Abstract
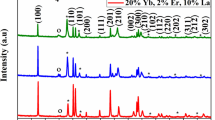
Tracking of cancer cells and cytotoxicity of normal tissue are the leading problem in cancer treatment. The magnetic and fluorescent multifunctional particles evolve as an emerging alternative for future target recognition. The ferromagnetic materials potentially treat the defects in the gene. Hence, ferromagnetic materials are the best for the treatment of cancer using gene therapy. Here, β-NaYF4: Yb, Er compounds doped with 10%, 20% and 30% Zirconium (Zr) are prepared through hydrothermal technique. Citrate itself is a highly biocompatible surface ligand that labels the imaging probe. The X-ray diffraction analysis is evident for transforming hexagonal to cubic phase via Zr doping in NaYF4: Yb, Er compounds. The electron microscopic images identify the hexagonal plates. This compound can emit visible light in response to infrared (IR) light irradiation. Especially β-NaYF4: Yb, Er, and 10% of Zr, Yb, Er tridoped NaYF4 compounds show enhanced red emission exploited in bioimaging applications. Insignificantly, 30% of Zr, Yb, Er tridoped NaYF4 concentration exhibit hexagonal and dominating cubic (α) phase, could decrease red emissions intensity and magnetisation value. This Zr material reveals peculiar magnetic properties, especially ferromagnetism at a lower magnetic field and produces paramagnetism at a higher magnetic field. Here, 10–20% Zr, Yb, Er tridoped NaYF4 concentrations exhibit better magnetic properties. The resultant compound is viable for the VERO cells.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Yadollahpour, S. Rashidi, Magnetic nanoparticles: a review of chemical and physical characteristics important in medical applications. Orient. J. Chem. 31(November), 25–30 (2015). https://doi.org/10.13005/ojc/31.Special-Issue1.03
P. Rasaili, N.K. Sharma, A. Bhattarai, Comparison of ferromagnetic materials: past work, recent trends, and applications. Condens. Matter. 7(1), 1–20 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat7010012
J. Liu, X. Liu, X. Kong, H. Zhang, Controlled synthesis, formation mechanism and upconversion luminescence of NaYF 4: Yb, Er nano-/submicrocrystals via ionothermal approach. J. Solid State Chem. 190, 98–103 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2012.01.058
N.C. Dyck, F.C.J.M. Van Veggel, G.P. Demopoulos, Size-dependent maximization of upconversion efficiency of citrate-stabilized β-phase NaYF4:Yb3+, Er3+ crystals via annealing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5(22), 11661–11667 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/am403100t
S. Kedar, R. Sudhir, M.I. Ahmad, M. Kumar, Green Route Synthesized Upconverting (NaYF4: Yb3+, Tm3+) Nanophosphors and Its Photophysical and Magnetic Properties, vol. 228 (Elsevier, New York, 2020)
P.S. Editorial, Doped nanostructures. Nanoscale 2(7), 1057 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1039/c005273f
G. Tian, Z. Gu, L. Zhou et al., Mn 2+ dopant-controlled synthesis of NaYF 4:Yb/Er upconversion nanoparticles for in vivo imaging and drug delivery. Adv. Mater. 24(9), 1226–1231 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201104741
Q. Huang, J. Yu, E. Ma, K. Lin, Synthesis and characterization of highly efficient near-infrared upconversion Sc3+/Er3+/Yb3+ tridoped NaYO 4. J. Phys. Chem. C 114(10), 4719–4724 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp908645h
F. Duttenhoefer, M.E. Mertens, J. Vizkelety, F. Gremse, V.A. Stadelmann, S. Sauerbier, Magnetic resonance imaging in zirconia-based dental implantology. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 26(10), 1195–1202 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12430
F. Zhang, G.B. Braun, A. Pallaoro et al., Mesoporous multifunctional upconversion luminescent and magnetic “nanorattle” materials for targeted chemotherapy. Nano Lett. 12(1), 61–67 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl202949y
E. Zhao, X. Liu, D. Tang et al., 800 nm laser induced white light upconversion of Nd/Yb/Pr triply doped NaYF4 through a dual-sensitization strategy. Mater. Res. Bull. 2021(133), 111027 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2020.111027
S. Fan, S. Wang, L. Yu, H. Sun, G. Gao, L. Hu, Ion-redistribution induced efficient upconversion in β-NaYF_4:20%Yb^3+,2%Er^3+ microcrystals with well controlled morphology and size. Opt. Express. 25(1), 180 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.25.000180
R. Zhou, T. Ma, B. Qiu, X. Li, Controlled synthesis of β-NaYF4:Yb, Er microphosphors and upconversion luminescence property. Mater. Chem. Phys. 194, 23–28 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.03.033
K. Du, X. Xu, S. Yao et al., Enhanced upconversion luminescence and controllable phase/shape of NaYF4:Yb/Er crystals through Cu2+ ion doping. CrystEngComm 20(14), 1945–1953 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ce02227a
H. Yu, W. Cao, Q. Huang, E. Ma, X. Zhang, J. Yu, Upcoversion performance improvement of NaYF4:Yb, Er by Sn codoping: enhanced emission intensity and reduced decay time. J. Solid State Chem. 207, 170–177 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2013.09.017
N. Jurga, D. Przybylska, P. Kamiński, A. Tymiński, B.F. Grześkowiak, T. Grzyb, Influence of the synthesis route on the spectroscopic, cytotoxic, and temperature-sensing properties of oleate-capped and ligand-free core/shell nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 606, 1421–1434 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.08.093
L.Y. Ang, M.E. Lim, L.C. Ong, Y. Zhang, Applications of upconversion nanoparticles in imaging, detection and therapy. Nanomedicine 6(7), 1273–1288 (2011). https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm.11.108
A. Sedlmeier, H.H. Gorris, Surface modification and characterization of photon-upconverting nanoparticles for bioanalytical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44(6), 1526–1560 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cs00186a
E. Ureña-Horno, M.E. Kyriazi, A.G. Kanaras, A method for the growth of uniform silica shells on different size and morphology upconversion nanoparticles. Nanoscale Adv. 3(12), 3522–3529 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/d0na00858c
U. Kostiv, M.M. Natile, D. Jirák et al., PEG-neridronate-modified NaYF4:Gd3+, Yb3+, Tm3+/NaGdF4 core-shell upconverting nanoparticles for bimodal magnetic resonance/optical luminescence imaging. ACS Omega 6(22), 14420–14429 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c01313
V. Oleksa, H. Macková, H. Engstová et al., Poly(N, N-dimethylacrylamide)-coated upconverting NaYF4:Yb, Er@NaYF4: Nd core–shell nanoparticles for fluorescent labeling of carcinoma cells. Sci. Rep. 11(1), 1–15 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-00845-y
V. Bastos, P. Oskoei, E. Andresen et al., Stability, dissolution, and cytotoxicity of NaYF4-upconversion nanoparticles with different coatings. Sci. Rep. 12(1), 1–13 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-07630-5
X. Zhai, J. Li, S. Liu et al., Polymer-based optical waveguide amplifiers. Opt. Mater. Express. 3(2), 270–277 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1364/OME.3.000270
X. Wu, Z. Tang, S. Hu, H. Yan, Z. Xi, Y. Liu, NaLuF4:Yb3+, Er3+ bifunctional microcrystals codoped with Gd3+ or Dy3+ ions: Enhanced upconversion luminescence and ferromagnetic-paramagnetic transition. J. Alloys Compd. 684, 105–111 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.05.074
Y. Li, C. Liu, P. Zhang et al., Doping lanthanide nanocrystals with non-lanthanide ions to simultaneously enhance up- and down-conversion luminescence. Front. Chem. (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.00832
D.Q. Chen, L. Lei, R. Zhang, A.P. Yang, J. Xu, Y.S. Wang, Intrinsic single-band upconversion emission in colloidal Yb/Er(Tm):Na3Zr(Hf)F7 nanocrystals. Chem. Commun. 48, 10630–10632 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC35480B
F. Paquin, J. Rivnay, A. Salleo, N. Stingelin, C. Silva, Multi-phase semicrystalline microstructures drive exciton dissociation in neat plastic semiconductors. J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 10715–10722 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/b000000x
K. Omri, F. Alharbi, Microstructural properties and improvement in photoluminescence thermometry of Mn-activated single-phased Zn–SO–Mn phosphors. J. Mater. Sci. 32(19), 24229–24239 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06888-1
W. Niu, S. Wu, S. Zhang, J. Li, L. Li, Multicolor output and shape controlled synthesis of lanthanide-ion doped fluorides upconversion nanoparticles. Dalt. Trans. 40(13), 3305–3314 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/c0dt01344g
A. Kumar, S.P. Tiwari, J.C.G.E. Da Silva, K. Kumar, Security writing application of thermal decomposition assisted NaYF4:Er3+/Yb3+upconversion phosphor. Laser Phys. Lett. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1612-202X/aab123
L.T. Kieu Giang, Ł Marciniak, K. Kamil Żur et al., Zirconium metal organic framework for design of tetragonal rare earth-doped zirconia nanoparticles. J. Rare Earths. 37(11), 1230–1236 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2019.03.003
J. Sun, J. Xian, X. Zhang, H. Du, Hydrothermal synthesis of SrF2:Yb3+/Er3+ micro-/nanocrystals with multiform morphologies and upconversion properties. J. Rare Earths. 29(1), 32–38 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0721(10)60396-1
S. Namagal, N.V. Jaya, M. Muralidharan, S. Sumithra, Optical and magnetic properties of pure and Er, Yb-doped β-NaYF4 hexagonal plates for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Sci. 31(14), 11398–11410 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03689-w
Y. Song, G. Gong, J. Du et al., Synthesis and inkjet printing of NaYF 4: Ln 3+ @NaYF 4 core-shell nanoparticles with enhanced upconversion fluorescence for anti-counterfeiting applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 20(3), 1511–1519 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2020.17353
D. Chen, L. Lei, R. Zhang, A. Yang, J. Xu, Y. Wang, Intrinsic single-band upconversion emission in colloidal Yb/Er(Tm): Na3Zr(Hf)F7nanocrystals. Chem. Commun. 48(86), 10630–10632 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cc35480b
X. He, B. Yan, High-energy organic group-induced spectrally pure upconversion emission in novel zirconate-/hafnate-based nanocrystals. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 17, 7169–7174 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CE01195G
K. Janani, S. Ramasubramanian, A.K. Soni, V.K. Rai, P. Thiyagarajan, Luminescence properties of LiYF4:Yb3+, Er3+ phosphors: a study on influence of synthesis temperature and dopant concentration. Optik (Stuttg). 169(May), 147–155 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.05.023
S. He, H. Xia, Q. Tang et al., Efficient upconversion luminescence in Er3+/Yb3+ co-doped cubic NaYF4 single crystals by vertical Bridgman method with KF flux. Chin. J. Phys. 54(2), 256–262 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2016.04.011
K. Omri, I. Najeh, L. El Mir, Influence of annealing temperature on the microstructure and dielectric properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 42(7), 8940–8948 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.02.151
K. Omri, N. Alonizan, Effects of ZnO/Mn concentration on the micro-structure and optical properties of ZnO/Mn–TiO2 nano-composite for applications in photo-catalysis. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 29(1), 203–212 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-0979-4
K. Omri, S. Gouadria, Dielectric investigation and effect of low copper doping on optical and morphology properties of ZO-Cu nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 32(12), 17021–17031 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06268-9
P. Padhye, P. Poddar, Static and dynamic photoluminescence and photocatalytic properties of uniform, monodispersed up/down-converting, highly luminescent, lanthanide-ion-doped β-NaYF4 phosphor microcrystals with controlled multiform morphologies. J. Mater. Chem. A 2(45), 19189–19200 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta04274c
A.A. Ansari, R. Yadav, S.B. Rai, Enhanced luminescence efficiency of aqueous dispersible NaYF4:Yb/Er nanoparticles and the effect of surface coating. RSC Adv. 6(26), 22074–22082 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra00265j
V.K. Komarala, Y. Wang, M. Xiao, Nonlinear optical properties of Er3+/Yb3+-doped NaYF4 nanocrystals. Chem. Phys. Lett. 490(4–6), 189–193 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2010.03.041
T.M.D. Cao, T.T.G. Le, T.P.N. Nguyen, T.A.N. Dau, V.T. Nguyen, T.T.V. Tran, Investigating the effect of Yb3+ and Er3+ concentration on red/green luminescent ratio in β-NaYF4: Er, Yb nanocrystals using spectroscopic techniques. J. Mol. Struct. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.128014
S.H. Nannuri, S.D. Kulkarni, C.C.K. Subash, S. Chidangil, S.D. George, Post annealing induced manipulation of phase and upconversion luminescence of Cr3+ doped NaYF4:Yb, Er crystals. RSC Adv. 9(17), 9364–9372 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra00115h
J.Y. Law, J. Rial, M. Villanueva et al., Study of phases evolution in high-coercive MnAl powders obtained through short milling time of gas-atomized particles. J. Alloys Compd. 712, 373–378 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.04.038
P.J. Van Der Zaag, A. Noordermeer, M.T. Johnson, P.F. Bongers, Comment on size-dependent Curie temperature in nanoscale MnFe2O4 particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68(20), 3112 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.68.3112
P.M. Md Gazzali, G. Chandrasekaran, Enhancement of hard magnetic properties of BaFe12O19 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 25(2), 702–709 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1632-1
K. Kombaiah, J.J. Vijaya, L.J. Kennedy, M. Bououdina, R.J. Ramalingam, H.A. Al-Lohedan, Okra extract-assisted green synthesis of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles and their optical, magnetic, and antimicrobial properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 204, 410–419 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.10.077
Q. Chen, Z. Li, B. Miao, Q. Ma, Thermal, nonlinear, magnetic and faraday rotation properties of sol-gel diamagnetic glass /NaYF4: Fe, Ho3+: role of magnetic ions. J. Alloys Compd. 858, 157631 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157631
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge the Department of Science & Technology, Government of India, for providing financial support to Mrs Namagal S vide reference no.SR/WOS-A/PM-97/2017 under Women Scientist Scheme (WOS-A) to carry out this work, CIF—Pondicherry University for characterisation facilities and Greensmed Labs for cytotoxicity study.
Funding
Funding was provided by Department of Science and Technology India (Grant Number SR/WOS-A/PM-97/2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Namagal, S., Victor Jaya, N., Nithyaa, N. et al. Upconversion of NaYF4: Yb, Er Nanoparticles Co-doped with Zr 4+ for Magnetic Phase Transition and Biomedical Imaging Applications. J Inorg Organomet Polym 32, 3128–3140 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02342-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02342-9