Abstract
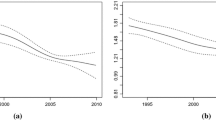
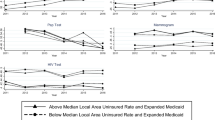
To use data from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) to examine trends in the lack of health insurance coverage among working-age US adults and to identify populations without coverage. The BRFSS data from 1993 to 2006 were analyzed. SUDAAN software was used to generate estimates of prevalence and corresponding standard errors, and logistic regression techniques were used to examine trends in the data. An estimated 18.59% of working adults (aged 18–64 years) did not have health insurance coverage in 2006. Trend in uninsurance remained somewhat stable from 1993 to 2000 (OR = 1.01; 95% CI 1.00–1.02); however, it changed more rapidly from 2001 to 2006 (OR = 1.03; 1.02–1.03). Similar patterns were observed from 2001 to 2006 for those <35 years of age, employed, Hispanics and those with less than or high school education. Effective approaches to reducing uninsurance and the consequences related to lack of coverage are needed in the face of increasing health disparities in the United States.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davidoff, A., & Kenney, G. M. (2005). Uninsured Americans with chronic health conditions: Key findings from the National Health Interview Survey. Princeton, NJ: Robert Wood Johnson Foundation.
Characteristics of the uninsured: A view from the States. (2005). Prepared for the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation by the State Health Access Data Assistance Center, University of Minnesota, using data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s 2003 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Survey (BRFSS), May 2005. Report available at http://www.shadac.org. Accessed 27 June 2006.
Powell-Griner, E., Bolen, J., & Bland, S. (1999). Health care coverage and use of preventive services among the near elderly in the United States. American Journal of Public Health, 89, 882–886.
Faulkner, L. A., & Schauffler, H. H. (1997). The effect of health insurance coverage on the appropriate use of recommended clinical preventive services. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 13, 453–458.
Cohen, R. A., & Martinez, M. E. (2007). Health insurance coverage: Early release of estimates from the National Health Interview Survey, January—March 2007. Available at www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhis.htm. Accessed 3 December 2007.
DeNavas-Walt, C., Proctor, B. D., & Lee, C. H. (2006). Income, poverty, and health insurance coverage in the United States: 2005. U.S. census bureau, current population reports. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office.
The uninsured: A primer—key facts about Americans without health insurance, October 2006. Available at www.kff.org. Accessed 13 November 2006.
Kenney, G., Holahan, J., & Nichols, L. (2006). Toward a more reliable federal survey for tracking health insurance coverage and access. Health Services Research, 41, 918–940.
Blewett, L. A., & Davern, M. (2006). Meeting the need for state-level estimates of health insurance coverage: use of state and federal survey data. Health Services Research, 41, 946–975.
Sheffet, A. M., Ridlen, S., & Louria, D. B. (2006). Baseline behavioral assessment for the New Jersey Health Wellness Promotion Act. American Journal of Health Promotion, 20, 401–410.
Nelson, D. E., Bolen, J., Wells, H. E., Smith, S. M., & Bland, S. (2004). State trends in uninsurance among persons aged 18–64, 1992–2001. American Journal of Public Health, 94, 1992–1997.
Nelson, D. E., Thompson, B. L., Davenport, N. J., & Penaloza, L. J. (2000). What people really know about their health insurance: A comparison of information obtained from individuals and their insurers. American Journal of Public Health, 90, 924–928.
Nelson, D. E., Holtzman, D., Bolen, J., Stanwyck, C. A., & Mack, K. A. (2001). Reliability and validity of measures from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS). Sozial- und Praventivmedizin, 46(Suppl 1), S3–S42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
OMB Disclaimer: The findings and conclusions in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the views of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahluwalia, I.B., Bolen, J. Lack of Health Insurance Coverage Among Working-age Adults, Evidence From the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, 1993–2006. J Community Health 33, 293–296 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10900-008-9106-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10900-008-9106-8