Abstract
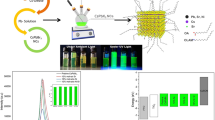
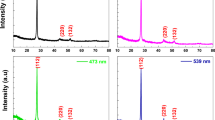
Current work reports the fabrication of cadmium, cobalt and cobalt doped cadmium semiconductor chalcogenide [Cd-(dtc)2 [dtc = dithiocarbmate], Co-(dtc)2, and Co:Cd-(dtc)2] complexes using iso-propylammonium dithiocarbamate precursor grown into thin films via physical vapor deposition (PVD) for the first time. Cubic crystals having 18 nm of average size were revealed via X-ray diffraction. Varied molecular arrangements and bonding types were disclosed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Bandgap tailoring was done by doping leading to a broadening in bandgap i.e., 3.72, and 3.5 eV direct and indirect bandgaps, respectively through ultra-violet visible spectrophotometry. PVD grown thin films indicated formation of clusters and irregular structures between the gaps and voids of micro-grains shown by field emission scanning electron microscopy. Rutherford back scattering spectroscopy expressed the remarkable thickness i.e., 615 nm with stronger signals for Cd, Co and S elements. Furthermore, the electrochemical analysis of the pristine and doped chalcogenide thin films done via cyclic, linear sweep voltammetry and chronoamperometry elucidated the excellent photo-response and functional stability and confirmed the potential of these films as future candidates for multitudinous photovoltaic and optoelectronic devices especially the utilization of [Co:Cd-(dtc)2]/SnO2 thin films in solar cell devices is expected to yield higher through put potentials and photo-currents if sandwiched between the active absorber layer and photo-electrodes.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.B. Jaffri, K.S. Ahmad, Interfacial engineering revolutionizers: perovskite nanocrystals and quantum dots accentuated performance enhancement in perovskite solar cells. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/10408436.2020.1758627
S.B. Jaffri, K.S. Ahmad, Prunus cerasifera Ehrh. fabricated ZnO nano falcates and its photocatalytic and dose dependent in vitro bio-activity. Open Chem. 16, 141 (2018)
S.B. Jaffri, K.S. Ahmad, Biomimetic detoxifier Prunus cerasifera Ehrh. silver nanoparticles: innate green bullets for morbific pathogens and persistent pollutants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 1, 1–10 (2020)
M. Tahir, S. Iram, K.S. Ahmad et al., Developmental abnormality caused by Fusarium mangiferae in mango fruit explored via molecular characterization. Biology 75, 465 (2020)
M.B. Tahir, A. Ahmad, T. Iqbal et al., Advances in photo-catalysis approach for the removal of toxic personal care product in aqueous environment. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 1, 1–24 (2019)
M.B. Tahir, S. Tufail, A. Ahmad et al., Semiconductor nanomaterials for the detoxification of dyes in real wastewater under visible-light photocatalysis. J. Int. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1, 1–15 (2019)
M. Ijaz, M. Aftab, S. Afsheen et al., Novel Au nano-grating for detection of water in various electrolytes. Appl. Nanosci. 10, 4029 (2020)
M. Ijaz, M. Zafar, T. Iqbal, Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by using various extracts: a review. Inorg. Nano-Metal Chem. 1, 1–12 (2020)
M. Gao, L. Zhu, C.K. Peh et al., Solar absorber material and system designs for photothermal water vaporization towards clean water and energy production. Energy Environ. Sci. 12(3), 841–864 (2019)
J. Zhu, L. Hu, P. Zhao et al., Recent advances in electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution using nanoparticles. Chem. Rev. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00248
K. Maeda, T.E. Mallouk, Two-dimensional metal oxide nanosheets as building blocks for artificial photosynthetic assemblies. Bull. Chem. Soc. Japan. 92(1), 38–54 (2019)
C.N.R. Rao, K. Pramoda, Borocarbonitrides, BxCyNz, 2D nanocomposites with novel properties. Bull. Chem. Soc. Japan. 92(2), 441–468 (2019)
K.S. Ahmad, S.N. Naqvi, S.B. Jaffri, Systematic review elucidating the generations and classifications of solar cells contributing towards environmental sustainability integration. Rev. Inorg. Chem. 1, 1–30 (2020)
S.B. Jaffri, K.S. Ahmad, Augmented photocatalytic, antibacterial and antifungal activity of prunosynthetic silver nanoparticles. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 46, 127 (2017)
X. Zong, H. Yan, G. Wu et al., Enhancement of photocatalytic H2 evolution on CdS by loading MoS2 as Co catalyst under visible light irradiation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130(23), 7176 (2008)
M.R. Heidari, R.S. Varma, M. Ahmadian et al., Photo-fenton like catalyst system: activated carbon/CoFe2O4 nanocomposite for reactive dye removal from textile wastewater. Appl. Sci. 9(5), 963 (2019)
A. Abbas, D. Meysing, M. Reese et al., Structural and chemical evolution of the CdS: o window layer during individual CdTe solar cell processing steps. Sol. Energy 159, 940 (2018)
Z. Alam, B. Verma, A.S.K. Sinha, Synthesis and characterization of MWCNT incorporated N, S-rGO supported CdS photocatalyst for the dissociation of water to hydrogen by visible light. J. Int. Hydrogen Energy 45(1), 175 (2020)
S.S. Hossain, M. Tarek, T.D. Munusamy et al., Facile synthesis of CuO/CdS heterostructure photocatalyst for the effective degradation of dye under visible light. Environ. Res. 188, 109803 (2020)
S. Seeger, K. Ellmer, M. Weise et al., Reactive magnetron sputtering of Nb-doped TiO2 film relationships between structure, composition and electrical properties. Thin Solid Films 695, 44 (2016)
V.R. Huse, V.D. Mote, B.N. Dole, The crystallographic and optical studies on cobalt doped CdS nanoparticles. World. J. Condens. Matter Phys. 3, 46 (2013)
A. Zafar, K.S. Ahmad, S.B. Jaffri et al., Physical vapor deposition of SnS: PbS-dithiocarbamate chalcogenide semiconductor thin films: elucidation of optoelectronic and electrochemical features. Phosph. Sulfur Silicon Relat. Element 1, 1–19 (2020)
H. Siraj, K.S. Ahmad, S.B. Jaffri et al., Synthesis, characterization and electrochemical investigation of physical vapor deposited barium sulphide doped iron sulphide dithiocarbamate thin films. Microelect. Eng. 233, 111400 (2020)
K.S. Ahmad, A. Zafar, S.B. Jaffri et al. Chemosynthesis and physical vapor deposition of acanthite thin films: characterization and electrochemistry exploration. Result. Phys. 1, 103647 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2020.103647
N.A. Abdul-Manaf, A.R. Weerasinghe, O.K. Echendu et al., Electro-plating and characterisation of cadmium sulphide thin films using ammonium thiosulphate as the sulphur source. J. Mater. Sci. 26(4), 2418 (2015)
X. Wang, A. Han, Y. Huang et al., Structural, optical and impurity-absorption properties of CdS thin films deposited by a chemical bath using four cadmium sources. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 32(7), 075008 (2017)
G. Balaji, R. Balasundaraprabhu, S. Prasanna et al., Investigations on hot-wall deposited cadmium sulphide buffer layer for thin film solar cell. Mater. Lett. 222, 82 (2018)
B. Lohitha, S. Thanikaikarasan, S.R. Marjorie, Growth and characterization of CdS and Fe doped CdS thin films through electrochemical route. Mater. Today 1, 1–10 (2020)
Y. Ding, H. Liu, L.N. Gao et al., Fe-doped Ag2S with excellent peroxidase-like activity for colorimetric determination of H2O2. J. Alloys Compd. 785, 1189–1197 (2019)
A.M.B. Leena, K. Raji, Room temperature ferromagnetism in cobalt doped CdS quantum dots. Adalya J. 9(1), 1153–1160 (2020)
M. Mall, L. Kumar, Optical studies of Cd2+ and Mn2+ Co-doped ZnS nanocrystals. J. Lum. 130(4), 660–665 (2010)
A. Rafiq, M. Imran, M. Aqeel, Study of transition metal ion doped CdS nanoparticles for removal of dye from textile wastewater. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 30(6), 1915–1923 (2020)
K.R. Gbashi, M.A. Muhi, A.A. Jabbar et al., Copper dopants impact enhanced behavior of Mn: Cu co-doped CdS nanocrystals (quantum dots) and their characteristics for optoelectronic applications. Appl. Phys. A 126(8), 1–16 (2020)
M. Junaid, M. Imran, M. Ikram et al., The study of Fe-doped CdS nanoparticle-assisted photocatalytic degradation of organic dye in wastewater. Appl. Nanosci. 9(8), 1593 (2019)
K. Karthik, S. Pushpa, M. Madhukara Naik et al., Influence of Sn and Mn on structural, optical and magnetic properties of spray pyrolysed CdS thin films. Mater. Res. Innov. 24(2), 82 (2020)
S. AlFaify, M. Shkir, A facile one pot synthesis of novel pure and Cd doped PbI2 nanostructures for electro-optic and radiation detection applications. Opt. Mater 88, 417 (2019)
S. AlFaify, M. Shkir, A one pot room temperature synthesis of pure and Zn doped PbI2 nanostructures and their structural, morphological, optical, dielectric and radiation studies. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 14(2), 255 (2019)
Z.R. Khan, A.S. Alshammari, M. Shkir et al., Enhancement in the photoluminescence, linear and third order nonlinear optical properties of nanostructured Na-CdS thin films for optoelectronic applications. J. Nano. Res. 22(4), 1–6 (2020)
K.M. Naik, S. Sampath, Two-step oxygen reduction on spinel NiFe2O4 catalyst: rechargeable, aqueous solution-and gel-based, Zn-air batteries. Electrochim. Acta 292, 268 (2018)
M.M. Rahman, In-situ preparation of cadmium sulphide nanostructure decorated CNT composite materials for the development of selective benzaldehyde chemical sensor probe to remove the water contaminant by electrochemical method for environmental remediation. Mater. Chem. Phy. 245, 122788 (2020)
J. Datta, A. Layek, M. Das et al., Growth of hierarchical strontium incorporated cadmium sulphide for possible application in optical and electronic devices. J. Mater. Sci. 28(2), 2049 (2017)
S.M. Lee, D.H. Yeon, S.S. Chon et al., Effect of double substitutions of Cd and Cu on optical band gap and electrical properties of non-colloidal PbS thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 685, 129 (2016)
B.C. Mohanty, K. Bector, R. Laha, Elucidating doping driven microstructure evolution and optical properties of lead sulfide thin films grown from a chemical bath. Appl. Surf. Sci. 435, 444 (2018)
X. Lan, O. Voznyy, A. Kiani et al., Passivation using molecular halides increases quantum dot solar cell performance. Adv. Mater. 28(2), 299 (2016)
E.M. Miller, D.M. Kroupa, J. Zhang et al., Revisiting the valence and conduction band size dependence of PbS quantum dot thin films. ACS Nano 10(3), 3302–3311 (2016)
H. Safardoust-Hojaghan, O. Amiri, M. Salavati-Niasari et al., Performance improvement of dye sensitized solar cells based on cadmium sulfide/S, N co doped carbon dots nanocomposites. J. Mol. Liq. 301, 112413 (2020)
T. Garmim, L. Soussi, A. Louardi et al., Structural and optical characterization of sprayed Mg and Ni co-doped CdS thin films for photovoltaic applications. IOP Conf. Ser. 948(1), 012019 (2020)
T. Iqbal, G. Ara, N.R. Khalid et al., Simple synthesis of Ag-doped CdS nanostructure material with excellent properties. Appl. Nanosci. 10(1), 23–28 (2020)
R.A. Devi, M. Latha, S. Velumani et al., Synthesis and characterization of cadmium sulfide nanoparticles by chemical precipitation method. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 15(11), 8434–8439 (2015)
K.R. Desai, A.A. Pathan, C.P. Bhasin, Synthesis, characterization of cadmium sulphide nanoparticles and its application as photocatalytic degradation of congored. Int. J. Nanomater. Chem. 3, 39 (2017)
I.B. Assaker, M. Gannouni, J.B. Naceur, Electrodeposited ZnIn2S4 onto TiO2 thin films for semiconductor-sensitized photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 351, 927 (2015)
S. Thanikaikarasan, T. Mahalingam, M. Raja et al., Electrochemical growth and characterization of iron doped cadmium sulfide thin films. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Proc. 37, 215 (2015)
Q. Zhao, H. Chao, M. Huang et al., Unique photoelectrocatalytic properties of a diphenyl-as-triazine-containing ruthenium (II) complex assembled on cadmium sulfide anode and cuprous oxide cathode towards ascorbate oxidation and oxygen reduction. Electrochim. Acta 252, 568 (2017)
J. Wen, C.J. Liu, Y. Du et al., Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange by CdS quantum dots sensitized platelike WO3 photoelectrodes. J. Cent South Univ. 22(12), 4551 (2015)
Z. Peimanifard, S. Rashid-Nadimi, Glassy carbon/multi walled carbon nanotube/cadmium sulphide photoanode for light energy storage in vanadium photoelectrochemical cell. J. Power Source 300, 395 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The concept, idea, data and writing is the intellectual property right of Dr. Khuram Shahzad Ahmad and Lab E-21 of Department of Environmental Sciences, Fatima Jinnah Women University, The Mall, 46000, Rawalpindi, Pakistan. Author want to thank Department of Environmental Sciences, Fatima Jinnah Women University, The Mall, 46000, Rawalpindi, Pakistan for the provisioning of the technical and financial facilities needed for the completion of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, K.S., Siraj, H., Jaffri, S.B. et al. Physical Vapor Deposited [Co:Cd-(dtc)2]/SnO2 Dual Semiconductor Systems: Synthesis, Characterization and Photo-Electrochemistry. J Inorg Organomet Polym 31, 2579–2593 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-01927-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-01927-0