Abstract
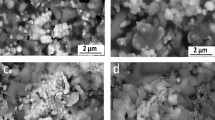
Wollastonite (CaSiO3) is one of the calcium silicate based material and is widely applied in hard tissue engineering applications. Combustion based sol–gel method was adopted to prepare the phase pure CaSiO3 with inclusion of Zn ions (1, 3 and 5 wt%) using glycine as a reducing agent. The synthesized pure and Zn doped CaSiO3 powders were characterized by attenuated total reflectance–Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR–FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), dynamic light scattering (DLS), scanning electron microscopy–energy dispersive spectroscopy (SEM–EDS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analyses to confirm their functional groups, phase composition, thermal stability, particle size, surface morphology and topography, respectively. In vitro biological examinations were carried out to evaluate the biological behaviour of pure and Zn doped CaSiO3 powders. The antibacterial activity was tested for 1–5 wt% of Zn doped CaSiO3 powders against E. coli and S. aureus by colony forming unit (CFU) which proved that with increase of Zn concentration, the microbial restriction was found to be enhanced for both pathogens than control and pure CaSiO3. In vitro apatite layer formation was observed on the surface of Zn doped CaSiO3 powders with existence of ball like crystals for 14 days. In vitro cytocompatible study revealed that 5 wt% of Zn doped CaSiO3 powder exhibited good cellular interaction of MG-63 cells at concentrations of 200–1000 µg/ml for 24 h. Thus, these biological studies reveal that the developed Zn doped CaSiO3 powders could be applied for better clinical applications.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Siriphannon, Y. Kameshima, A. Yasumori, K. Okada, S. Hayashi, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 22, 511–520 (2002)
P. Siriphannon, S. Hayashi, A. Yasumori, K. Okada, J. Mater. Res. 14, 529–536 (1999)
A.B.Y. Hazar, Ceram. Int. 33, 687–692 (2007)
L.H. Long, L.D. Chen, S.Q. Bai, J. Chang, K.L. Lin, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26, 1701–1706 (2006)
S.F.S. Shirazi, S. Gharehkhani, H.S.C. Metselaar, B. Nasiri-Tabrizi, H. Yarmand, M. Ahmadi, N.A.A. Osman, RSC Adv. 6, 190–200 (2016)
S. Kalaivani, R.K. Singh, V. Ganesan, S. Kannan, J. Mater. Chem. B 2, 846–858 (2014)
E.S. Thian, T. Konishi, Y. Kawanobe, P.N. Lim, C. Choong, B. Ho, M. Aizawa, Mater. Sci: Mater. Med. 24, 437–445 (2013)
J. Yu, K. Li, X. Zheng, D. He, X. Ye, M. Wang, PLoS ONE 8, e57564 (2013)
Q. Lin, X. Lan, Y. Li, Y. Ni, C. Lu, Y. Chen, Z. Xu, Mater. Sci. Eng. C 31, 629–636 (2011)
S. Priya, L.H. Larry, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 318, 1–13 (2013)
S. Vichaphund, M. Kitiwan, D. Atong, P. Thavorniti, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 31, 2435–2440 (2011)
K. Lin, J. Chang, J. Lu, Mater. Lett. 60, 3007–3010 (2006)
U. Anjaneyulu, S. Sasikumar, Bull. Mater. Sci. 37, 207–212 (2014)
M.V. Reddy, M. Pathak, Mater. Tech. 33, 38–47 (2017)
T. Kokubo, H. Kushitani, S. Sakka, T. Kitsugi, T. Yamamuro, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 24, 721–734 (1990)
R. Lakshmi, S. Sasikumar, Int. J. Nanomed. 10, 129–136 (2015)
L. Xuanyong, D. Chuanxian, K.C. Paul, Biomaterials 25, 1755–1761 (2004)
M.A. Sainz, P. Pena, S. Serena, A. Caballero, Acta Biomater. 6, 2797–2807 (2010)
S. Prabhu, E.K. Poulose, Int. Nano Lett. 2, 1–10 (2012)
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to Vellore Institute of Technology (VIT) Vellore India for provide all the necessary facilities and infrastructure to carry out this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reddy, M.V., Pathak, M. In Vitro Biological Evaluations of Zn Doped CaSiO3 Synthesized by Sol–Gel Combustion Technique. J Inorg Organomet Polym 28, 2187–2195 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-0922-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-0922-8