Abstract
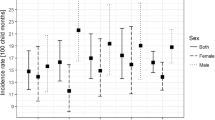
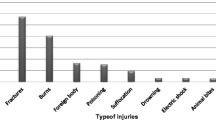
Injury is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in children aged 1–14 years, with home injuries a particular problem in the preschool-age group. The focus of this study was to determine the frequency, and the outcome of unintentional non-fatal injuries among children under 5 years of age in the household, and to describe the related risk factors through a community-based survey. A cross-sectional community based study was conducted on a random sample of 1,255 rural Egyptian children under 5 years of age. Data were collected by a questionnaire which included; socio-demographic data, history, type, and the outcome of unintentional home injuries in the previous year. Of 1,255 children, 55.9 % were males and 44.1 % were females, and their mean age was 28.6 ± 11.8 months. The frequency of unintentional non-fatal home-related injuries was 20.6 %. Injury rates were the highest among children during the third year of life, those of less educated parents, those whom mothers are of young age, and those with low household socioeconomic standard. Homes of injured children were not significantly different from the homes of non-injured children. Burns were the most common injuries among all the study groups (38 %) followed by falls (35.3 %). ‘Handicaps’ were more strongly associated with falls and burns (6.6 and 4.1 % respectively). Unintentional injuries are common among children under 5 years of age in rural Egypt. Therefore, measures should be taken to prevent children from the most frequently recorded home injuries such as burns and falls.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rivara, F, Grossman, D. (2000). Injury control. In Behrman RE, Kilegmann RM, Jenson HB (Eds.) Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 16th eds. Philadelphia; WB Saunders company: 231.
Paes, C., & Gaspar, V. (2005). Unintentional injuries in the home environment: Home safety. Jornal de Pediatria (Rio J), 81, 146–154.
Galal, S. (1999). Working with families to reduce the risk of home accidents in children. Eastern Mediterranean health journal, 5, 572–582.
Dal Santo, J., Goodman, R., Glik, D., & Jackson, K. (2004). Childhood unintentional injuries: Factors predicting injury risk among preschoolers. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 29, 273–283.
LeBlanc, J., Pless, I., King, W., et al. (2006). Home safety measures and the risk of unintentional injury among young children: A multicentre case-control study. Canadian Medical Association Journal, 175, 883–887.
WHO/WHD Brochure, Part IV. The priorities and solution for creating healthy places/unintentional injuries. http://www.who.int/world-health-day/2003/infomaterials/Brochure4/en/ [last Accessed 12 Jan 2009].
Tobin, M., Milligan, J., Shukla, R., et al. (2002). South Asian ethnicity and risk of childhood accidents: An ecological study at enumeration district level in Leicester. Journal of Public Health Medicine, 24(4), 313–466.
Pomerantz, W., Dowd, M., & Buncher, C. (2001). Relationship between socioeconomic factors and severe childhood injuries. Journal of Urban Health, 78(1), 141–151.
ICECI Coordination and Maintenance Group. International classification of external causes of injuries (ICECI), Version 1.2. Consumer Safety Institute, Amsterdam and AIHW National Injury Surveillance Unit, Adelaide; 2004. Retrieved August 23, 2004 from http://www.iceci.org.
Roberts, I., & Power, C. (1996). Does the decline in child injury mortality vary by social class? A comparison of class specific mortality in 1981 and 1991. BMJ, 313, 784–786.
Hyder, A., Sugerman, D., Puvanachandra, P., et al. (2009). Global childhood unintentional injury surveillance in four cities in developing countries: A pilot study. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 87, 345–352.
Bashour, H., & Kharouf, M. (2008). Community-based study of unintentional injuries among preschool children in Damascus. Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, 14(2), 398–405.
Erkal, S., & Safak, Ç. (2006). Determination of risks of home accidents for the 0–6 age group in the Tuzluçayir village clinic neighborhood. The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics, 48, 56–62.
Abd El-Aty, N., Moftah, F., Ibrahim, H., et al. (2005). Assessment of knowledge and practice of mothers towards home accidents among children under 6 years in Assiut governorate. Assiut University Bulletin for Environmental Research, 8(2), 11–28.
Rehmani, R. (2008). Childhood injuries seen at an emergency department. Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association, 58, 114–118.
Razzak, J., Luby, S., Laflamme, L., et al. (2004). Injuries among children in Karachi, Pakistan-what, where and how. Public Health, 118, 114–120.
Candan, Ö., Hatice Yildirim, S., Murat, B., et al. (2010). Home accidents and mothers measurements in preschool children. Anatolian. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 4(1), 15–21.
Dal Santo, J., Goodman, R., Glik, D., et al. (2004). Childhood unintentional injuries: Factors predicting injury risk among preschoolers. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 29, 273–283.
Hjern, A., Ringback-Weitoft, G., & Andersson, R. (2001). Socio-demographic risk factors for home-type injuries in Swedish infants and toddlers. Acta Paediatrica, 90, 61–68.
Wadsworth, J., Burnell, I., & Taylor, B. (2003). Family type and accidents in preschool children. Journal of epidemiology and Community Health, 37, 100–104.
Birken, C., & MacArthur, C. (2004). Socioeconomic status and injury risk in children. Paediatrics and child health, 9(5), 323–325.
LeBlanc, J., Pless, I., King, W., et al. (2006). Home safety measures and the risk of unintentional injury among young children: A multicentre case—control study. CMAJ, 175(8), 883–887.
Alptekin, F., Uskun, E., Kisioglu, A., et al. (2008). Unintentional non-fatal homerelated injuries in Central Anatolia, Turkey: frequencies, characteristics and outcomes. Injury, 39, 535–546.
Neghab, M., Rajaei, A., Habibi, M., et al. (2006). Home accidents in rural and urban areas of Shiraz, 2000–2002. Eastern Mediterranean health Journal, 12, 824–833.
Mack, K., & Liller, K. (2010). Home injuries: Potential for prevention. American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine, 4, 75–81.
Hyder, A., Wunderlich, C., Puvanachandra, P., et al. (2007). The impact of traumatic brain injuries: A global perspective. NeuroRehabilitation, 22(5), 341–353.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamal, N.N. Home Unintentional Non-fatal Injury Among Children Under 5 Years of Age in a Rural Area, El Minia Governorate, Egypt. J Community Health 38, 873–879 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10900-013-9692-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10900-013-9692-y