Abstract
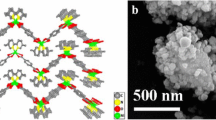
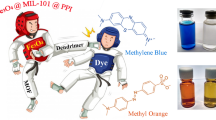
3D metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) can be appropriate templates for the fabrication of nanomaterials due to they have active sites exposed on the channel or surface, which thus provide them with improved catalytic performance. In this study, a 3D cobalt-based MOF [Co(H2bpta)]n (Co-MOF), where H4bpta denotes 2,2′,4,4′-biphenyltetracarboxylic acid, has been constructed with the use of a ligand with a high carbon content. On this basis, a 2D magnetic carbon-coated cobalt nanoparticle composite (Co@C) was prepared by using the title MOF under different temperatures. Magnetic Co@C can readily absorb dye from the solution and can thus act as an inexpensive and fast-acting adsorbent. Moreover, we have explored the adsorption isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics of the anion dyes in detail. The adsorption capacity of the Co@C-800 for investigated methyl orange (MO) and congo red (CR) dyes were 773.48 and 495.66 mg g−1, respectively. It is noteworthy that MO adsorption is higher in existing materials. Thermodynamic studies suggest that the adsorption processes are spontaneous and exothermic. This study opens a new insight into the synthesis and application of carbon-based materials that enable the selective removal of organic dyes.
Graphical Abstract
A Co-MOF has been solvothermal synthesized and structurally characterized, which was used as a combined catalyst and carbon source for the synthesis of magnetic Co@C. Interestingly, the as-grown Co@C-800 exhibits high-performance selective adsorption of anionic dyes (MO and CR) with high adsorption capacities.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.J. Vörösmarty, P.B. McIntyre, M.O. Gessner, D. Dudgeon, A. Prusevich, P. Green, S. Glidden, S.E. Bunn, C.A. Sullivan, C.R. Liermann, P.M. Davies, Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 467, 555–561 (2010)
S. Wang, B. Zhang, C. Shan, X. Yan, H. Chen, B. Pan, Occurrence and transformation of phosphonates in textile dyeing wastewater along full-scale combined treatment processes. Water Res. 184, 116173 (2020)
C. Ding, M. Yi, B. Liu, C. Han, X. Yu, Y. Wang, Forward osmosis-extraction hybrid process for resource recovery from dye wastewater. J Membrane Sci. 612, 118376 (2020)
Z. Gong, T. Ma, F. Liang, Syntheses of magnetic blackberry-like Ni@Cu@Pd nanoparticles for efficient catalytic reduction of organic pollutants. J Alloys Compd. 873, 159802 (2021)
L. Yang, Y. Zhan, R. Yu, J. Lan, J. Shang, B. Dou, H. Liu, R. Zou, S. Lin, Facile and scalable fabrication of antibacterial CO2-responsive cotton for ultrafast and controllable removal of anionic dyes. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 13, 2694–2709 (2021)
A. Malik, M. Nath, Synthesis of Ag/ZIF-7 by immobilization of Ag nanoparticles onto ZIF-7 microcrystals: a heterogeneous catalyst for the reduction of nitroaromatic compounds and organic dyes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 8, 104547 (2020)
Y. Gao, S. Yan, Y. He, Y. Fan, L. Zhang, J. Ma, R. Hou, L. Chen, J. Chen, A photo-Fenton self-cleaning membrane based on NH2-MIL-88B (Fe) and graphene oxide to improve dye removal performance. J. Membrane Sci. 626, 119192 (2021)
D. Wang, F. Zeng, X. Hu, C. Li, Z. Su, Synthesis of a magnetic 2D Co@NC-600 material by designing a MOF precursor for efficient catalytic reduction of water pollutants. Inorg. Chem. 59, 12672–12680 (2020)
S. Zhou, X. Feng, J. Zhu, Q. Song, G. Yang, Y. Zhang, B. Van der Bruggen, Self-cleaning loose nanofiltration membranes enabled by photocatalytic Cu-triazolate MOFs for dye/salt separation. J. Membrane Sci. 623, 119058 (2021)
X. Zhang, Z. Li, S. Lin, P. Théato, fibrous materials based on polymeric salicyl active esters as efficient adsorbents for selective removal of anionic dye. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 12, 21100–21113 (2020)
H.X. Chen, X.Y. Lu, H.H. Wang, D.P. Sui, F.B. Meng, W. Qi, Controllable fabrication of nitrogen-doped porous nanocarbons for high-performance supercapacitors via supramolecular modulation strategy. J. Energy Chem. 49, 348–357 (2020)
D.S. Wang, L. Xu, F.M. Zeng, X.L. Hu, B.L. Liu, C. Li, Z.M. Su, J. Sun, Synthesis of ultrafine Co/CoO nanoparticle-embedded N-doped carbon framework magnetic material and application for 4-nitrophenol catalytic reduction. New J. Chem. 45, 13751–13754 (2021)
X. Wu, D. Huang, Y. Wu, J. Zhao, X. Liu, W. Dong, S. Li, D. Li, J. Li, In Situ Synthesis of Nano CuS-Embedded MOF hierarchical structures and application in dye adsorption and hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2, 5698–5706 (2019)
W. Shao, C. He, M. Zhou, C. Yang, Y. Gao, S. Li, L. Ma, L. Qiu, C. Cheng, C. Zhao, Core–shell-structured MOF-derived 2D hierarchical nanocatalysts with enhanced Fenton-like activities. J. Mater. Chem. A 8, 3168–3179 (2020)
C. Yu, J. Chen, Y. Zhang, W. Song, X. Li, F. Chen, Y. Zhang, D. Liu, L. Liu, Highly efficient and selective removal of anionic dyes from aqueous solution by using a protonated metal-organic framework. J. Alloy Compd. 853, 157383 (2021)
T. Selkälä, T. Suopajärvi, J.A. Sirviö, T. Luukkonen, P. Kinnunen, A.L.C.B. de Carvalho, H. Liimatainen, Surface modification of cured inorganic foams with cationic cellulose nanocrystals and their use as reactive filter media for anionic dye removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 12, 27745–27757 (2020)
S. Das, P. Chakraborty, R. Ghosh, S. Paul, S. Mondal, A. Panja, A.K. Nandi, Folic acid-polyaniline hybrid hydrogel for adsorption/reduction of chromium(VI) and selective adsorption of anionic dye from water. ACS Sus. Chem. Eng. 10, 9325–9337 (2017)
Z. Li, K. Zou, X. Zhang, T. Han, Y. Yang, Hierarchically flower-like N-doped porous carbon materials derived from an explosive 3-fold interpenetrating diamondoid copper metal-organic framework for a supercapacitor. Inorg. Chem. 55, 6552–6562 (2016)
X. Wu, J. Zhao, Y. Wu, W. Dong, D. Li, J. Li, Q. Zhang, Ultrafine Pt nanoparticles and amorphous nickel supported on 3D mesoporous carbon derived from Cu-Metal–organic framework for efficient methanol oxidation and nitrophenol reduction. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 10, 12740–12749 (2018)
K. Nath, C.K. Karan, K. Biradha, Metal–organic frameworks and metal–organic framework-derived N-doped porous carbon materials as heterogeneous catalysts: chemical fixation of carbon dioxide under mild conditions and electrochemical hydrogen evolution. Cryst. Growth Des. 19, 6672–6681 (2019)
B. Volosskiy, H. Fei, Z. Zhao, S. Lee, M. Li, Z. Lin, B. Papandrea, C. Wang, Y. Huang, X. Duan, Tuning the catalytic activity of a metal–organic framework derived copper and nitrogen Co-doped carbon composite for oygen reduction reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 8, 26769–26774 (2016)
R. Rajak, M. Saraf, A. Mohammad, S.M. Mobin, Design and construction of a ferrocene based inclined polycatenated Co-MOF for supercapacitor and dye adsorption applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 17998–18011 (2017)
Y. Zhang, H. Zhang, X. Wu, Z. Deng, E. Zhou, Z. Yu, Nanolayered Cobalt@Carbon Hybrids derived from metal–organic frameworks for microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Nano. Mater. 2, 2325–2335 (2019)
M. Hasanzadeh, A. Simchi, H. Shahriyari Far, Nanoporous composites of activated carbon-metal organic frameworks for organic dye adsorption: synthesis, adsorption mechanism and kinetics studies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 81, 405–414 (2020)
O. Mahi, K. Khaldi, M.S. Belardja, A. Belmokhtar, A. Benyoucef, Development of a new hybrid adsorbent from Opuntia Ficus Indica NaOH activated with PANI reinforced and its potential use in orange G dye removal. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 31, 2095–2104 (2021)
Y. Zhang, H. Zhang, X. Wu, Z. Deng, E. Zhou, Z. Yu, Nanolayered cobalt@carbon hybrids derived from metal–organic frameworks for microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2, 2325–2335 (2019)
S.Y. Mendiola-Alvarez, P.G. Turnes, J. Guzman-Mar, A. Hernandez-Ramirez, L. Hinojosa-Reyes, C.C. Palomino, Magnetic porous carbons derived from cobalt(ii)-based metal-organic frameworks for the solid-phase extraction of sulfonamides. Dalton Trans. 49, 8959–8966 (2020)
J. Liu, S. Ma, L. Zang, Preparation and characterization of ammonium-functionalized silica nanoparticle as a new adsorbent to remove methyl orange from aqueous solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 265, 393–398 (2013)
M.A. Ahsan, O. Fernandez-Delgado, E. Deemer, H. Wang, A.A. El-Gendy, M.L. Curry, J.C. Noveron, Carbonization of Co-BDC MOF results in magnetic Co@C-800 nanoparticles that catalyze the reduction of methyl orange and 4-nitrophenol in water. J. Mol. Liquid 290, 111059 (2019)
M.A. Nazir, N.A. Khan, C. Cheng, S.S.A. Shah, T. Najam, M. Arshad, A. Sharif, S. Akhtar, A.U. Rehman, Surface induced growth of ZIF-67 at Co-layered double hydroxide: removal of methylene blue and methyl orange from water. Appl. Clay Sci. 190, 105564 (2020)
M. Trukawka, K. Cendrowski, M. Peruzynska, A. Augustyniak, P. Nawrotek, M. Drozdzik, E. Mijowska, Carbonized metal-organic frameworks with trapped cobalt nanoparticles as biocompatible and efficient azo-dye adsorbent. Environ. Sci. Eur. 31, 56 (2019)
Z. Pan, J. Xu, X. Yao, Y. Li, Z. Guo, H. Zheng, Syntheses, structures, magnetic and photoluminescence properties of metal–organic frameworks based on aromatic polycarboxylate acids. CrystEngComm 13, 1617–1624 (2011)
J. Long, K. Shen, Y. Li, Bifunctional N-doped Co@C-800 catalysts for base-free transfer hydrogenations of nitriles: Controllable selectivity to primary amines vs imines. ACS Catal. 7, 275–284 (2017)
I. Toumi, H. Djelad, F. Chouli, A. Benyoucef, Synthesis of PANI@ZnO hybrid material and evaluations in adsorption of congo red and methylene blue dyes: structural characterization and adsorption performance. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02084-0
S. Gutiérrez-Tarriño, J.L. Olloqui-Sariego, J.J. Calvente, G.M. Espallargas, F. Rey, A. Corma, P. Oña-Burgos, Cobalt metal–organic framework based on layered double nanosheets for enhanced electrocatalytic water oxidation in neutral media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 19198–19208 (2020)
P.L. Feng, J.J. Perry, S. Nikodemski, B.W. Jacobs, S.T. Meek, M.D. Allendorf, Assessing the purity of metal−organic frameworks using photoluminescence: MOF-5, ZnO quantum dots, and framework decomposition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 15487–15489 (2010)
D. Wang, J. Zhang, G. Li, J. Yuan, J. Li, Q. Huo, Y. Liu, Mesoporous hexanuclear copper cluster-based metal–organic framework with highly selective adsorption of gas and organic dye molecules. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 10, 31233–31239 (2018)
X. Yang, Y. Yan, W. Wang, Z. Hao, W. Zhang, W. Huang, Y. Wang, A 2-fold interpenetrated nitrogen-rich metal-organic framework: dye adsorption and CO2 capture and conversion. Inorg. Chem. 60, 3156–3164 (2021)
W. Fan, X. Wang, B. Xu, Y. Wang, D. Liu, M. Zhang, Y. Shang, F. Dai, L. Zhang, D. Sun, Amino-functionalized MOFs with high physicochemical stability for efficient gas storage/separation, dye adsorption and catalytic performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 6, 24486–24495 (2018)
S. Zhan, D. Zhu, G. Ren, Z. Shen, M. Qiu, S. Yang, H. Yu, Y. Li, Coaxial-electrospun magnetic core–shell Fe@TiSi nanofibers for the rapid purification of typical dye wastewater. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 6, 16841–16850 (2014)
J. Zhao, J. Luan, H.X. Yu, G.C. Liu, H.Y. Lin, X.L. Wang, B.K. Chen, Five naphthalene-amide-bridged Ni(II) complexes: electrochemistry, bifunctional fluorescence responses, removal of contaminants and optimization by pyrolysis. CrystEngComm 22, 1330–1339 (2020)
S.K. Konavarapu, A. Goswami, A.G. Kumar, S. Banerjee, K. Biradha, MOFs containing a linear bis-pyridyl-tris-amide and angular carboxylates: exploration of proton conductivity, water vapor and dye sorptions. Inorg. Chem. Front. 6, 184–191 (2019)
L.J. Han, F.Y. Ge, G.H. Sun, X.J. Gao, H.G. Zheng, Effective adsorption of Congo red by a MOF-based magnetic material. Dalton Trans. 48, 4650–4656 (2019)
W.A. El-Mehalmey, Y. Safwat, M. Bassyouni, M.H. Alkordi, Strong interplay between polymer surface charge and MOF cage chemistry in mixed-matrix membrane for water treatment applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 12, 27625–27631 (2020)
S.C.C. van der Lubbe, F. Zaccaria, X. Sun, C. Fonseca Guerra, Secondary electrostatic interaction model revised: prediction comes mainly from measuring charge accumulation in hydrogen-bonded monomers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 4878–4885 (2019)
F. Gritti, G. Guiochon, Analytical solution of the ideal model of chromatography for a Bi-Langmuir adsorption isotherm. Anal. Chem. 85, 8552–8558 (2013)
S. Nufer, M.J. Large, A.A.K. King, S.P. Ogilvie, A. Brunton, A.B. Dalton, Edge-selective gas detection using Langmuir films of graphene platelets. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 18, 21740–21745 (2018)
I. Abe, K. Hayashi, T. Hirashima, M. Kitagawa, Relationship between the Freundlich adsorption constants K and 1/N hydrophobic adsorption. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 104, 6452–6453 (1982)
A.J.S. Ribeiro, K. Zaleta-Rivera, E.A. Ashley, B.L. Pruitt, Stable, covalent attachment of laminin to microposts improves the contractility of mouse neonatal cardiomyocytes. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 6, 15516–15526 (2014)
X. Ni, G. Dong, L. Li, Q. Yang, Z. Wu, Kinetic study of electron transport behaviors used for ion sensing technology in air/EGR diluted methane flames. Fuel 288, 119825 (2021)
J.C. Moreno-López, A. Pérez Paz, S. Gottardi, L. Solianyk, J. Li, L. Monjas, A.K.H. Hirsch, D.J. Mowbray, M. Stöhr, Unveiling adatoms in on-surface reactions: combining scanning probe microscopy with van’t Hoff plots. J. Phys. Chem. C 125, 9847–9854 (2021)
Y. Yao, H. Bing, X. Feifei, C. Xiaofeng, Equilibrium and kinetic studies of methyl orange adsorption on multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 170, 82–89 (2011)
H.Y. Zhu, R. Jiang, L. Xiao, G.M. Zeng, Preparation, characterization, adsorption kinetics and thermodynamics of novel magnetic chitosan enwrapping nanosized γ-Fe2O3 and multi-walled carbon nanotubes with enhanced adsorption properties for methyl orange. Bioresour. Technol. 101, 5063–5069 (2010)
Y. Tian, X. Wang, Y. Pan, Simple synthesis of Ni-containing ordered mesoporous carbons and their adsorption/desorption of methylene orange. J. Hazard. Mater. 213–214, 361–368 (2012)
G. Li, Y. Du, Y. Tao, H. Deng, X. Luo, J. Yang, Iron(II) cross-linked chitin-based gel beads: preparation, magnetic property and adsorption of methyl orange. Carbohydr. Polym. 82, 706–713 (2010)
Z. Liu, W. He, Q. Zhang, H. Shapour, M.F. Bakhtari, Preparation of a GO/MIL-101(Fe) composite for the removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution. ACS Omega 6, 4597–4608 (2021)
W. Cheah, S. Hosseini, M.A. Khan, T.G. Chuah, T.S.Y. Choong, Acid modified carbon coated monolith for methyl orange adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 215–216, 747–754 (2013)
K. Guesh, C.A.D. Caiuby, Á. Mayoral, M. Díaz-García, I. Díaz, M. Sanchez-Sanchez, Sustainable preparation of MIL-100(Fe) and its photocatalytic behavior in the degradation of methyl orange in water. Cryst. Growth Des. 17, 1806–1813 (2017)
J. Ma, F. Yu, L. Zhou, L. Jin, M. Yang, J. Luan, Y. Tang, H. Fan, Z. Yuan, J. Chen, Enhanced adsorptive removal of methyl orange and methylene blue from aqueous solution by alkali-activated multiwalled carbon nanotubes. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 4, 5749–5760 (2012)
Z. Ni, S. Xia, L. Wang, F. Xing, G. Pan, Treatment of methyl orange by calcined layered double hydroxides in aqueous solution: Adsorption property and kinetic studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 316, 284–291 (2007)
N. Mohammadi, H. Khani, V.K. Gupta, E. Amereh, S. Agarwal, Adsorption process of methyl orange dye onto mesoporous carbon material–kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 362, 457–462 (2011)
T. Kou, Y. Wang, C. Zhang, J. Sun, Z. Zhang, Adsorption behavior of methyl orange onto nanoporous core–shell Cu@Cu2O nanocomposite. Chem. Eng. J. 223, 76–83 (2013)
P. Zhang, Q. An, J. Guo, C. Wang, Synthesis of mesoporous magnetic Co-NPs/carbon nanocomposites and their adsorption property for methyl orange from aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 389, 10–15 (2013)
W. Deligeer, Y.W. Gao, S. Asuha, Adsorption of methyl orange on mesoporous γ-Fe2O3/SiO2 nanocomposites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 3524–3528 (2011)
M. Arshadi, F. SalimiVahid, J.W.L. Salvacion, M. Soleymanzadeh, Adsorption studies of methyl orange on an immobilized Mn-nanoparticle: kinetic and thermodynamic. Rsc Adv. 4, 16005–16017 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Liaoning Provincial Department of Education Fund (LQ2019004 and LZ2019005).
Funding
The funder was funded by Department of Education of Liaoning Province, Grant Nos (LQ2019004) and (LZ2019005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL and YW—Crystal synthesis, writing-original draft preparation. XSZ and AAY–formal analysis, investigation; HZL and ZGW—Software; WZL and JL—Writing-review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, XS. et al. Synthesis of a Magnetic Co@C Material via the Design of a MOF Precursor for Efficient and Selective Adsorption of Water Pollutants. J Inorg Organomet Polym 32, 700–712 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02157-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02157-0