Abstract
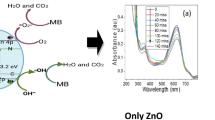
Nickel and sulfur-doped tin oxide powder materials were successfully prepared by a simple solid-state reaction method at low temperature using 2,4-dimethylbenzenesulfonic acid sodium (MSDS) and sodium xylenesulfonate (SXS) isomeric surfactants as templates. The synthesized powder materials were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), UV–Vis diffuse reflectance spectrum (DRS UV–Vis), scanning electron microscopy (SEM)/energy dispersive X-ray (EDX), infrared spectroscopy (IR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and the zetapotential and particle size distribution of the powder materials in solution were tested. The results show that the doping of S and Ni improves the absorption intensity of the materials in the UV–Vis region, and forming the p-n heterojunction of NiO/SnO2, as well as changing the relative diffraction intensity (I101/I110). SXS is beneficial to the doping of S and the formation of NiII and SIV, while MSDS is more favorable for the doping of Ni and the formation of NiIII and SVI ions during the process of calcination at 500 °C. The nickel single-doped and sulfur–nickel double-doped SnO2 powder materials with MSDS are more stable in the photocatalytic system than that with SXS, and exhibit high photocatalytic activity for methyl blue under UV-light irradiation, within 40 min and at 27 °C, the photodegradation rate (98.57%) of Ni–S–SnO2–MSDS is the highest than others, which is mainly derived from the obvious steric hindrance effect of MSDS and the results of the synergistic photocatalystic degradation of the multi-element.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Spence, The UV absorption edge of tin oxide thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 38, 3767–3771 (1967)
K.B. Sundaram, G.K. Bhagavat, Optical absorption studies on tin oxide films. J. Phys. D 14, 921–925 (1981)
Y.K. Liu, C.L. Zheng, W.Z. Wang, Synthesis and characterization of rutile SnO2 nanorods. Adv. Mater. 13, 1883–1885 (2001)
S. Samson, C.G. Fonstad, Defect structure and electronic donor levels in stannic oxide crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 44, 4618–4621 (1973)
M.K. Lv, Solid State Chemistry (Shandong University Press, Shandong, 1996), p. 31
S.Y. Liu, W.H. Tang, Q.G. Feng, C.Y. Luo, Correlation of microstructure and visible light catalytic property in Al-doped titanium dioxide powder materials. J. Mol. Catal. 25, 442–447 (2011)
A. Houas, H. Lachhe, M. Ksibi, E. Elaloui, C. Guillard, J.M. Herrmann, Photocatalytic degradation pathway of methylene blue in water. Appl. Catal. B 31, 145–157 (2001)
C.G. Fonstad, R.H. Reduker, Electrical properties of high-quality stannic oxide crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 42, 2911–2918 (1971)
Z.X. Zhai, J.Q. Liu, G.H. Jin, C.Y. Luo, Q.X. Jiang, Y.Q. Zhao, Characterization and gas sensing properties of copper-doped tin oxide thin films deposited by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. Mater. Sci. 22, 201–204 (2016)
B. Xu, H.M. Cheng, Y.Q. Wang, J.M. Ma, Preparation and properties of nanosized composite particle SnO2/CdS. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 15, 925–929 (1999)
H. Liu, A. Wang, Q. Sun, T.T. Wang, H.P. Zeng, Cu nanoparticles/fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) nano-composites for photocatalytic H2 evolution under visible light irradiation. Catalysts 7, 385–398 (2017)
G. Giusti, V. Consonni, E. Puyoo, D. Bellet, High performance ZnO–SnO2: F nanocomposite transparent electrodes for energy applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 6, 14096–14107 (2014)
G. Yang, Z. Yan, T. Xiao, Preparation and characterization of SnO2/ZnO/TiO2 composite semiconductor with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 8704–8712 (2012)
S. Wang, J. Huang, Y. Zhao, S. Wang, X. Wang, Preparation, characterization and catalytic behavior of SnO2 supported Au catalysts for low-temperature CO oxidation. J. Disper. Sci. Technol. 259, 245–252 (2010)
Y. Lu, P.J. Wang, C.W. Zhang, L. Jiang, G.L. Zhang, P. Song, Material optoelectronic properties of In, N co-doped SnO2 studied by first principles. Acta Phys. Sin 60, 223–229 (2011)
Y. Lu, P.J. Wang, C.W. Zhang, X.Y. Feng, L. Jiang, G.L. Zhang, Study of material properties of Fe, S co-doped SnO2 by first principles. Acta Phys. Sin 61, 23101–23106 (2012)
J.H. Chi, J. Wang, Synthesis, morphology and optical properties of Mn doped SnO2 one-dimensional nano-structures. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 26, 2306–2310 (2010)
S.Y. Liu, W.H. Tang, H.Y. Yang, C.Y. Luo, T.Z. Jiang, Regulation of surfactant on the microstructure and photocatalytic property of Al doped titanium dioxide powder. Finechemicals 30, 1–7 (2013)
Xu Hao, Tang Cheng-Li, Zhang Qian, Yan Wei, A microwave approach to the preparation of Sb-doped SnO2 electrode. J. Inorg. Mater. 27, 1–6 (2012)
M.A. Farrukh, P. Tan, R. Adnan, Influence of reaction parameters on the synthesis of surfactant-assisted tin oxide nanoparticles. Turk. J. Chem. 36, 303–314 (2012)
M.M. Rahman, X.B. Li, N.S. Lopa, J.J. Lee, Electrodeposition of gold on fluorine-doped tin oxide: characterization and application for catalytic oxidation of nitrite. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 35, 2072–2076 (2014)
S.B. Rawal, D.P. Ojha, Y.S. Choi, W.I. Lee, Coupling of W-doped SnO2 and TiO2 for efficient visible-light photocatalysis. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 35, 913–918 (2014)
W.B. Soltan, M.S. Lassoued, S. Ammar, T. Toupance, Vanadium doped SnO2 nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. J. Mater. Sci. 28, 15826–15834 (2017)
Z.B. He, S.Y. Liu, H.Y. Yang, Z.Y. Min, X. Nie, Sulfur doped tin oxide nanoparticles: solid state synthesis and performance for visible-light driven photocatalytic degradation of paraquat. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 31, 649–658 (2015)
X.D. Lou, T.X. Wang, Q.T. Cheng, Preparation and photocatalytic activity of nickel oxide catalysts. Technol. Water Treat. 31, 32–35 (2005)
Y.K. Sun, B. Bai, H.L. Wang, Y.R. Suo, Preparation of p–n heterojunction-like NiO/In2O3 photocatalysts and their degradation performance of doxycycline hyclate. Chem. Eng. 44, 26–31 (2016)
H.B. Li, G.Y. Huang, J. Zhang, S.H. Fu, T.G. Wang, H.W. Liao, Photochemical synthesis and enhanced photo-catalytic activity of MnOx/BiPO4 heterojunction. Trans. Nonferrous Metals Soc. China 27, 1127–1133 (2017)
W.B. Soltan, M.S. Lassoued, S. Ammar, T. Toupance, Vanadium doped SnO2 nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. J. Mater. Sci. 28, 15826–15834 (2017)
K.P. Gattu, K. Ghule, A.A. Kashale, V.B. Patil, D.M. Phase, Bio-green synthesis of Ni-doped tin oxide nano-particles and its influence on gas sensing properties. RSC Adv. 5, 72849–72856 (2015)
J.P. Cheng, B.B. Wang, M.G. Zhao, F. Liu, X.B. Zhang, Nickel-doped tin oxide hollow nanofibers prepared by electrospinning for acetone sensing. Sens. Actuators B 190, 78–85 (2014)
S.P. Bharti, E. Singh, U. Kumar, Synthesis and characterization of nickel doped tin oxide nanoparticles by hydrothermal method. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Res. 4, 115–119 (2017)
J.K. Xiao, C.W. Song, X.N. Zhang et al., Spectroscopic analysis and gas sensing performance of Ni-doped SnO2. Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 44, 2509–2512 (2015)
L.K. Randeniya, A.B. Murphy, I.C. Plumb, A study of S-doped TiO2 for photoelectrochemical hydrogen generation from water. J. Mater. Sci. 43, 1389–1399 (2008)
Y.H. Duan, Electronic properties and stabilities of bulk and low-index surfaces of SnO in comparison with SnO2: a first-principles density functional approach with an empirical correction of vander Waals interactions. Phys. Rev. B 77, 045332 (2008)
X.C. Xu, Organic Chemistry (Edit II) (Higher Education Press (HEP), Beijing, 1991), pp. 120–122
S. Huang, K. Matsubara, J. Cheng et al., Highly enhanced ultraviolet photosensitivity and recovery speed in electrospun Ni-doped SnO2 nanobelts. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 141108 (2013)
S.Y. Liu, C.G. Zuo, S.B. Zhou, Sulfur doped ceria mesoporous nanomaterial: solid-state synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic property of methyl orange. Sci. Adv. Mater. 10, 155–164 (2018)
S.Y. Liu, Y.D. Chen, T.Y. Qiu, L.H. Ou, C.G. Zuo, Q.G. Feng, Sulfur doped lead monoxide superfine powder materials: solid-state synthesis, characterization, adsorption and photocatalytic property of methylene blue. J. Inorg. Organomet. Poly. Mater. 28, 2584–2595 (2018)
S.Y. Zou, M.A. Kamran, G.L. Yang, R.B. Liu, L.J. Shi, Y.Y. Zhang, B.H. Jia, H.Z. Zhong, B.S. Zou, Excitonic magnetic polarons and their luminescence in II–VI diluted magnetic semiconductor micronanostructures. Acta Phys. Sin. 68, 17101–17120 (2019)
F.P. Zhang, J.X. Zhang, X.Y. Yang, H. Fang, F.S. Li, Study on effects of electrical field on electronic structure of nickel oxide. J. Synth. Cryst. 45, 783–789 (2016)
E. burstein, Anomalous optical absorption limit in InSb. Phys. Rev. 93, 632–636 (1954)
S.Y. Huang, H. Wu, K. Matsubara, J. Cheng, W. Pan, Facile assembly of n-SnO2 nanobelts-p-NiO heterojunctions with enhanced ultraviolet photoresponse. Chem. Commun. 50, 2847–2850 (2014)
J. Singleton, Band Theory and Electronic Properties of Solids (Science publishing press, Beijing, 2008), pp. 36–37
J.M. Themlin, M. Chtaib, L. Henrard et al., Characterization of tin oxides by X-ray-photoemission spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 46, 2460–2466 (1992)
P. Periyat, S.C. Pillai, E.D.M. Cormack, J. Colreavy, S.J. Hinder, Improved high-temperature stability and sun-light-driven photocatalytic activity of sulfur-doped anatase TiO2. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 7644–7652 (2008)
X.T. Yin, P. Chen, M.D. Que, Y.L. Xing, W.X. Que, M. NiuC, J.Y. Shao, Highly efficient flexible perovskite solar cells using soluiton-derived NiOx hole contacts. ACS Nano 10, 3630–3637 (2016)
H.W. Nesbitt, D. Legrand, G.M. Bancroft, Interpretation of Ni2p XPS spectra of Ni conductors and Ni insulators. Phys. Chem. Miner. 27, 357–366 (2000)
X.D. Guo, B.H. Zhong, Y. Tang, J.X. Ren, Y.K. Hu, H. Liu, W.M. Fang, The influence of primary particle size and secondary particle size on performances of LiFePO4. J. Chem. Eng. Chin. Univ. 27, 884–888 (2013)
A.V. Brontsov, L.V. Stovanova, D.V. Kolov, Kinetics of the photocatalytic oxidation of gaseous acetone over platinized titanium dioxide. J. Catal. 189, 360–369 (2000)
S.Y. Liu, L.D. Wu, Z.X. Zhao, Q.G. Feng, X. Wang, C.D. Yang, Synthesis of Ni-doped TiO2 mesoporous material via solid-state reaction at low temperature and its kinetics of methyl orange photodegradation. Chin. J. Inorg. Mater. 24, 902–908 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by Hunan Province Cooperative Innovation Center for the Construction and Development of Dongting Lake Economic Zone, and Key Research Project of Hunan Provincial Department of Education (17A145). Hunan University of Arts and Science Doctoral Research Foundation (E3127).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao-you, L., Yuan-dao, C., Cheng-gang, Z. et al. Solid-Phase Synthesis and Photocatalytic Property of Sulfur and Nickel Doped Tin Oxide Powder Materials by Isomeric Surfactant as Template. J Inorg Organomet Polym 30, 457–468 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01204-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01204-1