-cost, efficient natural materials for wastewater treatment in the textile industry.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.R. El-Aassar, H. Fakhry, A.A. Elzain et al., Rhizofiltration system consists of chitosan and natural Arundo donax L. for removal of basic red dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 120, 1508–1514 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.09.159
D. Bilba, D. Suteu, T. Malutan, Removal of reactive dye brilliant red HE-3B from aqueous solutions by hydrolyzed polyacrylonitrile fibres: equilibrium and kinetics modelling. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 6, 258–266 (2008)
C.L. Mack, B. Wilhelmi, J.R. Duncan, J.E. Burgess, A kinetic study of the recovery of platinum ions from an artificial aqueous solution by immobilized Saccharomyces cerevisiae biomass. Miner. Eng. 21, 31–37 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2007.07.001
T.H. Kim, C. Park, S. Kim, Water recycling from desalination and purification process of reactive dye manufacturing industry by combined membrane filtration. J. Clean. Prod. 13, 779–786 (2005)
B. Shi, G. Li, D. Wang, C. Feng, Removal of direct dyes by coagulation: the performance of performed polymeric aluminum species. J. Hazard. Mater. 143, 567–574 (2007)
V. Katheresan, J. Kansedo, S.Y. Lau, Efficiency of various recent wastewater dye removal methods: a review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 6, 4676–4697 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.06.060
L. Xu, H. Wang, Z. Chu, L. Cai, H. Shi, C. Zhu, Y. Lei, Temperature-responsive multilayer films of micelle-based composites for controlled release of a third-generation EGFR inhibitor. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2(2), 741–750 (2020)
L. Xu, Z. Chu, H. Wang, L. Cai, Z. Tu, H. Liu, X. Fei, Electrostatically assembled multilayered films of biopolymer enhanced nanocapsules for on-demand drug release. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2(8), 3429–3438 (2019)
L. Xu, X. Zhang, Z. Chu, H. Wang, Y. Li, X. Shen, Temperature-responsive multilayer films based on block copolymer-coated silica nanoparticles for long-term release of favipiravir. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 4(12), 14014–14025 (2021)
N.B. Shukla, S. Rattan, G. Madras, Swelling and dye-adsorption characteristics of an amphoteric swelling and dye-adsorption characteristics of an amphoteric superabsorbent polymer. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/ie301839z
S. Haider, F.F. Binagag, A. Haider, Electrospun oxime-grafted-polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membrane and its application to the adsorption of dyes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 51(46), 14941–14948 (2014)
S. Ahmed, M.S. Mohd, A.N. Ahmedy, J.K. Khairil, Removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution using alginate grafted polyacrylonitrile beads. Der Pharma Chem. 7(2), 237–242 (2015)
N. Giri, R.K. Natarajan, S. Gunasekaran, S. Shreemathi, C NMR and FTIR spectroscopic study of blend behavior of PVP and nano silver particles. Arch Appl Sci Res 3, 624–630 (2011)
M. Basibuyuk, S. Savci, O. Keskinkan, M.E. Cakmak, Investigation of a basic dye adsorption characteristics of a non-living submerged aquatic plant (Myriophyllum spicatum). Asian J. Chem. 19, 1693–1702 (2007)
D.E.A. Mammar, Decolorization of the aqueous Safranin O dye solution using Thuja orientalis as biosorbent. Iraq. J. Sci. 55, 886–898 (2014)
M.R. El-Aassar, Functionalized electrospun nanofibers from poly (AN-co-MMA) for enzyme immobilization. J. Mol. Catal. B 85, 141–148 (2013)
M. Wawrzkiewicz, E. Polska-Adach, Z. Hubicki, Polacrylic and polystyrene functionalized resins for direct dye removal from textile effluents. Sep. Sci. Technol. 55, 2122–2136 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2019.1583254
D. Sun, X. Zhang, Y. Wu, X. Liu, Adsorption of anionic dyes from aqueous solution on fly ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 181, 335–342 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.05.015
Z. Han, J. Jin, Y. Wang et al., Encapsulating TiO2 into polyvinyl alcohol coated polyacrylonitrile composite beads for the effective removal of methylene blue. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 30, 211–223 (2019). https://doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20180170
K.M. Koczkur, S. Mourdikoudis, L. Polavarapu, S.E. Skrabalak, Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) in nanoparticle synthesis. Dalton Trans. 44, 17883–17905 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5dt02964c
A.S. Abdulhameed, A.H. Jawad, A.T. Mohammad, Synthesis of chitosanethylene glycol diglycidyl ether/TiO2 nanoparticles for adsorption of reactive orange 16 dye using a response surface methodology approach. Bioresour. Technol. 293, 122071 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122071
J. Duraipandian, T. Rengasamy, S. Vadivelu, Experimental and modeling studies for the removal of crystal violet dye from aqueous solutions using eco-friendly Gracilaria corticata seaweed activated carbon/Zn/alginate polymeric composite beads. J. Polym. Environ. 25, 1062–1071 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-016-0879-z
T. Kekes, C. Tzia, Adsorption of indigo carmine on functional chitosan and β-cyclodextrin/chitosan beads: equilibrium, kinetics and mechanism studies. J. Environ. Manag. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110372
J. Nath, L. Ray, D. Bera, Continuous removal of malachite green by calcium alginate immobilized Bacillus cereus M116 in packed bed column. Environ. Technol. Innov. 6, 132–140 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2016.06.002
D. Bendaho, T.A. Driss, Removal of cationic dye methylene blue from aqueous solution by adsorption on algerian clay. Int. J. Waste Resour. 5, 1–6 (2015). https://doi.org/10.4303/2252-5211.1000175
M.F. El-Kady, M.R. El-Aassar, O.A. El Batrawy et al., Equilibrium and kinetic behaviors of cationic dye decolorization using poly (AN-co-Py)/ZrO2 novel nanopolymeric composites. Adv. Polym. Technol. 37, 740–752 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/adv.21716
A. Yildirim, Y. Bulut, Adsorption behaviors of malachite green by using crosslinked chitosan/polyacrylic acid/bentonite composites with different ratios. Environ. Technol. Innov. 17, 100560 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2019.100560
Z.A. Sutirman, M.M. Sanagi, K.J. Abd Karim et al., Enhanced removal of Orange G from aqueous solutions by modified chitosan beads: Performance and mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 133, 1260–1267 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.04.188
Y.S. Ho, J.F. Porter, G. McKay, Equilibrium isotherm studies for the sorption of divalent metal ions onto peat: copper, nickel and lead single component systems. Water Air Soil Pollution 141(1), 1–33 (2002)
M.S. Mohy-Eldin, M.F. Elkady, M.A. Abu-Saied, A.M. Abdel Rahman, E.A. Soliman, A.A. Elzatahry, M.E. Youssef, Removal of cadmium ions from synthetic aqueoussolutions with a novel nanosulfonated poly(glycidylmethacrylate) cation exchanger: kinetic and equilibrium studies. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 118, 111–3122 (2010)
Bayramoglu G, Arica MY (2013) Removal of reactive dyes from wastewater by acrylate polymer beads bearing amino groups : isotherm and kinetic studies Coloration Technology. 114–124. https://doi.org/10.1111/cote.12012
Y.S. Ho, G. Mckay, Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. 34, 451–465 (1999)
Y. Ho, Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. 136, 681–689 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.12.043
C. Cao, L. Xiao, C. Chen et al., In situ preparation of magnetic Fe3O4/chitosan nanoparticles via a novel reduction—precipitation method and their application in adsorption of reactive azo dye. Powder Technol 260, 90–97 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2014.03.025
J. Azimvand, K. Didehban, S.A. Mirshokraie, Safranin-O removal from aqueous solutions using lignin nanoparticle-g-polyacrylic acid adsorbent: synthesis, properties, and application. Adsorpt Sci Technol 36, 1422–1440 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/0263617418777836
G.A. Kayode, M. Amoakoh-Coleman, I. Akua Agyepong et al., Contextual risk factors for low birth weight: a multilevel analysis. PLoS ONE 9, 1–8 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0109333
M.R. Malekbala, S.M. Soltani, S.K. Yazdi, S. Hosseini, Equilibrium and kinetic studies of safranine adsorptionon alkali-treated mango seed integuments. Int J Chem Eng Appl 3, 160–166 (2012). https://doi.org/10.7763/ijcea.2012.v3.179
S. Chowdhury, R. Mishra, P. Saha, P. Kushwaha, Adsorption thermodynamics, kinetics and isosteric heat of adsorption of malachite green onto chemically modified rice husk. Desalination 265, 159–168 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.07.047
I.S. Samaka, Removal of basic Red 2 from industrial effluents using natural Iraqi material. Civil Environ Res 6(7), 138–148 (2014)
J. Kennedy, M. Maaza, AC SC. J Phys Chem Solids (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2018.07.009
G. McKay, J.F. Porter, G.R. Prasad, The removal of dye colours from aqueous solutions by adsorption on low- cost materials. Water Air Soil Pollut 114, 423–438 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005197308228
R.G. Harris, J.D. Wells, B.B. Johnson, Selective adsorption of dyes and other organic molecules to kaolinite and oxide surfaces. Colloids Surf A 180, 131–140 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7757(00)00747-0
M.R. Abukhadra, M.A. El-Meligy, A.M. El-Sherbeeny, Evaluation and characterization of Egyptian ferruginous kaolinite as adsorbent and heterogeneous catalyst for effective removal of safranin-O cationic dye from water. Arab J Geosci (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-5182-6
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at Jouf University under grant No (DSR-2021-03-0354).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that, there is no competing of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fakhry, H., Hassan, H.M.A., El-Aassar, M.R. et al. A Treatment of Wastewater Containing Safranin O Using Immobilized Myriophyllum spicatum L. onto Polyacrylonitrile/Polyvinylpyrrodlidone Biosorbent. J Inorg Organomet Polym 32, 3181–3195 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02354-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02354-5