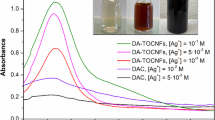
Abstract
The objective of the present study was to synthesize Cu doped ZnS nanocore crosslinked with lignocellulose (represented as Cu:ZnS-lignocellulose nanocomposite) for antifungal action against the devastating tea blister blight pathogen Exobasidium vexans. The characteristic features of the nanocomposite were analyzed via different physicochemical techniques like FTIR, XRD, XPS, SEM, SEM–EDX, Elemental mapping, PCS, and UV-PL studies. The FTIR and XPS investigations revealed the crosslinking between lignocellulose and the Cu:ZnS. The presence of lignocellulose was seen to attribute a potent antifungal efficacy, also enhancing the stability of the resulting nanocomposite in aqueous suspensions. The antifungal efficacy confirmed through disk diffusion and broth dilution assays have a maximum zone of inhibition of 1.75 cm2 and a MIC50 of 0.05 mg/ml against E. vexans. Additionally, the antisporulant activity was evident as the basidiospores failed to germinate in presence of the Cu:ZnS-lignocellulose nanocomposites. This shows potential for stemming the rapid infectivity of E. vexans by achieving disease inhibition at the early stage. Finally, the comparison with two commonly used commercial fungicides (copper oxychloride and fluconazole) demonstrated > tenfold higher antifungal activity for Cu:ZnS-lignocellulose nanocomposites.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
R. Ghosh, S. Kundu, R. Majumder, M.P. Chowdhury, Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of multifunctional ZnO nanomaterials. Mater. Today: Proc. 26, 77–81 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.04.217
J.R. Lamichhane, E. Osdaghi, F. Behlau, J. Köhl, J.B. Jones, J.N. Aubertot, Thirteen decades of antimicrobial copper compounds applied in agriculture. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 38, 28 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-018-0503-9
N. Pariona, A.I. Mtz-Enriquez, D. Sánchez-Rangel, G. Carrión, F. Paraguay-Delgado, G. Rosas-Saito, Green-synthesized copper nanoparticles as a potential antifungal against plant pathogens. RSC Adv. 9, 18835–18843 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA03110C
S. Chandra, N. Chakraborty, K. Panda, K. Acharya, Chitosan-induced immunity in Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze against blister blight disease is mediated by nitric-oxide. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 115, 298–307 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.04.008
M. Anastassiadou, G. Bernasconi, A. Brancato, L. Carrasco Cabrera, L. Greco, S. Jarrah, A. Kazocina, R. Leuschner, J.O. Magrans, I. Miron, S. Nave, R. Pedersen, H. Reich, A. Rojas, A. Sacchi, M. Santos, A. Stanek, A. Theobald, B. Vagenende, A. Verani, Modification of the existing maximum residue levels for mandipropamid in kohlrabies and herbs and edible flowers. EFSA J. 18, e05958 (2020). https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2020.5958
M. Young, A. Ozcan, M.E. Myers, E.G. Johnson, J.H. Graham, S. Santra, Multimodal generally recognized as safe ZnO/nanocopper composite: a novel antimicrobial material for the management of citrus phytopathogens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 66, 6604–6608 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b02526
A.F. Oussou-Azo, T. Nakama, M. Nakamura, T. Futagami, M.D.C.M. Vestergaard, Antifungal potential of nanostructured crystalline copper and its oxide forms. Nanomaterials 10, 1003 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10051003
S.K. Mani, M. Saroja, M. Venkatachalam, T. Rajamanickam, Antimicrobial activity and photocatalytic degradation properties of zinc sulfide nanoparticles synthesized by using plant extracts. J. Nanostruct. 8, 107–118 (2018). https://doi.org/10.22052/JNS.2018.02.001
Z. Morshedtalab, G. Rahimi, A. Emami-Nejad, A. Farasat, A. Mohammadbeygi, N. Ghaedamini, M. Negahdary, Antibacterial assessment of zinc sulfide nanoparticles against Streptococcus pyogenes and Acinetobacter baumannii. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 20, 1042–1055 (2020). https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612826666200406095246
M. Arshad, A. Qayyum, G.A. Shar, G.A. Soomro, A. Nazir, B. Munir, M. Iqbal, Zn-doped SiO2 nanoparticles preparation and characterization under the effect of various solvents: antibacterial, antifungal and photocatlytic performance evaluation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 185, 176–183 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.04.043
S.A. Khan, F. Noreen, S. Kanwal, A. Iqbal, G. Hussain, Green synthesis of ZnO and Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles from leaf extracts of Abutilon indicum, Clerodendrum infortunatum, Clerodendrum inerme and investigation of their biological and photocatalytic activities. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 82, 46–59 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.08.071
X. Li, X. Wu, T. Yuan, J. Zhu, Y. Yang, Influence of the iodine content of nitrogen-and iodine-doped carbon dots as a peroxidase mimetic nanozyme exhibiting antifungal activity against C. albicans. Biochem. Eng. J. 175, 108139 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2021.108139
G.T. Vidyavathi, B.V. Kumar, A.V. Raghu, T. Aravinda, U. Hani, H.A. Murthy, A.H. Shridhar, Punica granatum pericarp extract catalyzed green chemistry approach for synthesizing novel ligand and its metal (II) complexes: Molecular docking/DNA interactions. J. Mol. Struct. 1249, 131656 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.131656
K.V. Karthik, A.V. Raghu, K.R. Reddy, R. Ravishankar, M. Sangeeta, N.P. Shetti, C.V. Reddy, Green synthesis of Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles and its application for the photocatalytic degradation of hazardous organic pollutants. Chemosphere 287, 132081 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132081
K. Kannan, D. Radhika, K.R. Reddy, A.V. Raghu, K.K. Sadasivuni, G. Palani, K. Gurushankar, Gd3+ and Y3+ co-doped mixed metal oxide nanohybrids for photocatalytic and antibacterial applications. Nano Express. 2(1), 010014 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/2632-959X/abdd87
K.R. Reddy, M.S. Jyothi, A.V. Raghu, V. Sadhu, S. Naveen, T.M. Aminabhavi, Nanocarbons-supported and polymers-supported titanium dioxide nanostructures as efficient photocatalysts for remediation of contaminated wastewater and hydrogen production, in Nanophotocatalysis and Environmental Applications (Springer, Cham, 2020), pp. 139–169
S. Kumar, K.R. Reddy, C. Reddy, N.P. Shetti, V. Sadhu, M.V. Shankar, T.M. Aminabhavi, Metal nitrides and graphitic carbon nitrides as novel photocatalysts for hydrogen production and environmental remediation, in Nanostructured Materials for Environmental Applications (Springer, Cham, 2021), pp. 485–519. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72076-6
J.L. Hodala, D.J. Moon, K.R. Reddy, C.V. Reddy, T.N. Kumar, M.I. Ahamed, A.V. Raghu, Catalyst design for maximizing C5+ yields during Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. Int. J. Hydrog 46(4), 3289–3301 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.12.021
A. Aradmehr, V. Javanbakht, A novel biofilm based on lignocellulosic compounds and chitosan modified with silver nanoparticles with multifunctional properties: synthesis and characterization. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 600, 124952 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.124952
W. Zuo, M. Shahriari, M. Shahriari, M. Javadi, H. Mohebi, N. Abbasi, H. Ghaneialvar, Synthesis and application of Au NPs-chitosan nanocomposite in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia in vitro and in vivo. Arab. J. Chem. 14, 102929 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2020.102929
F. Lobo, A.R. Franco, E.M. Fernandes, R.L. Reis, An overview of the antimicrobial properties of lignocellulosic materials. Molecules 26, 1749 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061749
C. Chaliha, B.K. Nath, P.K. Verma, E. Kalita, Synthesis of functionalized Cu:ZnS nanosystems and its antibacterial potential. Arab. J. Chem. 12, 515–524 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2016.05.002
C. Chaliha, E. Kalita, P.K. Verma, Optimizing in vitro culture conditions for the biotrophic fungi exobasidium vexans through response surface methodology. Indian J. Microbiol. 60, 167–174 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-019-00846-6
S.K. Rai, J.K. Roy, A.K. Mukherjee, Application of poly (vinyl alcohol)-assisted silver nanoparticles immobilized β-keratinase composite as topical antibacterial and dehairing agent. J. Protein. Proteomics 11, 119–134 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42485-020-00034-x
J. Chen, L. Wu, M. Lu, S. Lu, Z. Li, W. Ding, Comparative study on the fungicidal activity of metallic MgO nanoparticles and macroscale MgO against soilborne fungal phytopathogens. Front. Microbiol. 11, 365 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.00365
M. Kuppayee, G.V. Nachiyar, V. Ramasamy, Synthesis and characterization of Cu2+ doped ZnS nanoparticles using TOPO and SHMP as capping agents. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 6779–6786 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.02.124
F. Niu, M. Li, Q. Huang, X. Zhang, W. Pan, J. Yang, J. Li, The characteristic and dispersion stability of nanocellulose produced by mixed acid hydrolysis and ultrasonic assistance. Carbohydr. Polym. 165, 197–204 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.02.048
W.Q. Xie, K.X. Yu, Y.X. Gong, Preparation of fluorescent and antibacterial nanocomposite films based on cellulose nanocrystals/ZnS quantum dots/polyvinyl alcohol. Cellulose 26, 2363–2373 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02245-y
A.V. Raghu, G.S. Gadaginamath, M. Priya, P. Seema, H.M. Jeong, T.M. Aminabhavi, Synthesis and characterization of novel polyurethanes based on N1, N4-bis [(4-hydroxyphenyl) methylene] succinohydrazide hard segment. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 110(4), 2315–2320 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.27366
A.V. Raghu, G.S. Gadaginamath, H.M. Jeong, N.T. Mathew, S.B. Halligudi, T.M. Aminabhavi, Synthesis and characterization of novel Schiff base polyurethanes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 113(5), 2747–2754 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.28257
J.T. Orasugh, N.R. Saha, G. Sarkar, D. Rana, D. Mondal, S.K. Ghosh, D. Chattopadhyay, A facile comparative approach towards utilization of waste cotton lint for the synthesis of nano-crystalline cellulose crystals along with acid recovery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 109, 1246–1252 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.11.123
W. Yang, E. Fortunati, F. Dominici, G. Giovanale, A. Mazzaglia, G.M. Balestra, J.M. Kenny, D. Puglia, Effect of cellulose and lignin on disintegration, antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of PLA active films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 89, 360–368 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.04.068
S. Reghuram, A. Arivarasan, R. Kalpana, R. Jayavel, CdSe and CdSe/ZnS quantum dots for the detection of C-reactive protein. J. Exp. Nanosci. 10, 787–802 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/17458080.2014.902542
J.F. Luna-Martínez, D.B. Hernández-Uresti, M.E. Reyes-Melo, C.A. Guerrero-Salazar, V.A. González-González, S. Sepúlveda-Guzmán, Synthesis and optical characterization of ZnS–sodium carboxymethyl cellulose nanocomposite films. Carbohydr. Polym. 84, 566–570 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.12.021
Y.W. Chen, H.V. Lee, Revalorization of selected municipal solid wastes as new precursors of “green” nanocellulose via a novel one-pot isolation system: a source perspective. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 107, 78–92 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.143
F. Li, J. Gao, Y. Li, X. He, L. Chen, Y. Zhang, Selective and sensitive determination of celastrol in traditional Chinese medicine based on molecularly imprinted polymers modified Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots optosensing materials. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 190, 110929 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.110929
A. Shehabeldine, H. El-Hamshary, M. Hasanin, A. El-Faham, M. Al-Sahly, Enhancing the antifungal activity of griseofulvin by incorporation a green biopolymer-based nanocomposite. Polymers 13, 542 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040542
W. Lu, Y. Sun, H. Dai, P. Ni, S. Jiang, Y. Wang, Z. Li, Z. Li, Fabrication of cuprous sulfide nanorods supported on copper foam for nonenzymatic amperometric determination of glucose and hydrogen peroxide. RSC Adv. 6, 90732–90738 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA18641F
X. Zhuang, H. Zhan, Y. Song, C. He, Y. Huang, X. Yin, C. Wu, Insights into the evolution of chemical structures in lignocellulose and non-lignocellulose biowastes during hydrothermal carbonization (HTC). Fuel 236, 960–974 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.09.019
L.P. Xiao, Z.J. Shi, F. Xu, R.C. Sun, Hydrothermal carbonization of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 118, 619–623 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/ef101745
H.K. Ardani, C. Imawan, W. Handayani, D. Djuhana, A. Harmoko, V. Fauzia, Enhancement of the stability of silver nanoparticles synthesized using aqueous extract of Diospyros discolor Willd. leaves using polyvinyl alcohol. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 188, 012056 (2017)
K. Sowndhararajan, S. Marimuthu, S. Manian, Biocontrol potential of phylloplane bacterium O chrobactrum anthropi BMO-111 against blister blight disease of tea. J. Appl. Microbiol. 114, 209–218 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.12026
U.T. Khatoon, G.N. Rao, M.K. Mohan, A. Ramanaviciene, A. Ramanavicius, Antibacterial and antifungal activity of silver nanospheres synthesized by tri-sodium citrate assisted chemical approach. Vacuum 146, 259–265 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2017.10.003
U.T. Khatoon, G.N. Rao, M.K. Mohan, A. Ramanaviciene, A. Ramanavicius, Comparative study of antifungal activity of silver and gold nanoparticles synthesized by facile chemical approach. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 6(5), 5837–5844 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.08.009
R. Chougale, D. Kasai, S. Nayak, S. Masti, A. Nasalapure, A.V. Raghu, Design of eco-friendly PVA/TiO2-based nanocomposites and their antifungal activity study. Green Mater. 8(1), 40–48 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1680/jgrma.19.00002
C. Vanlalveni, S. Lallianrawna, A. Biswas, M. Selvaraj, B. Changmai, S.L. Rokhum, Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plant extracts and their antimicrobial activities: a review of recent literature. RSC Adv. 11(5), 2804–2837 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA09941D
A.T. Babu, M. Sebastian, O. Manaf, R. Antony, Heterostructured nanocomposites of Ag doped Fe3O4 embedded in ZnO for antibacterial applications and catalytic conversion of hazardous wastes. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 30(6), 1944–1955 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01366-y
D. Wang, B. Zhang, L.F. Xu, L.N. Huang, Construction of a new In (III)-based coordination polymer for selective luminescent detection of Cr2O72− and anti-bacterial protective effect on Staphylococcus aureus infection after missed abortion. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 93(1), 92–98 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1246/bcsj.20190206
E. Priyadarshini, S.S. Priyadarshini, B.G. Cousins, N. Pradhan, Metal-fungus interaction: review on cellular processes underlying heavy metal detoxification and synthesis of metal nanoparticles. Chemosphere 274, 129976 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129976
P.S.S. Selvam, G.S. Chinnadurai, D. Ganesan, P. Perumal, V. Kandan, Cadmium oxide-zinc oxide nanocomposites synthesized using waste eggshell membrane and its in-vitro assessments of the antimicrobial activities and minimum inhibitory concentration. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 31(2), 816–835 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01688-2
G. Mamatha, P. Sowmya, D. Madhuri, N.M. Babu, D.S. Kumar, G.V. Charan, K. Madhukar, Antimicrobial cellulose nanocomposite films with in situ generations of bimetallic (Ag and Cu) nanoparticles using Vitex negundo leaves extract. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 31(2), 802–815 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01819-9
G.L. Vanti, S. Masaphy, M. Kurjogi, S. Chakrasali, V.B. Nargund, Synthesis and application of chitosan-copper nanoparticles on damping off causing plant pathogenic fungi. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 156, 1387–1395 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.11.179
L.A. Hermida-Montero, N. Pariona, A.I. Mtz-Enriquez, G. Carrión, F. Paraguay-Delgado, G. Rosas-Saito, Aqueous-phase synthesis of nanoparticles of copper/copper oxides and their antifungal effect against Fusarium oxysporum. J. Hazard. Mater. 380, 120850 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120850
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge DBT, Govt. of India, for the Twinning Research Grant (Grant No. BT/427/NE/TBP/2013). Author CC would like to acknowledge DST, Govt. of India for her DST INSPIRE Junior Research Fellowship (IF-150964). The authors thank Ananda Tea Estate, North Lakhimpur District, Assam, India, for providing the blister blight infected tea leaf samples used in the study.
Funding
This work was supported by DST INSPIRE, Govt. of India (Grant No. IF-150964) and DBT, Govt. of India, Twinning Research Grant (Grant No. BT/427/NE/TBP/2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CC: Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing—original draft. JB: Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing—review and editing. EK: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Verification, Writing—review and editing, Project administration, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors CC, JB, and EK certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Ethical Approvals
The authors CC, JB, and EK have seen and approved the manuscript, and it hasn’t been accepted and published elsewhere.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaliha, C., Baruah, J. & Kalita, E. Nanoarchitectonics of Crosslinked Cu:ZnS-Lignocellulose Nanocomposite: A Potent Antifungal and Antisporulant System Against the Tea Pathogen Exobasidium vexans. J Inorg Organomet Polym 32, 954–966 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02225-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02225-z