Abstract
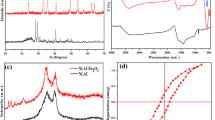
The paper reports on the successful use of the nano crystalline cobalt ferrite doped Nerium oleander leaf waste activated carbon (CoFe2O4/NOAC) synthesized by an urea assisted auto combustion technique to assess accurate kinetics and equilibrium parameters regarding the investigation of adsorption. The specific features of nano composite were investigated by various analytical techniques such as Scanning electron microscope with EDAX, powder X-ray diffraction study, BET surface area analysis, TG and DSC, Vibrating Sample Magnetometer. The BET analysis indicates that CoFe2O4 nano particles embedded in NOAC have increased the pore diameter for better adsorption. TG and DSC show the thermal stability of composite. The VSM study shows the Ferro magnetic behavior of nano composite which revealed that CoFe2O4/NOAC could be separated and retrieved easily by an external magnet after adsorption of AV49. The efficiency of adsorption of AV49 from aqueous solution was investigated through a series of batch experiments by using CoFe2O4/NOAC. The batch adsorption experiments showed the efficient removal on CoFe2O4/NOAC under optimum conditions such as pH 6.5, contact time-55 min and adsorbent dosage-50 mg. Adsorption kinetics—Pseudo first order and second order, Isotherms—Langmuir and Freundlich have been adapted to analyze the adsorption capacity. The results showed that the adsorption followed the pseudo second order kinetics and Langmuir isotherm equation is the best to describe the adsorption process. According to the thermodynamic study, it was very effective at higher temperatures also. The thermodynamic parameters ∆Go, ∆Ho and ∆So were also evaluated for this adsorption.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Regti, M.R. Laamari, S.-E. Stiriba, M.E. Haddad, Removal of basic blue 41 dyes using Persea americana-activated carbon prepared by phosphoric acid action. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 8, 187–195 (2017)
M.T. Sulak, H.C. Yatmaz, Removal of textile dyes from aqueous solutions with eco-friendly biosorbent. Desalination Water Treat. 37, 169–177 (2012)
K. Zare, V.K. Gupta, O. Moradi, A.S.H. Makhlouf, M. Sillanpaa, M.N. Nadagouda, H. Sadegh, R. Shahryari-ghoshekandi, A. Pal, Z. Wang, I. Tyagi, M. Kazemi, A comparative study on the basis of adsorption capacity between CNTs and activated carbon as adsorbents for removal of noxious synthetic dyes: a review. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 5, 227–236 (2015)
A.T. Ojedokun, O.S. Bello, Kinetic modeling of liquid-phase adsorption of Congo red dye using guava leaf-based activated carbon. Appl. Water Sci. 7, 1965–1977 (2017)
M.N. Aydogana, N.P. Arslanb, Removal of textile dye reactive black 5 by the coldadapted, alkali- and halotolerant fungus Aspergillus flavipes MA-25 under non-sterile conditions. Desalination Water Treat 56, 1–9 (2015)
A. Wasti, M.A. Awan, Adsorption of textile dye onto modified activated alumina. J. Assoc. Arab Iniversities Basic Appl. Sci. 20, 26–31 (2016)
G.B. Oguntimein, Biosorption of dye from textile wastewater effluent onto alkali treateddried sunflower seed hull and design of a batch adsorber. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 3, 2647–2661 (2015)
D.L. Postai, C.A. Demarchi, F. Zanatta, D.C.C. Melo, C.A. Rodigues, Adsorption of rhodamine B and methylene blue dyes using waste of seeds of Aleurites Moluccano, a low cost adsorbent. Alexandia Eng. J. 55, 1713–1723 (2016)
R. Subramanium, S.K. Ponnusamy, Novel adsorbent from agricultural waste (Cashew NUT Shell) for methylene blue dye removal: optimization by response surface methodology. Water Resour Ind. 11, 64–70 (2015)
K.S. Hameed, P. Muthirulan, M.M. Sundaram, Adsorption of chromotrope dye onto activated carbons obtained from the seeds of various plants: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Arab. J. Chem. 10, 2225–2233 (2017)
H. Tounsadiab, A. Khalidia, M. Abdennourib, N. Barkab, Potential capability of natural biosorbents: Diplotaxis harra and Glebionis coronaria L. on the removal efficiency of dyes from aqueous solutions. Desalination Water Treat 57, 16633–16642 (2016)
S. Kanchi, K. Bisetty, G. Kumar, M.I. Sabela, Robust adsorption of Direct Navy Blue-106 from textile industrial effluents by bio-hydrogen fermented waste derived activated carbon: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Arab. J. Chem. 10, 3084–3096 (2017)
E. Altıntıg, H. Altundag, M. Tuzen, A. Sari, Effective removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions using magnetic loaded activated carbon as novel adsorbent. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 122, 151–163 (2017)
M.A. Mekewi, A.S. Darwish, M.S. Amin, Gh Eshaq, H.S. Bourazan, Copper nano particles supported onto montmorillonite clays as efficient catalyst for methylene blue dye degradation. Egypt. J. Pet. 25, 269–279 (2016)
R. Istratie, M. Stoia, C. Pacurariu, C. Locovei, Single and simultaneous adsorption of methyl orange and phenol onto magnetic iron oxide/carbon nano composites. Arab. J. Chem. 2, 1–19 (2016)
J. Rinku, S. Shripal, P. Hemant, Removal of Malachite green dye from Aqueous solution using magnetic activated carbon. Res. J. Chem. Sci. 5, 38–43 (2015)
M.H. Do, N.H. Phan, T.D. Nguyen, T.T.S. Phan, V.K. Nguyen, T.T. Trang, T.K.P. Nguyen, Activated carbon/Fe3O4 nanoparticle composite: fabrication, methyl orange removal and regeneration by hydrogen peroxide. Chemosphere 85, 1296–1276 (2011)
G. Wang, Y.M.Z. Wei, M. Qi, Development of multifunctional cobalt ferrite/graphene oxide nano composites for magnetic resonance imaging and controlled drug delivery. Chem. Eng. J. 289, 150–160 (2016)
W. Qiu, D. Yang, J. Xu, B. Hong, H. Jin, D. Jin, X. Peng, J. Li, H. Ge, X. Wang, Efficient removal of Cr(VI) by magnetically separable CoFe2O4/activated carbon composite. J. Alloys Compd. 678, 179–184 (2016)
F. Mehrabi, A. Vafaei, M. Ghaedi, A.M. Ghaedi, E.A. Dil, A. Asfaram, Ultrasound assisted extraction of Maxilon Red GRL dye from water samples using cobalt ferrite nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon as sorbent: optimization and modeling. Ultrason. Sonochem. 38, 672–680 (2017)
A. Almasian, F. Najafi, M. Mirjalili, M.P. Gashti, G.C. Fard, Zwitter ionic modification of cobalt-ferrite nano fiber for the removal of anionic and cationic dyes. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 67, 306–317 (2016)
P. Chitra, A. Muthusamy, S. Dineshkumar, R. Jayaprakash, J. Chandrasekar, Temperature and frequency dependence on electrical properties of polyaniline/Ni(1–x)CoxFe2O4 nano composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 384, 204–212 (2015)
E.R. Kumar, R. Jayaprakash, T. ArunKumar, S. Kumar, Effect of reaction time on particle size and dielectric properties of manganese substituted CoFe2O4 nano particles. J. Phys. Chem. Solid 74, 110–114 (2013)
T. Prakash, R. Jayaprakash, G. Neri, A comparative study of the synthesis of CdO nanoplatelets by an albumen-assisted isothermal evaporation method. J. Alloys Compd. 624, 258–265 (2015)
D. Chen, Z. Zeng, Y. Zeng, F. Zhang, M. Wang, Removal of methylene blue and mechanism on magnetic γ-Fe2O3/SiO2 nano composite from aqueous solution. Water Resour. Ind. 15, 1–13 (2016)
Y. Huang, W. Wang, Q. Feng, F. Dong, Preparation of magnetic clinoptilolite/CoFe2O4 composites for removal of Sr2+ from aqueous solutions: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 21, 58–66 (2017)
S. Sheshmani, B. Falahat, F.R. Nikmaram, Preparation of magnetic graphene oxide-ferrite nanocomposites for oxidative decomposition of Remazol Black B. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 97, 671–678 (2017)
P. Ganesan, R. Kamaraj, G. Sozhan, S. Vasudevan, Oxidized multiwall carbon nano tubes as adsorbent for the removal of manganese from aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 20, 987–996 (2013)
R. Kamaraj, P. Ganesan, S. Vasudevan, Removal of lead from aqueous solutions by electro coagulation: isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamic studies. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 12, 683–692 (2015)
S. Vasudevan, J. Lakshmi, Electrochemical removal of boron from water: adsorption and thermodynamic studies. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 90, 1017–1026 (2012)
R. Kamaraj, P. Ganesan, J. Lakshmi, S. Vasudevan, Removal of copper from water by electro coagulation process—effect of alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 20, 399–412 (2013)
N.P. Bhagya, P.A. Prashanth, R.S. Raveendra, S. Sathyanarayani, S. Ananda, B.M. Nagabhushana, H. Nagabhushana, Adsorption of hazardous cationic dye onto the combustion derived SrTiO3 nano particles: kinetic and isotherm studies. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 4, 68–74 (2016)
H.Y. Zhu, Y.Q. Fu, R. Jiang, J.H. Jiang, L. Xiao, G.M. Zeng, S.L. Zhao, Adsorption removal of congo red of magnetic cellulose/Fe3O4/activated carbon composite: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chem. Eng. J. 173, 494–502 (2011)
R. Jamal, L. Zhang, M. Wang, Q. Zhao, T. Abdiryim, Synthesis of poly(3,4-propylene dioxy thiophene)/MnO2 composites and their applications in the adsorptive removal of methylene blue. Progr. Nat. Sci. 26, 32–40 (2016)
M. Dargahi, H. Ghasemzadeh, A. Bakhtiary, Highly efficient absorption of cationic dyes by nano composite hydrogels based on κ-carrageenan and nano silver chloride. Carbohydr. Polym. 181, 587–595 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suba, V., Rathika, G., Ranjith Kumar, E. et al. Influence of Magnetic Nanoparticles on Surface Changes in CoFe2O4/Nerium Oleander Leaf Waste Activated Carbon Nanocomposite for Water Treatment. J Inorg Organomet Polym 28, 1706–1717 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-0831-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-0831-x