Abstract
In this study, iron manganese composite oxide (FeMnOx) were integrated with multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNTs) to synthesize an effective adsorbent for acid orange (AO) and basic violet (BV), two widely used organic dyestuffs belonging to anionic and cationic, respectively. Among all the composites evaluated, the FeMnOx-MWCNTs with Fe–Mn ratios of 1:1 and load ratio of 45% achieved superior adsorption capacity than others, and was selected as the best adsorbent. The Characterization data indicated that the physicochemical properties and structural characteristics of FeMnOx-MWCNTs have changed obviously after modification, with larger specific surface area and richer groups. The maximum adsorption capacity of AO (403.23 mg/g) and BV (165.29 mg/g) could be attained under optimal conditions: 300 min, 0.05 g adsorbent dosage, 100 mg/L dyes and pH 2.0 (for AO) or pH 10.0 (for BV). Moreover, the adsorption kinetics of the two dyes were both well fitted the pseudo-second-order kinetics model, and the adsorption isotherms agreed well with the Freundlich model for AO while Langmuir model for BV. Moreover, the FeMnOx-MWCNTs with optimal FeMnOx content showed relatively higher final adsorption amount and faster adsorption rate, thus better fitting with the kinetics. A mechanism was proposed that physical adsorption is the dominator during the process. The results indicated that the introduction of FeMnOx into the MWCNTs significantly enhanced the dye removal efficiency, providing a promising method for the improvement of carbon nanometer adsorbents.
Graphic Abstract
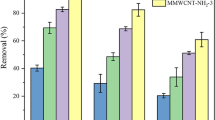
The selected graph can not only express the synthetic methods of FeMnOx-MWCNTs by chemical coprecipitation, but also presented the adsorption process and mechanism of AO and BV, which showed the purposes of this work simultaneously.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Rajoriya, S. Bargole, S. George, V.K. Saharan, Treatment of textile dyeing industry effluent using hydrodynamic cavitation in combination with advanced oxidation reagents. J. Hazard. Mater. 344, 1109–1115 (2018)
L.F. da Silva, A.D. Barbosa, H.M. de Paula, L.L. Romualdo, L.S. Andrade, Treatment of paint manufacturing wastewater by coagulation/electrochemical methods: proposals for disposal and/or reuse of treated water. Water Res. 101, 467–475 (2016)
T. Bhagavathi Pushpa, J. Vijayaraghavan, K. Vijayaraghavan, J. Jegan, Utilization of Effective Microorganisms based water hyacinth compost as biosorbent for the removal of basic dyes. Desalin. Water Treat. 57, 24368–24377 (2016)
S. Rangabhashiyam, N. Anu, M.S. Giri Nandagopal, N. Selvaraju, Relevance of isotherm models in biosorption of pollutants by agricultural byproducts. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2, 398–414 (2014)
M.-H. Cui, D. Cui, L. Gao, H.-Y. Cheng, A.-J. Wang, Analysis of electrode microbial communities in an up-flow bioelectrochemical system treating azo dye wastewater. Electrochim. Acta. 220, 252–257 (2016)
X. Tao, Y. Wu, H. Sha, Cuprous oxide-modified diatomite waste from the brewery used as an effective adsorbent for removal of organic dye: adsorption performance, kinetics and mechanism studies. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 229, 322 (2018)
P.A. Carneiro, G.A. Umbuzeiro, D.P. Oliveira, M.V.B. Zanoni, Assessment of water contamination caused by a mutagenic textile effluent/dyehouse effluent bearing disperse dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 174, 694–699 (2010)
G. Actis Grande, G. Rovero, S. Sicardi, M. Giansetti, Degradation of residual dyes in textile wastewater by ozone: comparison between mixed and bubble column reactors. can. J. Chem. Eng. 95, 297–306 (2017)
A. Pirkarami, M.E. Olya, N.Y. Limaee, Decolorization of azo dyes by photo electro adsorption process using polyaniline coated electrode. Prog. Org. Coat. 76, 682–688 (2013)
S. Zhao, Z. Wang, A loose nano-filtration membrane prepared by coating HPAN UF membrane with modified PEI for dye reuse and desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 524, 214–224 (2017)
H. Zhang, S. Zhang, F. He, X. Qin, X. Zhang, Y. Yang, Characterization of a manganese peroxidase from white-rot fungus Trametes sp. 48424 with strong ability of degrading different types of dyes and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Hazard. Mater. 320, 265–277 (2016)
M. Atrous, L. Sellaoui, M. Bouzid, E.C. Lima, P.S. Thue, A. Bonilla-Petriciolet, A. Ben Lamine, Adsorption of dyes acid red 1 and acid green 25 on grafted clay: modeling and statistical physics interpretation. J. Mol. Liq. 294, 111610 (2019)
A. Asfaram, M. Ghaedi, S. Hajati, A. Goudarzi, A.A. Bazrafshan, Simultaneous ultrasound-assisted ternary adsorption of dyes onto copper-doped zinc sulfide nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon: optimization by response surface methodology. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 145, 203–212 (2015)
Y. Li, W. Cui, L. Liu, R. Zong, W. Yao, Y. Liang, Y. Zhu, Removal of Cr (VI) by 3D TiO2-graphene hydrogel via adsorption enriched with photocatalytic reduction. Appl. Catal. B 199, 412–423 (2016)
N. Liu, Y. Wu, H. Sha, Magnesium oxide modified diatomite waste as an efficient adsorbent for organic dye removal: adsorption performance and mechanism studies. Sep. Sci. Technol. 55, 1–13 (2019)
S.X. Hou. Adsorption properties of pomelo peels against methylene blue in dye wastewater. in Advanced Materials Research. 2013. Trans Tech Publ.
L. Zhang, L. Sellaoui, D. Franco, G.L. Dotto, A. Bajahzar, H. Belmabrouk, A. Bonilla-Petriciolet, M.L.S. Oliveira, Z. Li, Adsorption of dyes brilliant blue, sunset yellow and tartrazine from aqueous solution on chitosan: Analytical interpretation via multilayer statistical physics model. Chem. Eng. J. 238, 122952 (2019)
M.S. Shamsudin, S.F. Azha, M. Shahadat, S. Ismail, Cellulose/bentonite-zeolite composite adsorbent material coating for treatment of N-based antiseptic cationic dye from water. J. Water Process. Eng. 29, 100764 (2019)
B. Sarkar, S. Mandal, Y.F. Tsang, P. Kumar, K.-H. Kim, Y.S. Ok, Designer carbon nanotubes for contaminant removal in water and wastewater: a critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 612, 561–581 (2018)
D. Zhang, B. Pan, R.L. Cook, B. Xing, Multi-walled carbon nanotube dispersion by the adsorbed humic acids with different chemical structures. Chem. Eng. J. 196, 292–299 (2015)
M.K. AlOmar, M.A. Alsaadi, M. Hayyan, S. Akib, R.K. Ibrahim, M.A. Hashim, Lead removal from water by choline chloride based deep eutectic solvents functionalized carbon nanotubes. J. Mol. Liq. 222, 883–894 (2016)
M. Bahgat, A.A. Farghali, W. El Rouby, M. Khedr, M.Y. Mohassab-Ahmed, Adsorption of methyl green dye onto multi-walled carbon nanotubes decorated with Ni nanoferrite. Appl. Nanosci. 3, 251–261 (2013)
M.M. Khan, W. Khan, A. Kumar, A.N. Alhazaa, Synthesis of nanosized Cu2O decorated single-walled carbon nanotubes and their superior catalytic activity. Colloids Surf. A 581, 123933 (2019)
M. Agarwal, P. Kumari, S. Dubey, R. Gupta, R. Kumar Dohare, Adsorption behavior of azo dyes on carbon nanotubes grown on alumina: process optimization, kinetics, and equilibrium study. J. Environ. Eng. 145, 04018134 (2018)
W. Zhang, Q. Yang, Q. Luo, L. Shi, S. Meng, Laccase-Carbon nanotube nanocomposites for enhancing dyes removal. J. Cleaner Prod. 242, 118425 (2020)
S. Deng, X. Liu, J. Liao, H. Lin, F. Liu, PEI modified multiwalled carbon nanotube as a novel additive in PAN nanofiber membrane for enhanced removal of heavy metal ions. Chem. Eng. J. 375, 122086 (2019)
H.-Y. Xu, T.-N. Shi, H. Zhao, L.-G. Jin, F.-C. Wang, C.-Y. Wang, S.-Y. Qi, Heterogeneous Fenton-like discoloration of methyl orange using Fe 3 O 4/MWCNTs as catalyst: process optimization by response surface methodology. Frontiers of Materials Science. 10, 45–55 (2016)
S.Q. Kong, Y.X. Wang, C. Wang, L.L. Jin, M.L. Liu, and M. Yu. Nanoscale iron-manganese binary oxide for As (III) removal in synthesized groundwater. in Applied Mechanics and Materials. 2013. Trans Tech Publ.
C. Luo, Z. Tian, B. Yang, L. Zhang, S. Yan, Manganese dioxide/iron oxide/acid oxidized multi-walled carbon nanotube magnetic nanocomposite for enhanced hexavalent chromium removal. Chem. Eng. J. 234, 256–265 (2013)
K. Wu, H. Wang, R. Liu, X. Zhao, H. Liu, J. Qu, Arsenic removal from a high-arsenic wastewater using in situ formed Fe–Mn binary oxide combined with coagulation by poly-aluminum chloride. J. Hazard. Mater. 185, 990–995 (2011)
L. Jiang, S. Xiao, J. Chen, Removal behavior and mechanism of Co(II) on the surface of Fe–Mn binary oxide adsorbent. Colloids Surf. A 479, 1–10 (2015)
K. Yang, Y. Liu, Y. Li, Z. Cao, C. Zhou, Z. Wang, X. Zhou, S.A. Baig, X. Xu, Applications and characteristics of Fe-Mn binary oxides for Sb(V) removal in textile wastewater: Selective adsorption and the fixed-bed column study. Chemosphere 232, 254–263 (2019)
K. Omri, N. Alonizan, Effects of ZnO/Mn concentration on the micro-structure and optical properties of ZnO/Mn–TiO 2 nano-composite for applications in photo-catalysis. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 29, 203–212 (2019)
K. Omri, A. Alyamani, L. El Mir, Photoluminescence and cathodoluminescence of Mn doped zinc silicate nanophosphors for green and yellow field emissions displays. Appl. Phys. A 124, 215 (2018)
V.K.K. Upadhyayula, S. Deng, M.C. Mitchell, G.B. Smith, Application of carbon nanotube technology for removal of contaminants in drinking water: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 408, 1–13 (2009)
M.-S. Park, K.H. Kim, Y.-S. Lee, Fluorination of single-walled carbon nanotube: the effects of fluorine on structural and electrical properties. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 37, 22–26 (2016)
Q. Zhou, H. Kang, M. Bielec, X. Wu, Q. Cheng, W. Wei, H. Dai, Influence of different divalent ions cross-linking sodium alginate-polyacrylamide hydrogels on antibacterial properties and wound healing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 197, 292–304 (2018)
A. Hosseini, M. Allahyari, S.D. Besheli, Synthesis of carbon nanotubes, nano fibbers and nano union by electric arc discharge method using NaCl accuse as solution and Fe and Ni particles and catalysts. IJEST. 1, 217–229 (2012)
X. Huang, C. Pan, X. Huang, Preparation and characterization of γ-MnO2/CNTs nanocomposite. Mater. Lett. 61, 934–936 (2007)
C. Cunha, S. Panseri, D. Iannazzo, A. Piperno, A. Pistone, M. Fazio, A. Russo, M. Marcacci, S. Galvagno, Hybrid composites made of multiwalled carbon nanotubes functionalized with Fe3O4 nanoparticles for tissue engineering applications. Nanotechnology. 23, 465102 (2012)
R. Sharma, A.K. Sharma, V. Sharma, Synthesis of carbon nanotubes by arc-discharge and chemical vapor deposition method with analysis of its morphology, dispersion and functionalization characteristics. Cogent Eng. 2, 1094017 (2015)
S. Liang, G. Li, R. Tian, Multi-walled carbon nanotubes functionalized with a ultrahigh fraction of carboxyl and hydroxyl groups by ultrasound-assisted oxidation. J. Mater. Sci. 51, 3513–3524 (2016)
D.L. Pavia, G.M. Lampman, G.S. Kriz, and J.A. Vyvyan, Introduction to spectroscopy. 2008: Cengage Learning.
P. Cañete-Rosales, V. Ortega, A. Álvarez-Lueje, S. Bollo, M. González, A. Ansón, M.T. Martínez, Influence of size and oxidative treatments of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on their electrocatalytic properties. Electrochim. Acta 62, 163–171 (2012)
C. Luo, R. Wei, D. Guo, S. Zhang, S. Yan, Adsorption behavior of MnO2 functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes for the removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 225, 406–415 (2013)
B. Yang, Q. Gong, L. Zhao, H. Sun, N. Ren, J. Qin, J. Xu, H. Yang, Preconcentration and determination of lead and cadmium in water samples with a MnO2 coated carbon nanotubes by using ETAAS. Desalination 278, 65–69 (2011)
W. Chen, J. Mo, X. Du, Z. Zhang, W. Zhang, Biomimetic dynamic membrane for aquatic dye removal. Water Res. 151, 243–251 (2019)
R.H. Bradley, K. Cassity, R. Andrews, M. Meier, S. Osbeck, A. Andreu, C. Johnston, A. Crossley, Surface studies of hydroxylated multi-wall carbon nanotubes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 4835–4843 (2012)
M. Khraisheh, M. Al-Ghouti, S. Allen, M. Ahmad, Effect of OH and silanol groups in the removal of dyes from aqueous solution using diatomite. Water Res. 39, 922–932 (2005)
B. Yang, Z. Tian, L. Zhang, Y. Guo, S. Yan, Enhanced heterogeneous Fenton degradation of Methylene Blue by nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI) assembled on magnetic Fe3O4/reduced graphene oxide. J. Water Process Eng. 5, 101–111 (2015)
J. Xu, D. Xu, B. Zhu, B. Cheng, C. Jiang, Adsorptive removal of an anionic dye Congo red by flower-like hierarchical magnesium oxide (MgO)-graphene oxide composite microspheres. Appl. Surf. Sci. 435, 1136–1142 (2018)
C. Mangwandi, A.B. Albadarin, Y. Glocheux, G.M. Walker, Removal of ortho-phosphate from aqueous solution by adsorption onto dolomite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2, 1123–1130 (2014)
J. Fu, Z. Chen, M. Wang, S. Liu, J. Zhang, J. Zhang, R. Han, Q. Xu, Adsorption of methylene blue by a high-efficiency adsorbent (polydopamine microspheres): kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamics and mechanism analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 259, 53–61 (2015)
Y. Salameh, A.B. Albadarin, S. Allen, G. Walker, M.N.M. Ahmad, Arsenic(III, V) adsorption onto charred dolomite: Charring optimization and batch studies. Chem. Eng. J. 259, 663–671 (2015)
M.E. Argun, D. Güclü, M. Karatas, Adsorption of Reactive Blue 114 dye by using a new adsorbent: pomelo peel. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 20, 1079–1084 (2014)
S. Agarwal, V.K. Gupta, M. Ghasemi, J. Azimi-Amin, Peganum harmala-L seeds adsorbent for the rapid removal of noxious brilliant green dyes from aqueous phase. J. Mol. Liq. 231, 296–305 (2017)
S. Li, X. Zhang, Y. Huang, Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 derived nanoporous carbon as an effective and recyclable adsorbent for removal of ciprofloxacin antibiotics from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 321, 711–719 (2017)
X. Song, L. Li, Z. Geng, L. Zhou, L. Ji, Effective and selective adsorption of As(III) via imprinted magnetic Fe3O4/HTCC composite nanoparticles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 5, 16–25 (2017)
F. Marrakchi, M. Ahmed, W. Khanday, M. Asif, B. Hameed, Mesoporous-activated carbon prepared from chitosan flakes via single-step sodium hydroxide activation for the adsorption of methylene blue. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 98, 233–239 (2017)
J. Dhal, M. Sethi, B. Mishra, G. Hota, MgO nanomaterials with different morphologies and their sorption capacity for removal of toxic dyes. Mater. Lett. 141, 267–271 (2015)
B. Choudhary, D. Paul, Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics of hexavalent chromium removal using biochar. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 6, 2335–2343 (2018)
K.F. Hayes, C. Papelis, J.O. Leckie, Modeling ionic strength effects on anion adsorption at hydrous oxide/solution interfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 125, 717–726 (1988)
H.N. Tran, S.-J. You, A. Hosseini-Bandegharaei, H.-P. Chao, Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: a critical review. Water Res. 120, 88–116 (2017)
Z. Zou, Z. Shi, L. Deng, Highly efficient removal of Cu (ii) from aqueous solution using a novel magnetic EDTA functionalized CoFe2O4. RSC Adv. 7, 5195–5205 (2017)
J. Cao, Y. Wu, Y. Jin, P. Yilihan, W. Huang, Response surface methodology approach for optimization of the removal of chromium (VI) by NH2-MCM-41. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 45, 860–868 (2014)
M. Ghaedi, M.D. Ghazanfarkhani, S. Khodadoust, N. Sohrabi, M. Oftade, Acceleration of methylene blue adsorption onto activated carbon prepared from dross licorice by ultrasonic: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 20, 2548–2560 (2014)
F. Zhu, L. Li, J. Xing, Selective adsorption behavior of Cd (II) ion imprinted polymers synthesized by microwave-assisted inverse emulsion polymerization: Adsorption performance and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 321, 103–110 (2017)
N.M. Mahmoodi, R. Salehi, M. Arami, Binary system dye removal from colored textile wastewater using activated carbon: kinetic and isotherm studies. Desalination 272, 187–195 (2011)
J.-P. Simonin, On the comparison of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws in the modeling of adsorption kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 300, 254–263 (2016)
R. Li, L. Liu, F. Yang, Removal of aqueous Hg (II) and Cr (VI) using phytic acid doped polyaniline/cellulose acetate composite membrane. J. Hazard. Mater. 280, 20–30 (2014)
H. Spahn, E. Schlünder, The scale-up of activated carbon columns for water purification, based on results from batch tests—I: theoretical and experimental determination of adsorption rates of single organic solutes in batch tests. Chem. Eng. Sci. 30, 529–537 (1975)
J. Lalley, C. Han, X. Li, D.D. Dionysiou, M.N. Nadagouda, Phosphate adsorption using modified iron oxide-based sorbents in lake water: kinetics, equilibrium, and column tests. Chem. Eng. J. 284, 1386–1396 (2016)
K. Vinadgopal, D. Wynkop, Photosensitized degradation of a textile azo dye, acid orange 7, on TiO2 particles using visible light. Environ. Sci. Technol. 30, 1660–1668 (1996)
P. Ji, J. Zhang, F. Chen, M. Anpo, Study of adsorption and degradation of acid orange 7 on the surface of CeO2 under visible light irradiation. Appl. Catal. B 85, 148–154 (2009)
Y. Pei, M. Wang, D. Tian, X. Xu, L. Yuan, Synthesis of core–shell SiO2@ MgO with flower like morphology for removal of crystal violet in water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 453, 194–201 (2015)
K.P. Singh, S. Gupta, A.K. Singh, S. Sinha, Optimizing adsorption of crystal violet dye from water by magnetic nanocomposite using response surface modeling approach. J. Hazard. Mater. 186, 1462–1473 (2011)
K. Lu, T. Wang, L. Zhai, W. Wu, S. Dong, S. Gao, L. Mao, Adsorption behavior and mechanism of Fe-Mn binary oxide nanoparticles: adsorption of methylene blue. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 539, 553–562 (2019)
P. Wang, M. Cao, C. Wang, Y. Ao, J. Hou, J. Qian, Kinetics and thermodynamics of adsorption of methylene blue by a magnetic graphene-carbon nanotube composite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 290, 116–124 (2014)
S. Ye, W. Jin, Q. Huang, Y. Hu, Y. Li, B. Li, KGM-based magnetic carbon aerogels matrix for the uptake of methylene blue and methyl orange. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 92, 1169–1174 (2016)
W. Konicki, I. Pełech, E. Mijowska, I. Jasińska, Adsorption kinetics of acid dye acid red 88 onto magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes-Fe3C nanocomposite. CLEAN–Soil Air Water. 42, 284–294 (2014)
H. Gao, S. Zhao, X. Cheng, X. Wang, L. Zheng, Removal of anionic azo dyes from aqueous solution using magnetic polymer multi-wall carbon nanotube nanocomposite as adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 223, 84–90 (2013)
S. Moussavi, M. Emamjomeh, M. Ehrampoush, M. Dehvari, S. Jamshidi, Removal of acid orange 7 dye from synthetic textile wastewater by single-walled carbon nanotubes: adsorption studies, isotherms and kinetics. J. Rafsanjan Univ. Med. Sci. 12, 907–918 (2014)
Y.-L. Ge, Y.-F. Zhang, Y. Yang, S. Xie, Y. Liu, T. Maruyama, Z.-Y. Deng, X. Zhao, Enhanced adsorption and catalytic degradation of organic dyes by nanometer iron oxide anchored to single-wall carbon nanotubes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 488, 813–826 (2019)
M.A. Gabal, E.A. Al-Harthy, Y.M. Al Angari, M. Abdel Salam, MWCNTs decorated with Mn0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4 nanoparticles for removal of crystal-violet dye from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 255, 156–164 (2014)
A. Rodríguez, G. Ovejero, J.L. Sotelo, M. Mestanza, J. García, Adsorption of dyes on carbon nanomaterials from aqueous solutions. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 45, 1642–1653 (2010)
N.M. Mahmoodi, J. Ghobadi, Extended isotherm and kinetics of binary system dye removal using carbon nanotube from wastewater. Desalin. Water Treat. 54, 2777–2793 (2015)
A. Azari, M. Gholami, Z. Torkshavand, A. Yari, E. Ahmadi, B. Kakavandi, Evaluation of basic violet 16 adsorption from aqueous solution by magnetic zero valent iron-activated carbon nanocomposite using response surface method: isotherm and kinetic studies. J. Mazandaran Univ. Med. Sci. 24, 333–347 (2015)
Funding
This work was supported by a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, T., Wu, Y., Liu, N. et al. Iron manganese Oxide Modified Multi-walled Carbon Nanotube as Efficient Adsorbent for Removal of Organic Dyes: Performance, Kinetics and Mechanism Studies. J Inorg Organomet Polym 30, 4027–4042 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01552-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01552-3