Abstract
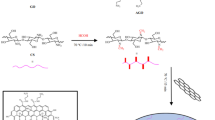
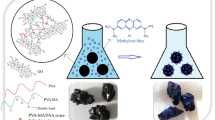
In this paper, chitosan/Fe3O4/graphene oxide hydrogel was synthesized then modified with 2,6-pyridinedicarbonyl dichloride to obtain a novel composite hydrogel. The modified hydrogel formed via interfacial polymerization crosslinking of amino groups of chitosan in chitosan/Fe3O4/graphene oxide hydrogel with acyl groups of 2,6-pyridinedicarbonyl dichloride. The synthesized hydrogels were characterized using different tools such as FT-IR, XRD, TGA, VSM, BET, HR-TEM, and FE-SEM instruments. The successful modification was demonstrated through FE-SEM where sphere and rod shapes were noticed due to the presence of Fe3O4/graphene oxide. The XRD diffraction peaks of the modified hydrogel were close to that of Fe3O4 without any changes in its structure. Also, there are no distinguishing XRD diffraction peaks due to the graphene oxide owing to the disorders that happen in graphene during the formation of the composite. The modified hydrogel was efficiently utilized for removing eriochrome black T and methylene blue dyes from aqueous media. The optimum pH for removing eriochrome black-T and methylene blue dyes is 2 and 8, respectively. Also, the optimum contact time and temperature for removing eriochrome black-T and methylene blue dyes are 140 min and 318 K, respectively. The maximum adsorption capacity of the modified hydrogel toward eriochrome black T and methylene blue dyes is 289.85 and 261.78 mg/g, respectively. The equilibrium and kinetic results were best fitted to the Langmuir isotherm and pseudo-second-order. The thermodynamic results confirmed that the adsorption process was spontaneous and endothermic.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
N.A. Matrose, K. Obikese, Z.A. Belay, O.J. Caleb, A decade development in the application of chitosan-based materials for dye adsorption: a short review. Sci. Total Environ. 30, 135907 (2019)
C. Osagie, A. Othmani, S. Ghosh, A. Malloum, Z. Kashitarash Esfahani, S. Ahmadi, Dyes adsorption from aqueous media through the nanotechnology: a review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 14, 2195–2218 (2021)
W. Xiao, X. Jiang, X. Liu, W. Zhou, Z.N. Garba, I. Lawan, L. Wang, Z. Yuan, Adsorption of organic dyes from wastewater by metal-doped porous carbon materials. J. Clean. Prod. 284, 124773 (2021)
A. Abu-Nada, A. Abdala, G. McKay, Removal of phenols and dyes from aqueous solutions using graphene and graphene composite adsorption: a review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9, 105858 (2021)
D. Jiang, M. Chen, H. Wang, G. Zeng, D. Huang, M. Cheng, Y. Liu, W. Xue, Z.W. Wang, The application of different typological and structural MOFs-based materials for the dyes adsorption. Coord. Chem. Rev. 380, 471–483 (2019)
A. Kumar, A. Kumar, A. Pal, D. Pal, T. Pal, Ammonium phosphomolybdate [(NH4)3 PMo12O40] an inorganic ion exchanger for environmental application for purification of dye contaminant wastewater. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 418, 113427 (2021)
M.M. Hassan, C.M. Carr, A critical review on recent advancements of the removal of reactive dyes from dye house effluent by ion-exchange adsorbents. Chemosphere 209, 201–219 (2018)
V. Kumar, Adsorption kinetics and isotherms for the removal of rhodamine B dye and Pb+2 ions from aqueous solutions by a hybrid ion-exchanger. Arab. J. Chem. 12, 316–329 (2019)
J. Pang, X. Cui, Y. Feng, Z. Guo, G. Kong, L. Yu, C. Zhang, Fabrication of graphene oxide membrane with multiple “Plug-ins” for efficient dye nanofiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 278, 119504 (2022)
T. My, H. Le, S. Singto, W. Sajomsang, R. Mongkolnavin, Hydrophobic PVDF hollow fiber membrane modified with pulse inductively coupling plasma activation and chloroalkylsilanes for efficient dye wastewater treatment by ozonation membrane contactor. J. Membr. Sci. 635, 119443 (2021)
E. Oyarce, B. Butter, P. Santander, J. Sánchez, Polyelectrolytes applied to remove methylene blue and methyl orange dyes from water via polymer enhanced ultrafiltration. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9(6), 106297 (2021)
D. Liu, J. Yin, H. Tang, H. Wang, S. Liu, T. Huang, S. Fang, K. Zhu, Z. Xie, Fabrication of ZIF-67 @ PVDF ultrafiltration membrane with improved antifouling and separation performance for dye wastewater treatment via sulfate radical enhancement. Sep. Purif. Technol. 279, 119755 (2021)
B. Ramírez-pereda, G. Rangel-peraza, V. Bustos-Terrones, M.N. Rojas-valencia, M. Vaca, Removal of BB9 textile dye by biological, physical, chemical, and electrochemical treatments. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 121, 29–37 (2021)
E.F.D. Januário, T.B. Vidovix, R. Bergamasco, A.M.S. Vieira, Performance of a hybrid coagulation/flocculation process followed by modified microfiltration membranes for the removal of solophenyl blue dye. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 168, 108577 (2021)
M. Adel, M.A. Ahmed, A.A. Mohamed, Effective removal of indigo carmine dye from wastewaters by adsorption onto mesoporous magnesium ferrite nanoparticles. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 16, 100550 (2021)
E.A. Abdelrahman, R.M. Hegazey, Facile synthesis of HgO nanoparticles using hydrothermal method for efficient photocatalytic degradation of crystal violet dye under UV and sunlight irradiation. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 29, 346–358 (2019)
E.A. Abdelrahman, R.M. Hegazey, Y.H. Kotp, A. Alharbi, Facile synthesis of Fe2O3 nanoparticles from Egyptian insecticide cans for efficient photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue and crystal violet dyes. Spectrochim. Acta A 222, 117195 (2019)
A. Alharbi, E.A. Abdelrahman, Efficient photocatalytic degradation of malachite green dye using facilely synthesized hematite nanoparticles from Egyptian insecticide cans. Spectrochim. Acta A 226, 117612 (2020)
R.M. Hegazey, E.A. Abdelrahman, Y.H. Kotp, A.M. Hameed, A. Subaihi, Facile fabrication of hematite nanoparticles from Egyptian insecticide cans for efficient photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B dye. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 1652–1661 (2020)
M.M. Abdelghany, I.S. Ahmed, H.A. Dessouki, E.A. Abdelrahman, Facile synthesis of CuO and Ag nanoparticles by thermal decomposition of novel Schiff base complexes. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02032-y
E.A. Abdelrahman, Synthesis of zeolite nanostructures from waste aluminum cans for efficient removal of malachite green dye from aqueous media. J. Mol. Liq. 253, 72–82 (2018)
X. Qi, L. Wu, T. Su, J. Zhang, W. Dong, Polysaccharide-based cationic hydrogels for dye adsorption. Colloids Surf. B 170, 364–372 (2018)
Y. Qi, M. Yang, W. Xu, S. He, Y. Men, Natural polysaccharides-modified graphene oxide for adsorption of organic dyes from aqueous solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 486, 84–96 (2017)
E.A. Abdelrahman, R.M. Hegazey, Utilization of waste aluminum cans in the fabrication of hydroxysodalite nanoparticles and their chitosan biopolymer composites for the removal of Ni(II) and Pb(II) ions from aqueous solutions: kinetic, equilibrium, and reusability studies. Microchem. J. 145, 18–25 (2019)
E.A. Abdelrahman, R.M. Hegazey, Exploitation of Egyptian insecticide cans in the fabrication of Si/Fe nanostructures and their chitosan polymer composites for the removal of Ni(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) ions from aqueous solutions. Composites B 166, 382–400 (2019)
J. Cui, X. Wang, S. Yu, C. Zhong, N. Wang, J. Meng, Facile fabrication of chitosan-based adsorbents for effective removal of cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 165, 2805–2812 (2020)
H. Mittal, A. Al, P.P. Morajkar, S.M. Alhassan, GO crosslinked hydrogel nanocomposites of chitosan/carboxymethyl cellulose—a versatile adsorbent for the treatment of dyes contaminated wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 167, 1248–1261 (2021)
S. Krishna, K. Soontarapa, R. Kumar, K. Kannan, Preparation of novel chitosan polymeric nanocomposite as an efficient material for the removal of Acid Blue 25 from aqueous environment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 168, 760–768 (2021)
M. Usman, A. Ahmed, B. Yu, S. Wang, Y. Shen, H. Cong, Simultaneous adsorption of heavy metals and organic dyes by β-cyclodextrin-chitosan based cross-linked adsorbent. Carbohydr. Polym. 255, 117486 (2021)
R. Chanajaree, M. Sriuttha, V. Sanghiran, K. Wittayanarakul, Thermodynamics and kinetics of cationic/anionic dyes adsorption on cross-linked chitosan. J. Mol. Liq. 322, 114507 (2021)
N.P. Raval, S. Mukherjee, N.K. Shah, P. Gikas, M. Kumar, Hexametaphosphate cross-linked chitosan beads for the eco-efficient removal of organic dyes: tackling water quality. J. Environ. Manag. 280, 111680 (2021)
Z. Yang, H. Yang, Z. Jiang, T. Cai, H. Li, H. Li, A. Li, R. Cheng, Flocculation of both anionic and cationic dyes in aqueous solutions by the amphoteric grafting flocculant carboxymethyl chitosan-graft-polyacrylamide. J. Hazard. Mater. 254–255, 36–45 (2013)
X. Zhao, X. Wang, T. Lou, Preparation of fibrous chitosan/sodium alginate composite foams for the adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 403, 124054 (2021)
N.F. El-harby, S.M.A. Ibrahim, N.A. Mohamed, Adsorption of Congo red dye onto antimicrobial terephthaloyl thiourea cross-linked chitosan hydrogels. Water Sci. Technol. 76, 2719–2732 (2017)
I. Olalekan, W. Da, F. Bukhari, M. Suah, Chitosan modifications for adsorption of pollutants—a review. J. Hazard. Mater. 408, 124889 (2021)
H. Zhang, Q. Dang, C. Liu, D. Yu, Y. Wang, X. Pu, Y. Liu, Fabrication of methyl acrylate and tetraethylenepentamine grafted magnetic chitosan microparticles for capture of Cd(II) from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 366, 346–357 (2019)
L. Fan, C. Luo, M. Sun, X. Li, H. Qiu, Highly selective adsorption of lead ions by water-dispersible magnetic chitosan/graphene oxide composites. Colloids Surf. B 103, 523–529 (2013)
M. Verma, I. Lee, J. Oh, V. Kumar, H. Kim, Synthesis of EDTA-functionalized graphene oxide–chitosan nanocomposite for simultaneous removal of inorganic and organic pollutants from complex wastewater. Chemosphere 287, 132385 (2022)
D. Cho, B. Jeon, C. Chon, F.W. Schwartz, Y. Jeong, H. Song, Magnetic chitosan composite for adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes in aqueous solution. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 28, 60–66 (2015)
S. Korde, S. Tandekar, R.M. Jugade, Novel mesoporous chitosan–zirconia–ferrosoferric oxide as magnetic composite for defluoridation of water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 8, 104360 (2020)
G.R. Mahdavinia, E. Shokri, Synthesis and characterization of magnetic amidoximated chitosan-g poly (polyacrylonitrile)/laponite RD nanocomposites with enhanced adsorption capacity for Cu2+. Turk. J. Chem. 41, 135–152 (2017)
H. Zhang, R. Xiao, R. Li, A. Ali, A. Chen, Z. Zhang, Chemosphere enhanced aqueous Cr(VI) removal using chitosan-modified magnetic biochars derived from bamboo residues. Chemosphere 261, 127694 (2020)
L. Carvalho, F.P. De Freitas, M. Ana, O. Carneiro, M.A. De Magalh, M.F. Xisto, Adsorption of neutral red dye by chitosan and activated carbon composite films. Heliyon 7, e07629 (2021)
M.S. Samuel, S. Sheriff, J. Bhattacharya, K. Subramaniam, N.D.P. Singh, Adsorption of Pb(II) from aqueous solution using a magnetic chitosan/graphene oxide composite and its toxicity studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 115, 1142–1150 (2018)
H. Wu, Y. Liu, B. Chen, F. Yang, L. Wang, Q. Kong, T. Ye, J. Lian, Enhanced adsorption of molybdenum(VI) from aquatic solutions by chitosan-coated zirconium–iron sulfide composite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 279, 119736 (2021)
H.Y. Zhu, R. Jiang, Y. Fu, J. Jiang, L. Xiao, G. Zeng, Preparation, characterization and dye adsorption properties of γ-Fe2O3/SiO2/chitosan composite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 1337–1344 (2011)
H. Jin, J. Dong, Enhanced performance of Ag3PO4/Fe3O4/GO bifunctional catalysts on p-chlorophenol degradation in advanced catalytic oxidation systems. Colloids Surf. A 581, 123803 (2019)
M.E. Khalifa, E.A. Abdelrahman, M.M. Hassanien, W.A. Ibrahim, Application of mesoporous silica nanoparticles modified with dibenzoylmethane as a novel composite for efficient removal of Cd(II), Hg(II), and Cu(II) ions from aqueous media. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 30, 2182–2196 (2020)
D. Boudouh, D. Hamana, H. Simon, C. Metselaar, S. Achour, L. Chetibi, A. Reza, Low-temperature green route synthesis of Fe3O4–C nanocomposite using olive leaves extract. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 271, 115276 (2021)
G. Vinodha, P.D. Shima, L. Cindrella, Mesoporous magnetite nanoparticle-decorated graphene oxide nanosheets for efficient electrochemical detection of hydrazine. J. Mater. Sci. 54, 4073–4088 (2019)
A. Sayah, F. Habelhames, A. Bahloul, B. Nessark, Y. Bonnassieux, D. Tendelier, M. El Jouad, Electrochemical synthesis of polyaniline-exfoliated graphene composite films and their capacitance properties. J. Electroanal. Chem. 818, 26–34 (2018)
P. Tambe, Synthesis and characterization of acid treated reduced graphene oxide. Mater. Today Proc. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.06.381
H.-Y. Liu, H.-X. Xu, L.-L. Zhu, J.-J. Wen, Y.-B. Qiu, C.-C. Gu, Colorimetric detection of hydrogen peroxide and glutathione based on peroxidase mimetic activity of Fe3O4–sodium lignosulfonate nanoparticles. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 49, e21160–e21169 (2021)
E.A. Abdelrahman, Y.G. Abou El-Reash, H.M. Youssef, Y.H. Kotp, R.M. Hegazey, Utilization of rice husk and waste aluminum cans for the synthesis of some nanosized zeolite, zeolite/zeolite, and geopolymer/zeolite products for the efficient removal of Co(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) ions from aqueous media. J. Hazard. Mater. 401, 123813 (2021)
A. Subaihi, M. Morad, A.M. Hameed, A. Alharbi, Y.G. Abou, F.K. Algethami, R.M. Hegazey, E.A. Abdelrahman, Studying some analytical parameters affecting the removal of Mn(II) ions from aqueous media using facilely synthesised analcime. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1750608
A.M. Hameed, A. Alharbi, E.A. Abdelrahman, R.M. Hegazey, Facile hydrothermal fabrication of analcime and zeolite X for efficient removal of Cd(II) ions from aqueous media and polluted water. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 30, 4117–4128 (2020)
E.A. Abdelrahman, A. Alharbi, A. Subaihi, A.M. Hameed, M.A. Almutairi, F.K. Algethami, H.M. Youssef, Facile fabrication of novel analcime/sodium aluminum silicate hydrate and zeolite Y/faujasite mesoporous nanocomposites for efficient removal of Cu(II) and Pb(II) ions from aqueous media. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 7900–7914 (2020)
T. Chen, Y. Zhao, Y. Sang, M. Tang, G. Hu, X. Han, J. Gao, R. Ma, Facile synthesis of magnetic CS-g-SPSS microspheres via electron beam radiation for efficient removal of methylene blue. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 25, 101299 (2021)
S. Sohni, R. Hashim, J. Lamaming, O. Sulaiman, Chitosan/nano-lignin based composite as a new sorbent for enhanced removal of dye pollution from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 132, 1304–1317 (2019)
I. Mustafa, Methylene blue removal from water using H2SO4 crosslinked magnetic chitosan nanocomposite beads. Microchem. J. 144, 397–402 (2019)
J. Bu, L. Yuan, Y. Ren, Y. Lv, Y. Meng, Enhanced removal of eriochrome black T in wastewater by zirconium-based MOF/graphene oxide. Can. J. Chem. 98, 1–25 (2020)
I. Khurana, A.K. Shaw, Bharti, J.M. Khurana, P.K. Rai, Batch and dynamic adsorption of eriochrome black T from water on magnetic graphene oxide: experimental and theoretical studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 6, 468–477 (2018)
O.A. Attallah, M.A. Al-Ghobashy, M. Nebsen, M.Y. Salem, Removal of cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solution with magnetite/pectin and magnetite/silica/pectin hybrid nanocomposites: kinetic, isotherm and mechanism analysis. RSC Adv. 6, 11461–11480 (2016)
M.D.G. de Luna, E.D. Flores, D.A.D. Genuino, C.M. Futalan, M.W. Wan, Adsorption of eriochrome black T (EBT) dye using activated carbon prepared from waste rice hulls—optimization, isotherm and kinetic studies. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 44, 646–653 (2013)
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia for funding the work through Researchers Supporting Project (No. RSP-2021/359).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that there is no conflict of interest for this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Wasidi, A.S., Abouelreash, Y.G., AlReshaidan, S. et al. Application of Novel Modified Chitosan Hydrogel Composite for the Efficient Removal of Eriochrome Black T and Methylene Blue Dyes from Aqueous Media. J Inorg Organomet Polym 32, 1142–1158 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02168-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02168-x