Abstract
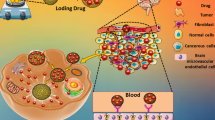
Nitidine chloride (NC) is a natural alkaloid and has strong antitumor activity. However, its clinical application is limited due to the observed non-specific toxicity and low bioavailability. In this study, we synthesized nanoscale metal–organic frameworks MIL-100(Fe), which was used as a nanocarrier to deliver NC. MIL-100(Fe) was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FT-IR), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET), dynamic light scattering (DLS), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). NC was encapsulated in MIL-100(Fe) with a high loading capacity of 33.43 wt%. It shown that NC has progressive releasing behavior with 68% in 4 days under phosphate-buffered saline. The in vitro cytotoxicity of free NC and NC@MIL-100(Fe) were investigated by the MTT assay using the healthy liver cell line (LO2) and a liver cancer cell line (HepG2). Interestingly, NC@MIL-100(Fe) exhibited low toxicity on LO2 cells and high cytotoxicity in HepG2 cells compared to free NC.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Hu, W.D. Zhang, R.H. Liu, C. Zhang, Y.H. Shen, H.L. Li, M.J. Liang, X.K. Xu, Benzophenanthridine alkaloids from Zanthoxylum nitidum (ROXB) DC, and their analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities. Chem. Biodivers 3, 990–995 (2006)
J. Bouquet, M. Rivaud, S. Chevalley, E. Deharo, V. Jullian, A. Valentin, Biological activities of nitidine, a potential antimalarial lead compound. Malar. J. 11(1), 67 (2012)
H. Khan, T.B. Hadda, R. Touzani, Diverse therapeutic potential of nitidine a comprehensive review. Curr. Drug Metab. 19, 986–991 (2018)
L.M. Liu, P. Lin, H. Yang, Y.W. Dang, G. Chen, Gene profiling of HepG2 cells following nitidine chloride treatment: an investigation with microarray and Connectivity Mapping. Oncol. Rep. 41, 3244–3256 (2019)
L.H. Kim, S. Khadka, J.A. Shin, J.Y. Jung, M.H. Ryu, H.J. Yu, H.N. Lee, B. Jang, I.H. Yang, D.H. Won, H.J. Kwon, J.H. Jeong, S.D. Hong, N.P. Cho, S.D. Cho, Nitidine chloride acts as an apoptosis inducer in human oral cancer cells and a nude mouse xenograft model via inhibition of STAT3. Oncotarget. 8, 91306–91315 (2017)
H. Xu, T. Cao, X. Zhang, Y. Shi, Q. Zhang, S. Chai, L. Yu, G. Jin, J. Ma, P. Wang, Y. Li, Nitidine chloride inhibits SIN1 expression in osteosarcoma cells. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics. 12, 224–234 (2019)
H.P. Mou, P. Guo, X.M. Li, C.L. Zhang, J. Jiang, L.H. Wang, Q. Wang, Z.P. Yuan, Nitidine chloride inhibited the expression of S phase kinase-associated protein 2 in ovarian cancer cells. Cell Cycle 16, 1366–1375 (2017)
M.J. Sun, N. Zhang, X.L. Wang, Y.M. Li, W.W. Qi, H.W. Zhang, Z.J. Li, Q.F. Yang, Hedgehog pathway is involved in nitidine chloride induced inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells-like properties in breast cancer cells. Cell. Biosci. 6(1), 44 (2016)
J. Liao, T. Xu, J.X. Zheng, J.M. Lin, Q.Y. Cai, D.B. Yu, J. Peng, Nitidine chloride inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth in vivo through the suppression of the JAK1/STAT3 signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 32, 79–84 (2013)
X.H. Ou, Y. Lu, L.F. Liao, D.N. Li, L.M. Liu, H.G. Liu, H. Xu, Nitidine chloride induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through a pathway involving p53, p21, Bax and Bcl-2. Oncol. Rep. 33, 1264–1274 (2015)
M. Wei, H.G. Liu, L.M. Liu, D.N. Li, In vitro nephrotoxicity of nitidine chloride in human liver L-02 and kidney 293 cells. Chin. J. New Drugs. 19, 56–59 (2010)
T.S. Yarza, A. Mielcarek, P. Couvreur, C. Serre, Nanoparticles of metal-organic frameworks: on the road to in vivo efficacy in biomedicine. Adv. Mater. 30(37), 1707365 (2018)
Q.H. Hu, H. Li, L.H. Wang, H.Z. Gu, C.H. Fan, DNA nanotechnology-enabled drug delivery systems. Chem. Rev. 119, 6459–6506 (2019)
K. Bhattacharyya, S. Mukherjee, Fluorescent metal nano-clusters as next generation fluorescent probes for cell imaging and drug delivery. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 91, 447–454 (2018)
G.X. Lan, K.Y. Ni, W.B. Lin, Nanoscale metal-organic frameworks for phototherapy of cancer. Coord. Chem. Rev. 379, 65–81 (2019)
A. Ali, S. Ahmed, A review on chitosan and its nanocomposites in drug delivery. J. Biol. Macromol. 109, 273–286 (2018)
K. Fukunaga, H. Tsutsumi, H. Mihara, Self-assembling peptides as building blocks of functional materials for biomedical applications. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 92, 391–399 (2019)
W.C. Liu, Y. Pan, W.W. Xiao, H.J. Xum, D. Liu, F. Ren, X.S. Peng, J.Q. Liu, Recent developments on zinc(II) metal–organic framework nanocarriers for physiological pH responsive drug delivery. Med. Chem. Commun. 10, 2038–2051 (2019)
P. Horcajada, C. Serre, M. Vallet-Regi, M. Sebban, F. Taulelle, G. Ferey, Metal-organic frameworks as efficient materials for drug delivery. Angew Chem Int. Ed. 45, 5974–5978 (2006)
D. Cunha, M.B. Yahia, S. Hall, S.R. Miller, H. Chevreau, E. Elkaim, G. Maurin, P. Horcajada, C. Serre, Rationale of drug encapsulation and release from biocompatible porous metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Mater. 25, 2767–2776 (2013)
M. Rezaei, A. Abbasi, R. Varshochian, R. Dinarvand, M. Jeddi-Tehrani, NanoFe-MIL-100 containing docetaxel for breast cancer therapy. Artif. Cells. Nanomed. Biotechnol. 46, 1390–1401 (2018)
M.R. di Nunzio, V. Agostoni, B. Cohen, R. Gref, A. Douhal, A "ship in a bottle" strategy to load a hydrophilic anticancer drug in porous metal organic framework nanoparticles: efficient encapsulation, matrix stabilization, and photodelivery. J. Med. Chem. 57, 411–420 (2014)
W.Y. Li, H. Yin, D. Bardelang, J.B. Xiao, Y. Zheng, R.B. Wang, Supramolecular formulation of nitidine chloride can alleviate its hepatotoxicity and improve its anticancer activity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 109, 923–929 (2017)
F.M. Zhang, J. Shi, Y. Jin, Y.H. Fu, Y.J. Zhong, W.D. Zhu, Facile synthesis of Fe-MIL-100 under HF-free conditions and its application in the acetalization of aldehydes with diols. Chem. Eng. J. 259, 183–190 (2015)
Y.P. Wu, J.W. Tian, S. Liu, B. Li, J. Zhao, L.F. Ma, D.S. Li, Y.Q. Lan, X. Bu, Bi-microporous metal-organic-frameworks with cubane [M4(OH)4] (M = Ni, Co) clusters and pore space partition for electrocatalytic methanol oxidation reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 12185–12189 (2019)
H.R. Fu, L.B. Yan, N.T. Wu, L.F. Ma, S.Q. Zang, Stable dye-encapsulated indium–organic framework as dual-emitting sensor for the detection of Hg2+/Cr2O72- and a wide range of nitro-compounds. J. Mater. Chem. C 6, 6440–6448 (2018)
X. Shen, Y. Pan, Z.H. Sun, D. Liu, H.J. Xu, M. Trivedi, A. Kumar, J.X. Chen, J.Q. Liu, Design of metal-organic frameworks for ph-responsive drug delivery application mini-rev med. Chem. 19, 1644–1665 (2019)
H.R. Fu, L.B. Yan, N.T. Wu, L.F. Ma, S.Q. Zang, Dual-emission MOFI dye sensor for ratiometric fluorescence recognition of RDX and detection of a broad class of nitro-compounds. J. Mater. Chem. A 6, 9183–9191 (2018)
X. Feng, F. Li, L.Y. Wang, A series of homonuclear lanthanide coordination polymers based on a fluorescent conjugated ligand: syntheses, luminescence and sensor. CrystEngComm 17, 7878–7887 (2015)
G. Chen, X. Leng, J. Luo, L. You, C. Qu, X. Dong, H. Huang, X. Yin, J. Ni, In vitro toxicity study of a porous iron(iii) metal organic framework. Molecules 24, 1211–1220 (2019)
Y. Han, W. Liu, J. Huang, S. Qiu, H. Zhong, D. Liu, J. Liu, Cyclodextrin-based metal-organic frameworks (CD-MOFs) in pharmaceutics and biomedicine. Pharmaceutics. 10, 271–283 (2018)
L.P. Li, M.J. Tu, X. Yang, S.Y. Sun, X.D. Wu, H. Zhou, S. Zeng, H.D. Jiang, The contribution of human OCT1, OCT3, and CYP3A4 to nitidine chloride-induced hepatocellular toxicity. Drug Metab Dispos. 42, 1227–1234 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (No. 2016GXNSFAA380063) and Guangxi Science Foundation (No. AD18126005) and and Special Funds for Scientific Technological Innovation of Undergraduates in Guangdong Province (pdjh2019b0222, pdjh2019b0219, pdjh2019b0221 and pdjh2020b0267).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bi, J., Zheng, Y., Fang, L. et al. Nano-Sized MIL-100(Fe) as a Carrier Material for Nitidine Chloride Reduces Toxicity and Enhances Anticancer Effects In Vitro. J Inorg Organomet Polym 30, 3388–3395 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01548-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01548-z