Abstract
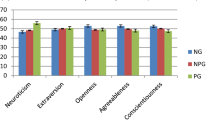
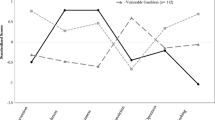
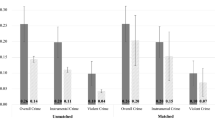
Research suggests that high frequency gambling is a component of the “generality of deviance”, which describes the observation that various forms of risky and antisocial behavior tend to co-occur among individuals. Furthermore, risky and antisocial behaviors have been associated with such personality traits as low self-control, and impulsivity, and sensation-seeking. We conducted a replication (and extension) of two previous studies examining whether high frequency gambling is part of the generality of deviance using a large and diverse community sample (n = 328). This study was conducted as a response to calls for more replication studies in the behavioral and psychological sciences (recent systematic efforts suggest that a significant proportion of psychology studies do not replicate). The results of the present study largely replicate those previously found, and in many cases, we observed stronger associations among measures of gambling, risk-taking, and antisocial behavior in this diverse sample. Together, this study provides evidence for the generality of deviance inclusive of gambling (and, some evidence for the replicability of research relating to gambling and individual differences).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arneklev, B. J., Grasmick, H. G., Tittle, C. R., & Bursik, R. J, Jr. (1993). Low self-control and imprudent behavior. Journal of Quantitative Criminology, 9, 225–247.
Bagby, R. M., Vachon, D. D., Bulmash, E., Toneatto, T., Quilty, L. C., & Costa, P. T. (2007). Pathological gambling and the five factor model of personality. Personality and Individual Differences, 43, 873–880.
Blais, A., & Weber, E. U. (2006). A domain-specific risk-taking (DOSPERT) scale for adult populations. Judgment and Decision Making, 1, 33–47.
Blaszczynski, A., & McConaghy, N. (1994). Antisocial personality disorder and pathological gambling. Journal of Gambling Studies, 10, 129–145.
Blaszczynski, A., McConaghy, N., & Frankova, A. (1989). Crime, antisocial personality and pathological gambling. Journal of Gambling Studies, 5, 137–152.
Blaszczynski, A., Steel, Z., & McConaghy, N. (1997). Impulsivity in pathological gambling: The antisocial impulsivist. Addiction, 92, 75–87.
Brase, G. L. (2009). How different types of participant payments alter task performance. Judgment and Decision Making, 4, 419–428.
Bromiley, P., & Curley, S. P. (1992). Individual differences in risk-taking. In J. F. Yates (Ed.), Risk taking behaviour (pp. 87–132). Chichester: Wiley.
Buss, A. H., & Perry, M. (1992). The aggression questionnaire. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 63, 452–459.
Camerer, C. F., & Hogarth, R. M. (1999). The effects of financial incentives in experiments: A review and capital-labor-production framework. Journal of Risk and Uncertainty, 19, 7–42.
Costa, P. T., & McRae, R. R. (1992). The revised NEO personality inventory (NEO-PI-R) and NEO five factor inventory (NEO-FFI) professional manual. Odessa, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources.
Donovan, J. E., & Jessor, R. (1985). Structure of problem behavior in adolescence and young adulthood. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 53, 890–904.
Ehrhart, M. G., Ehrhart, K. H., Roesch, S. C., Chung-Herrera, B. G., Nadler, K., & Bradshaw, K. (2009). Testing the latent factor structure and construct validity of the ten-item personality inventory. Personality and Individual Differences, 47, 900–905.
Eysenck, H. J., & Eysenck, M. W. (1985). Personality and individual differences: A natural science approach. New York: Plenum.
Eysenck, S. B. G., Pearson, P. R., Easting, G., & Allsopp, J. F. (1985). Age norms for impulsiveness, venturesomeness and empathy in adults. Personality and Individual Differences, 6, 613–619.
Farrington, D. P. (1995). Development of offending and antisocial behaviour from childhood: Key findings from the Cambridge Study in Delinquent Development. Journal of Child Psychology, 360, 929–964.
Ferrey, A. E., & Mishra, S. (2014). Compensation method affects risk-taking in the Balloon Analogue Risk Task. Personality and Individual Differences, 64, 111–114.
Ferris, J., & Wynne, H. (2001). The Canadian Problem Gambling Index: Final report (Submitted to the Canadian Centre on Substance Abuse). Ottawa, ON: Canadian Centre on Substance Abuse.
Fessler, D. M. T., Pillsworth, E. G., & Flamson, T. J. (2004). Angry men and disgusted women: An evolutionary approach to the influence of emotions on risk-taking. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 95, 107–123.
Friedman, M., & Savage, L. J. (1948). The utility analysis of choice involving risk. Journal of Political Economy, 56, 279–304.
Gneezy, U., & Rustichini, A. (2000). Pay enough or don’t pay at all. The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 115, 791–810.
Gomà-i-Freixanet, M. (1995). Prosocial and antisocial aspects of personality. Personality and Individual Differences, 19, 125–134.
Gomà-i-Freixanet, M. (2001). Prosocial and antisocial aspects of personality in women: A replication study. Personality and Individual Differences, 30, 1401–1411.
Gosling, S. D., Rentfrow, P. J., & Swann, W. B, Jr. (2003). A very brief measure of the Big-Five personality domains. Journal of Research in Personality, 37, 504–528.
Gottfredson, M. R., & Hirschi, T. (1990). A general theory of crime. Stanford: Stanford University Press.
Grasmick, H. J., Tittle, C. R., Bursik, R. J, Jr, & Arneklev, B. J. (1993). Testing the core empirical implications of Gottfredson and Hirschi’s general theory of crime. Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency, 30, 5–29.
Hanoch, Y., Johnson, J. G., & Wilke, A. (2006). Domain specificity in experimental measures and participant recruitment: An application to risk-taking behavior. Psychological Science, 17, 300–304.
Harris, G. T., Rice, M. E., & Quinsey, V. L. (1994). Psychopathy as a taxon: Evidence that psychopaths are a discrete class. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 62, 387–397.
Hirschi, T., & Gottfredson, M. R. (1994). The generality of deviance. In T. Hirschi & M. R. Gottfredson (Eds.), The generality of deviance. New Brunswick, NJ: Transaction Publishers.
Jones, S., & Quisenberry, N. (2004). The general theory of crime: How general is it? Deviant Behavior, 25, 401–426.
Junger, M., & Tremblay, R. E. (1999). Self-control, accidents and crime. Criminal Justice and Behavior, 26, 485–501.
Lalumière, M. L., Harris, G. T., Quinsey, V. L., & Rice, M. E. (2005). The causes of rape: Understanding individual differences in male propensity of sexual aggression. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Lalumière, M. L., & Quinsey, V. L. (1996). Sexual deviance, antisociality, mating effort, and the use of sexually coercive behaviors. Personality and Individual Differences, 21, 33–48.
Lejuez, C. W., Read, J. P., Wahler, C. W., Richards, J. B., Ramsey, S. E., Stuart, G. L., et al. (2002). Evaluation of a behavioral measure of risk-taking: The Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART). Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied, 8, 75–84.
Levenson, M. R. (1990). Risk taking and personality. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 58, 1073–1080.
Levenson, M. R., Kiehl, K. A., & Fitzpatrick, C. M. (1995). Assessing psychopathic attributes in a noninstitutionalized population. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 68, 151–158.
Lynam, D. R., Whiteside, S., & Jones, S. (1999). Self-reported psychopathy: A validation study. Journal of Personality Assessment, 73, 110–132.
MacLaren, V. V., Best, L. A., Dixon, M. J., & Harrigan, K. A. (2011). Problem gambling and the five factor model in university students. Personality and Individual Differences, 50, 335–338.
Marcus, B. (2003). An empirical examination of the construct validity of two alternative self-control measures. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 63, 674–706.
Miller, J. D., MacKillop, J., Fortune, E. E., Maples, J., Lance, C. E., Campbell, W. K., & Goodie, A. S. (2013). Personality correlates of pathological gambling derived from Big Three and Big Five personality models. Psychiatry Research, 206, 50–55.
Mishra, S. (2014). Decision-making under risk: Integrating perspectives from biology, economics, and psychology. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 18, 280–307.
Mishra, S., Barclay, P., & Sparks, A. (in press). The relative state model: Integrating need-based and ability-based pathways to risk-taking. Personality and Social Psychology Review.
Mishra, S., & Carleton, R. N. (2015). Subjective relative deprivation is associated with poorer physical and mental health. Social Science and Medicine, 147, 144–149.
Mishra, S., & Lalumière, M. L. (2009). Is the crime drop of the 1990s in Canada and the USA associated with a general decline in risky and health-related behaviors? Social Science and Medicine, 68, 39–48.
Mishra, S., & Lalumière, M. L. (2010). You can’t always get what you want: The motivational effect of need on risk-sensitive decision-making. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 46, 605–611.
Mishra, S., Lalumière, M. L., Morgan, M., & Williams, R. J. (2011a). An examination of the relationship between gambling and antisocial behavior. Journal of Gambling Studies, 27, 409–426.
Mishra, S., Lalumière, M. L., & Williams, R. J. (2010a). Gambling as a form of risk-taking: Individual differences in personality, risk-accepting attitudes, and behavioral preferences for risk. Personality and Individual Differences, 49, 616–621.
Mishra, S., Logue, D. M., Abiola, I. O., & Cade, W. H. (2011b). Developmental environment affects risk-acceptance in the hissing cockroach, Gromphadorhina portentosa. Journal of Comparative Psychology, 125, 40–47.
Mishra, S., Morgan, M., Lalumière, M. L., & Williams, R. J. (2010b). Mood and audience effects on video lottery terminal gambling. Journal of Gambling Studies, 26, 373–386.
Mishra, S., & Novakowski, D. (2016). Personal relative deprivation and risk: An examination of individual differences in personality, attitudes, and behavioral outcomes. Personality and Individual Differences, 90, 22–26.
Moffitt, T. E., Arsenault, L., Belsky, D., Dickson, N., Hancox, R. J., & Caspi, A. (2011). A gradient of childhood self-control predicts health, wealth, and public safety. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 108, 2693–2698.
Moffitt, T. E., Caspi, A., Harrington, H., & Milne, B. J. (2002). Males on the life-course-persistent and adolescence-limited antisocial pathways: Follow-up at age 26 years. Development and Psychopathology, 1, 179–207.
Moffitt, T. E., & Silva, P. A. (1988). Self-reported delinquency: Results from an instrument for New Zealand. Australia and New Zealand Journal of Criminology, 21, 227–240.
Open Science Collaboration. (2015). Estimating the reproducibility of psychological science. Science, 349, 943–951.
Orford, J., Wardle, H., Griffiths, M., Sproston, K., & Erens, B. (2010). PGSI and DSM-IV in the 2007 British Gambling Prevalence Survey: Reliability, item response, factor structure, and inter-scale agreement. International Gambling Studies, 10, 31–44.
Osgood, D. W., Johnston, L. D., O’Malley, P. M., & Bachman, J. G. (1988). The generality of deviance in late adolescence and early adulthood. American Sociological Review, 53, 81–93.
Pashler, H., & Wagenmakers, E. (2012). Editor’s introduction to the special section on replicability in psychological science: A crisis of confidence? Perspectives on Psychological Science, 7, 528–530.
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Lee, J.-Y., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88, 879–903.
Pratt, J. W. (1964). Risk aversion in the small and in the large. Econometrica, 32, 122–136.
Rode, C., Cosmides, L., Hell, W., & Tooby, J. (1999). When and why do people avoid unknown probabilities in decisions under uncertainty? Testing some predictions from optimal foraging theory. Cognition, 72, 269–304.
Simonsohn, U. (2015). Small telescopes: Detectability and the evaluation of replication results. Psychological Science, 26, 559–569.
Slovic, P. (1964). Assessment of risk taking behavior. Psychological Bulletin, 61, 330–333.
Smith, G., Wynne, H., & Hartnagel, T. (2003). Examining police records to assess gambling impacts: A study of gambling-related crime in the city of Edmonton. Edmonton, Canada: Alberta Gaming Research Institute.
Stinchfield, R. (2004). Demographic, psychosocial, and behavioural factors associated with youth gambling and problem gambling. In J. L. Derevensky & R. Gupta (Eds.), Gambling problems in youth: Theoretical and applied perspectives. New York: Kluwer.
Stinchfield, R., McCready, J., Turner, N. E., Jiminez-Murcia, S., Petry, N. M., Grant, J., et al. (in press). Reliability, validity, and classification accuracy of the DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for gambling disorder and comparison to DSM-IV. Journal of Gambling Studies.
Toneatto, T., & Nguyen, L. (2007). Individual characteristics and problem gambling behavior. In G. Smith, D. C. Hodgins, & R. J. Williams (Eds.), Research and measurement Issues in gambling studies (pp. 279–303). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Turner, N. E., Preston, D. L., McAvoy, S., & Saunders, C. (2007). Problem gambling in Canadian federal offenders: Prevalence, comorbidity, and correlates (Submitted to the Ontario Problem Gambling Research Centre). Guelph, ON: Ontario Problem Gambling Research Centre.
Vitaro, F., Brendgen, M., Ladouceur, R., & Tremblay, R. E. (2001). Gambling, delinquency, and drug use during adolescence: Mutual influences and common risk factors. Journal of Gambling Studies, 17, 171–190.
Williams, R. J., Royston, J., & Hagen, B. F. (2005). Gambling and problem gambling within forensic populations: A review of literature. Criminal Justice and Behavior, 32, 665–689.
Williams, R. J., & Volberg, R. A. (2014). Classification accurancy of four problem gambling assessment instruments. International Gambling Studies, 14, 15–28.
Wood, A. P., Dawe, S., & Gullo, M. J. (2013). The role of personality, family influences, and prosocial risk-taking behavior on substance use in early adolescence. Journal of Adolescence, 36, 871–881.
Zuckerman, M. (1994). Behavioural expressions and biosocial bases of sensation-seeking. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Zuckerman, M. (2007). Sensation seeking and risky behavior. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a research grants and fellowships from the Ontario Problem Gambling Research Centre and the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada. The authors would like to thank Thomas Fox, Sara Kafashan, Lindsay Kleiner, Christine Mishra, and Alix Shriner for their help with data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, S., Lalumière, M.L. & Williams, R.J. Gambling, Risk-Taking, and Antisocial Behavior: A Replication Study Supporting the Generality of Deviance. J Gambl Stud 33, 15–36 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10899-016-9608-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10899-016-9608-8