Abstract
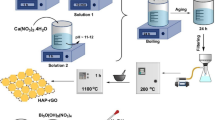
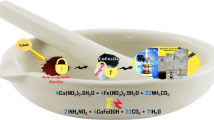
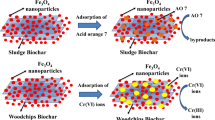
CoFe2O4 nanoparticles were synthesized using environmentally friend sucrose auto-combustion method. PANI/CoFe2O4 nano-composites were prepared via in situ polymerization of aniline in the presence of various ferrite ratios. The structure, thermal, and electro-magnetic properties of the nano-composites were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), thermo-gravimetric analysis (TG), vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM), ac-conductivity and dielectric measurements. The structural properties exhibited the existence of the two phases and indicated core–shell structure. This core–shell was confirmed further through thermal and electrical properties measurements. The different PANI properties such as thermal stability, magnetic and the dielectric were obviously improved by ferrite incorporation whereas its conductivity remained unaffected. The nano-composites (10 and 30%) were investigated for the efficient removal of acid red dye (AR) from wastewater. In this category, the effect of various parameters including pH, contact time, temperature and mass on the removal capacity were investigated. The adsorption kinetics indicated that the adsorption followed the pseudo-second-order equation model through spontaneous endothermic adsorption process. The incorporation of ferrite within PANI increases the magnetic sensitivity of the nano-composite, which will facilitate the ease of separation of dispersed nano-composite from aqueous solutions using simple magnet after dye removing process. Generally, the moderate magnetic sensitivity, cost effective synthesis besides the acceptable obtained adsorption capability of the entire nano-composites could enhance their future use in the remediation applications.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Jin, M. Zhong, F. Wang, Y. Dong, Z. Lei, Q. Wang, B. Su, Enhanced magnetic and electrochemical properties of one-step synthesized PANI-Fe3O4 composite nanomaterial by a novel green solvothermal method. J. Alloys Compds. 695, 1807–1812 (2017)
M. Khairy, Polyaniline–Zn0.2Mn0.8Fe2O4, ferrite core–shell composite: preparation, characterization and properties. J. Alloys Compd. 608, 283–291 (2014)
C.D. Pina, A.M. Ferretti, A. Ponti, E. Falletta, A green approach to magnetically-hard electrically-conducting polyaniline/CoFe2O4 nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 110, 138–144 (2015)
P. Chitra, A. Muthusamy, S. Dineshkumar, Temperature and frequency dependence on electrical properties of polyaniline/Ni(1-x)CoxFe2O4 nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 384, 204–212 (2015)
V. Divya, M.V. Sangaranarayanan, A facile synthetic strategy for mesoporous crystalline copper–polyaniline composite. Eur. Polym. J. 48, 560–568 (2012)
C.V. Tuan, M.A. Tuan, N.V. Hieu, T. Trung, Electrochemical synthesis of polyaniline nanowires on Pt interdigitated microelectrode for room temperature NH3 gas sensor application. Curr. Appl. Phys. 12, 1011–1018 (2012)
Q. Tan, Y. Xu, J. Yang, L. Qiu, Y. Chen, X. Chen, Preparation and electrochemical properties of the ternary nanocomposite of polyaniline/activated carbon/TiO2 nanowires for supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 88, 526–529 (2013)
M. Tumma, R. Srivastava, Transition metal nanoparticles supported on mesoporous polyaniline catalyzed reduction of nitroaromatics. Catal. Commun. 37, 64–68 (2013)
N. Dong, M. Zhong, P. Fei, Z. Lei, B. Su, Magnetic and electrochemical properties of PANI-CoFe2O4 nanocomposites synthesized via a novel one-step solvothermal method. J. Alloys Compds. 660, 382–386 (2016)
A.P. Alivisator, Semiconductor clusters, nanocrystals, and quantum dots. Science 271, 933–937 (1996)
S. Sun, C.B. Murray, D. Weller, L. Folks, A. Moser, Monodisperse FePt nanoparticles and ferromagnetic FePt nanocrystal superlattices. Science 287, 1989–1992 (2000)
J. Smith, H.P.J. Wijn, Ferrites (Philips Technical Library, Eindhovan, 1959)
A.B. Salunkhe, V.M. Khot, M.R. Phadatare, S.H. Pawar, Combustion synthesis of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles-Influence of fuel to oxidizer ratio. J. Alloys Compds 514, 91–96 (2012)
K. Rana, P. Thakur, P. Sharma, M. Tomar, V. Guptab, A. Thakur, Improved structural and magnetic properties of cobalt nanoferrites: influence of sintering temperature. Ceram. Int. 41, 4492–4497 (2015)
M.A. Gabal, R.M. El-Shishtawy, Y.M. Al Angari, Structural and magnetic properties of nano-crystalline Ni–Zn ferrites synthesized using egg-white precursor. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 2258–2264 (2012)
Y.I. Kim, D. Kim, C.S. Lee, Synthesis and characterization of CoFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles prepared by temperature-controlled coprecipitation method. Physica B 337, 42–51 (2003)
J. Jiang, L. Li, M. Zhu, Polyaniline/magnetic ferrite nanocomposites obtained by in situ polymerization. React. Funct. Polym. 68, 57–62 (2008)
G. Li, S. Yan, E. Zhou, Y. Chen, Preparation of magnetic and conductive NiZn ferrite-polyaniline nanocomposites with core-shell structure. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 276, 40–44 (2006)
O. Yavuz, M.K. Ram, M. Aldissi, P. Poddar, S. Hariharan, Synthesis and the physical properties of MnZn ferrite and NiMnZn ferrite–polyaniline nanocomposite particles. J. Mater. Chem. 15, 810–817 (2005)
L. Li, C.H. Xiang, X. Liang, B. Hao, Zn0.6Cu0.4Cr0.5Fe1.46Sm0.04O4 ferrite and its nanocomposites with polyaniline and polypyrrole: Preparation and electromagnetic properties. Synth. Met. 160, 28–34 (2010)
J. Jiang, L. Li, F. Xu, Polyaniline–LiNi ferrite core–shell composite: preparation, characterization and properties. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 456, 300–304 (2007)
J. Jiang, L.-H. Ai, D.-B. Qin, H. Liu, L.-C. Li, Preparation and characterization of electromagnetic functionalized polyaniline/BaFe12O19 composites. Synth. Met. 159, 695–699 (2009)
N. Gandhil, K. Singh, A. Ohlan, D.P. Singh, S.K. Dhawan, Thermal, dielectric and microwave absorption properties of polyaniline–CoFe2O4 nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 71, 1754–1760 (2011)
E.E. Tanrıverdi, A.T. Uzumcu, H. Kavas, A. Demir, A. Baykal, Conductivity Study of Polyaniline-Cobalt Ferrite (PANI-CoFe2O4) Nanocomposite. Nano-Micro Lett. 3, 99–107 (2011)
J.A. Khan, M. Qasim, B.R. Singh, S. Singh, M. Shoeb, W. Khan, D. Das, A.H. Naqvi, Synthesis and characterization of structural, optical, thermal and dielectric properties of polyaniline/CoFe2O4 nanocomposites with special reference to photocatalytic activity. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 109, 313–321 (2013)
P. Antonel, F.M. Berho, G. Jorge, F.V. Molina, Magnetic composites of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles in a poly (aniline) matrix: Enhancement of remanence ratio and coercivity. Synth. Met. 199, 292–302 (2015)
M.A. Gabal, A.A. Al-Juaid, S.M. Al-Rashed, M.A. Hussein, F. Al-Marzouki, Synthesis, characterization and electromagnetic properties of Zn-substituted CoFe2O4 via sucrose assisted combustion route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 426, 670–679 (2017)
M.A. Gabal, A.A. Al-Juaid, S. El-Rashed, M.A. Hussein, Synthesis and characterization of nano-sized CoFe2O4 via facile methods: a comparative study. Mater. Res. Bull. 89, 68–78 (2017)
M.A. Gabal, M. Hussein, A. Hermas, Synthesis, characterization and electrical conductivity of polyaniline-Mn0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4 nano-composites. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci 11, 4526–4538 (2016)
M. AbdelSalam, Coating carbon nanotubes with crystalline manganese dioxide nanoparticles and their application for lead ions removal from model and real water. Colloids Surf. A419, 69–79 (2013)
R.D. Waldron, Infrared spectra of ferrites. Phys. Rev. 99, 1727 (1955)
S. Sultana, M.Z. Rafiuddin, K. Khan, Umar, Synthesis and characterization of copper ferrite nanoparticles doped polyaniline. J. Alloys Compds. 535, 44–49 (2012)
L. Li, J. Jiang, F. Xu, Synthesis and ferrimagnetic properties of novel Sm-substituted LiNi ferrite–polyaniline nanocomposite. Mater. Lett. 61, 1091–1096 (2007)
H. Sozeri, U. Kurtan, R. Topkaya, A. Baykal, M.S. Toprak, Polyaniline (PANI)–Co0.5Mn0.5Fe2O4 nanocomposite: synthesis, characterization and magnetic properties evaluation. Ceram. Int. 39, 5137–5143 (2013)
A. Gok, B. Sari, M. Talu, Synthesis and characterization of conducting substituted polyanilines. Synth. Met. 142, 41–48 (2004)
M. Khairy, Synthesis, characterization, magnetic and electrical properties of polyaniline/NiFe2O4 nanocomposite. Synth. Met. 189, 34–41 (2014)
M. Caizer, Stefanescu, magnetic characterization of nanocrystalline Ni–Zn ferrite powder prepared by the glyoxylate precursor method. J. Phys. D 35, 3035–3040 (2002)
A.A. Farghali, M. Moussa, M.H. Khedr, Synthesis and characterization of novel conductive and magnetic nano-composites. J. Alloys Compds. 499, 98–103 (2010)
K.R. Reddy, K.-P. Lee, A.I. Gopalan, H.-D. Kang, Organosilane modified magnetite nanoparticles/poly (aniline-co-o/m-aminobenzenesulfonic acid) composites: synthesis and characterization. React. Funct. Polym. 67, 943–954 (2007)
L. Zhang, W. Jiao, J. He, A. Zhang, Synthesis of PAA/NiFe2O4 composite nanoparticles and the effect of microstructure on magnetism. J. Alloys Compds. 577, 538–542 (2013)
M.A. Gabal, A.A. Al-Juaid, S. El-Rashed, M.A. Hussein, Y.M. Al Angari, Polyaniline/Co0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4 core-shell nano-composites. Synthesis, characterization and properties. J. Alloys Compd. 747, 83–90 (2018)
H. Deligoz, A. Baykal, E.E. Tanrıverdi, Z. Durmus, M.S. Toprak, Synthesis, structural and electrical properties of triethylene glycol (TREG) stabilized Mn0.2Co0.8Fe2O4 NPs. Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 537–543 (2012)
M.B. Mohamed, K. EL-Sayed, Structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of (PANI)–Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe1.5Cr0.5O4 nanocomposite. Composites Part B 56, 270–278 (2014)
X. Yuan, L. Cheng, Y. Zhang, S. Guo, L. Zhang, Fe-doped SiC/SiO2 composites with ordered inter-filled structure for effective high-temperature microwave attenuation. Mater. Des. 92, 563–570 (2016)
M. Bhaumik, R. McCrindle, A. Maity, Efficient removal of Congo red from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto interconnected polypyrrole–polyaniline nanofibres. Chem. Eng. J. 228, 506–515 (2013)
M.A. Gabal, E.A. Al-Harthy, Y.M. Al Angari, M. Abdel Salam, MWCNTs decorated with Mn0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4 nanoparticles for removal of crystal-violet dye from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 255, 156–164 (2014)
S. Lagergren, Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption gelöster stoffe. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar 24, 1–39 (1898)
W. Rudzinski, W. Plazinski, On the applicability of the pseudo-second order equation to represent the kinetics of adsorption at solid/solution interfaces: a theoretical analysis based on the statistical rate theory. Adsorption 15, 181–192 (2009)
H.M. Al-Saidi, M.A. Abdel-Fadeel, A.Z. El-Sonbati, A.A. El-Bindary, Multi-walled carbon nanotubes as an adsorbent material for the solid phase extraction of bismuth from aqueous media: kinetic and thermodynamic studies and analytical applications. J. Mol. Liq. 216, 693–698 (2016)
S. Karagoz, T. Tay, S. Ucar, M. Erdem, Activated carbons from waste biomass by sulfuric acid activation and their use on methylene blue adsorption. Bioresour. Technol. 99, 6214–6222 (2008)
L. Vlaev, S. Turmanova, A. Dimitrova, Kinetics and thermodynamics of water adsorption onto rice husks ash filled polypropene composites during soaking. J. Polym. Res. 16, 151–164 (2009)
W. Konicki, I. Petech, E. Mijowaska, I. Jasinska, Adsorption kinetics of acid dye acid red 88 onto magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes Fe3C nanocomposite. Clean-Soil Air Water 42, 284–294 (2014)
A.H. Aydin, O. Yavuz, Removal of acid red 183 from aqueous solution using clay and activated carbon. Ind. J. Chem. Technol. 11, 89–94 (2014)
D. Xu, C. Gu, X. Chen, Adsorption and removal of acid red 3R from aqueous solution using flocculent humic acid isolated from lignite. Procedia Environ. Sci. 18, 127–134 (2013)
X. Yang, B. Al-Duri, Kinetic modeling of liquid-phase adsorption of reactive dyes on activated carbon. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 287, 25–34 (2005)
A.K. Kumar, S.V. Mohan, P.N. Sarma, Sorptive removal of endocrine-disruptive compound (estriol, E3) from aqueous phase by batch and column studies: kinetic and mechanistic evaluation. J. Hazard. Mater. 164, 820–828 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The corresponding author (M.A. Gabal) stated that the absence of any grant or fund. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gabal, M.A., Al-Juaid, A.A., El-Rashed, S. et al. Structural, Thermal, Magnetic and Electrical Properties of Polyaniline/CoFe2O4 Nano-composites with Special Reference to the Dye Removal Capability. J Inorg Organomet Polym 29, 2197–2213 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01179-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01179-z