Abstract
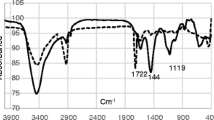
The purpose of this study is to investigate the capability of novel peripheral metal-free and metallo (2H, Fe, Co, Zn) mono nuclear phthalocyanines coated quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) sensor for the detection of nitrate ions in water. Although the synthesis of phthalocyanines is usually difficult and expensive, the novel phthalocyanine complexes are planned to be used as nitrate ion detectors in water because their synthesis is easy and cheap. The starting compound and the phthalocyanines were characterized by elemental analyses, FT-IR, UV–vis 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR and MALDI-TOF mass spectral data. The effect of metals on spectroscopic properties and aggregation behaviours of these novel phthalocyanines were investigated in different solvents. From nitrate ion detection tests, it was observed that the 2(3),9(10),16(17),23(24)-tetrachloro-2(3),9(10),16(17),23(24)-tetrakis(3,4,5-trimethoxyphen-oxy)phthalocyaninatozinc(II) functionalized sensor exhibits a low detection limit of 0.08 mg/mL with a rapid response within 15–22 s, which is superior to most of the commonly used methods. Our study provides a new strategy for rapid, and sensitive, detection of nitrates, and is promising for real-time and in-situ water quality monitoring. In addition, the nitrate ion adsorption kinetics of these compounds was also modelled according to three different kinetic models, namely pseudo first order kinetic model, Elovich model and interparticle diffusion kinetic model. It was observed that the adsorption kinetics obeys to the first order model for low concentrations of nitrate ions, while the Elovich model is the most appropriate to model nitrate ions adsorption for high concentration of nitrate ions.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.M. Fan, V.E. Steinberg, Health implications of nitrate and nitrite in drinking water: an update on methemoglobinemia occurrence and reproductive and developmental toxicity. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 23(1), 35–43 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1006/rtph.1996.0006
R.A. Al-Okab, A.A. Syed, Novel reactions for simple and sensitive spectrophotometric determination of nitrite. Talanta 72(4), 1239–1247 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2007.01.027
T.E. Arbuckle, G.J. Sherman, P.N. Corey, D. Walters, B. Lo, Water nitrates and CNS birth defects: a population-based case-control study. Arch. Environ. Health 43(2), 162–167 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1080/00039896.1988.9935846
B.C.K. Choi, N-NFrROSO compounds and human cancer: a molecular epidemiologic approach. Am. J. Epidemiol. 121(5), 737–743 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/121.5.737
W.L. Daniel, M.S. Han, J.-S. Lee, C.A. Mirkin, Colorimetric nitrite and nitrate detection with gold nanoparticle probes and kinetic end points. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131(18), 6362–6363 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja901609k
K.M. Miranda, M.G. Espey, D.A. Wink, A rapid, simple spectrophotometric method for simultaneous detection of nitrate and nitrite. Nitric Oxide 5(1), 62–71 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1006/niox.2000.0319
A. Dudwadkar, N. Shenoy, J.M. Joshi, S.D. Kumar, H. Rao, A.V.R. Reddy, Application of ion chromatography for the determination of nitrate in process streams of thermal denitration plant. Sep. Sci. Technol. 48(16), 2425–2430 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2013.807831
R. Guidelli, F. Pergola, G. Raspi, Voltammetric behavior of nitrite ion on platinum in neutral and weakly acidic media. Anal. Chem. 44(4), 745–755 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60312a018
J. Liang, Y. Zheng, Z. Liu, Nanowire-based Cu electrode as electrochemical sensor for detection of nitrate in water. Sens. Actuators B 232, 336–344 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.03.145
M. Bertotti, D. Pletcher, Amperometric determination of nitrite via reaction with iodide using microelectrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 337, 49–55 (1997)
M. Badea, A. Amine, G. Palleschi, D. Moscone, G. Volpe, A. Curulli, New electrochemical sensors for detection of nitrites and nitrates. J. Electroanal. Chem. 509(1), 66–72 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0728(01)00358-8
M.E.E. Alahi, A. Nag, S.C. Mukhopadhyay, L. Burkitt, A temperature-compensated graphene sensor for nitrate monitoring in real-time application. Sens. Actuators A 269, 79–90 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2017.11.022
G. Högg, G. Steiner, K. Cammann, Development of a sensor card with integrated reference for the detection of nitrate. Sens. Actuators B 19(1), 376–379 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0925-4005(93)01001-K
M.E.E. Alahi, L. Xie, S. Mukhopadhyay, L. Burkitt, A temperature compensated smart nitrate-sensor for agricultural industry. IEEE Trans. Industr. Electron. 64(9), 7333–7341 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2017.2696508
S. Shahnia, H. Ebendorff-Heidepriem, D. Evans, S. Afshar, A fibre-optic platform for sensing nitrate using conducting polymers. Sensors (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010138
R. Lumpp, J. Reichert, H.J. Ache, An optical sensor for the detection of nitrate. Sens. Actuators B 7(1), 473–475 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1016/0925-4005(92)80346-Y
X. Chen, H. Pu, Z. Fu, X. Sui, J. Chang, J. Chen, S. Mao, Real-time and selective detection of nitrates in water using graphene-based field-effect transistor sensors. Environ. Sci. Nano 5(8), 1990–1999 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8EN00588E
W. Xuejiang, S.V. Dzyadevych, J.-M. Chovelon, N.J. Renault, C. Ling, X. Siqing, Z. Jianfu, Conductometric nitrate biosensor based on methyl viologen/Nafion/nitrate reductase interdigitated electrodes. Talanta 69(2), 450–455 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2005.10.014
M.E.E. Alahi, S.C. Mukhopadhyay, L. Burkitt, Imprinted polymer coated impedimetric nitrate sensor for real- time water quality monitoring. Sens. Actuators B 259, 753–761 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.12.104
S.M. Shariar, T. Hinoue, Simultaneous voltammetric determination of nitrate and nitrite ions using a copper electrode pretreated by dissolution/redeposition. Anal. Sci. 26(11), 1173–1179 (2010). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.26.1173
A. Jang, Z. Zou, K.K. Lee, C.H. Ahn, P.L. Bishop, Potentiometric and voltammetric polymer lab chip sensors for determination of nitrate, pH and Cd(II) in water. Talanta 83(1), 1–8 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2010.07.061
P. Suvarnaphaet, S. Pechprasarn, Graphene-based materials for biosensors: a review. Sensors (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102161
S.J. Rowley-Neale, E.P. Randviir, A.S. Abo Dena, C.E. Banks, An overview of recent applications of reduced graphene oxide as a basis of electroanalytical sensing platforms. Appl. Mater. Today 10, 218–226 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2017.11.010
W. Tang, J. Ping, K. Fan, Y. Wang, X. Luo, Y. Ying, J. Wu, Q. Zhou, All-solid-state nitrate-selective electrode and its application in drinking water. Electrochim. Acta 81, 186–190 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.07.073
R.-I. Stefan-van Staden, M. Mincu, J.F. van Staden, L.A. Gugoasa, Molecular recognition of nitrites and nitrates in water samples using graphene-based stochastic microsensors. Anal. Chem. 90(16), 9997–10000 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b02467
G. de la Torre, M. Nicolau, T. Torres, Chapter 1—phthalocyanines: synthesis, supramolecular organization, and physical properties, in Supramolecular Photosensitive and Electroactive Materials. ed. by H.S. Nalwa (Academic Press, San Diego, 2001), pp. 1–111
G. de la Torre, C.G. Claessens, T. Torres, Phthalocyanines: old dyes, new materials. Putt. Color Nanotechnol. 20, 2000–2015 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1039/B614234F
D. Wöhrle, G. Schnurpfeil, S. Makarov, A. Kazarin, O. Suvorova, Practical applications of phthalocyanines—from dyes and pigments to materials for optical, electronic and photo-electronic devices. Macroheterocycles 5, 191–202 (2012). https://doi.org/10.6060/mhc2012.120990w
Petergregory, Industrial applications of phthalocyanines. J. Porphyrins Phthalocyanines (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1409(200006/07)4:4%3c432::AID-JPP254%3e3.0.CO;2-N
Y. Zhang, J.F. Lovell, Recent applications of phthalocyanines and naphthalocyanines for imaging and therapy. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/wnan.1420
Y. Yılmaz, M. Kasım Şener, İ Erden, U. Avcıata, Derivatization and in situ metallation of phthalocyanines using click chemistry. Polyhedron 28(16), 3419–3424 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2009.07.033
A.M. Schmidt, M.J.F. Calvete, Phthalocyanines: an old dog can still have new (photo)tricks! Molecules 26(9), 2823 (2021)
J. Chen, N. Chen, J. Huang, J. Wang, M. Huang, Derivatizable phthalocyanine with single carboxyl group: synthesis and purification. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 9, 313–315 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2005.12.002
A. Snow, Phthalocyanine aggregation. Porphyrin Handbook 17, 129–176 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-092391-8.50009-1
C. Jing, R. Wang, H. Ou, A. Li, Y. An, S. Guo, L. Shi, Axial modification inhibited H-aggregation of phthalocyanines in polymeric micelles for enhanced PDT efficacy. Chem. Commun. 54(32), 3985–3988 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CC09954A
M.Á. Revuelta-Maza, T. Torres, T. Gdl, Synthesis and aggregation studies of functional binaphthyl-bridged chiral phthalocyanines. Org. Lett. 21(20), 8183–8186 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.9b02718
D. Zhang, M. Zhu, L. Zhao, J. Zhang, K. Wang, D. Qi, Y. Zhou, Y. Bian, J. Jiang, Ratiometric fluorescent detection of Pb2+ by FRET-based phthalocyanine-porphyrin dyads. Inorg. Chem. 56(23), 14533–14539 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.7b02261
V. Sajjan, S. Aralekallu, M. Nemakal, M. Palanna, C.P.K. Prabhu, K.S. Lokesh, Nanomolar detection of lead using electrochemical methods based on a novel phthalocyanine. Inorg. Chim. Acta 506, 119564 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2020.119564
A. Beduoğlu, A.M. Sevim, A. Koca, A. Altındal, Z. Altuntaş Bayır, Thiazole-substituted non-symmetrical metallophthalocyanines: synthesis, characterization, electrochemical and heavy metal ion sensing properties. New J. Chem. 44(14), 5201–5210 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NJ00466A
N. Can, B.C. Ömür, A. Altındal, Modeling of heavy metal ion adsorption isotherms onto metallophthalocyanine film. Sens. Actuators B 237, 953–961 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.07.026
J. Deng, B. Wang, Y. Shi, Q. Song, A. Wang, L. Hao, B. Luo, X. Li, Z. Wang, F. Wang, L.J. Zhi, Poly (zinc phthalocyanine) nanoribbons and their application in the high-sensitive detection of lead ions. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 213(10–11), 1051–1059 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/macp.201100613
D. Gounden, S. Khene, N. Nombona, Electroanalytical detection of heavy metals using metallophthalocyanine and silica-coated iron oxide composites. Chem. Pap. 72(12), 3043–3056 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-018-0545-0
E. Hande Alici, A. Günsel, M. Akin, A.T. Bilgiçli, G. Arabaci, M. Nilüfer Yarasir, Synthesis, characterization, antioxidant and antibacterial properties of non-peripherally and peripherally tetra-substituted phthalocyanines. J. Coord. Chem. 71(19), 3077–3089 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/00958972.2018.1511778
S. Şahin, S. Altun, A. Altındal, Z. Odabaş, Synthesis of novel azo-bridged phthalocyanines and their toluene vapour sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B 206, 601–608 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.09.110
M. Pişkin, N. Can, Z. Odabaş, A. Altındal, Toluene vapor sensing characteristics of novel copper(II), indium(III), mono-lutetium(III) and tin(IV) phthalocyanines substituted with 2,6-dimethoxyphenoxy bioactive moieties. J. Porphyrins Phthalocyanines 22(01n03), 189–197 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1142/S1088424617500900
G. Sauerbrey, Verwendung von Schwingquarzen zur Wägung dünner Schichten und zur Mikrowägung. Z. Phys. 155(2), 206–222 (1959). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01337937
M. Stillman, T. Nyokong, C. Leznoff, A. Lever, Phthalocyanines: properties and applications (VCH, New York, 1989), p. 133
T. Nyokong, Electronic spectral and electrochemical behavior of near infrared absorbing metallophthalocyanines, in Functional Phthalocyanine Molecular Materials. ed. by J. Jiang (Springer, 2010), pp. 45–87
J. Janczak, R. Kubiak, M. Śledź, H. Borrmann, Y. Grin, Synthesis, structural investigations and magnetic properties of dipyridinated manganese phthalocyanine, MnPc(py)2. Polyhedron 22(19), 2689–2697 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0277-5387(03)00361-9
Lagergren S Zur Theorie der sogenannten Adsorption gelöster Stoffe. Zeitschrift für Chemie und Industrie der Kolloide 2, 15
A. Altındal, Ö. Kurt, A. Şengül, Ö. Bekaroğlu, Kinetics of CO2 adsorption on ball-type dicopper phthalocyanine thin film. Sens. Actuators B 202, 373–381 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.05.107
J. Weber Walter, J.C. Morris, Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 89(2), 31–59 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1061/JSEDAI.0000430
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to The Foundation of Marmara University, The Commission of Scientific Research (BAPKO) (Project No: FEN-C-YLP-140115-0010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bilen Şentürk, C., Şahin, A.N., Çetin, A. et al. Nitrate Ion Sensing Properties of Peripheral 3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenoxy and Chlorine Substituted Metallo and Metal-free Phthalocyanines. J Inorg Organomet Polym 32, 1436–1447 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02203-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02203-x