Abstract
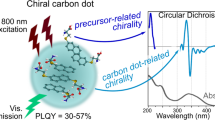
Chiral carbon quantum dots (cCQDs) , as a new type of carbon nano-functional material with tunable emission wavelength, superior photostability, low toxicity, biocompatibility and chirality, are playing an increasingly important role in the fields of chemistry, biology and medicine. This paper reviews the preparation methods (one-step and two-step), optical properties (UV, fluorescence, chirality) and applications in chiral catalysis, chiral recognition, targeted imaging as well as other fields, while lists some of the issues and challenges in the research of chiral carbon quantum dots. Finally, due to its good fluorescence and other properties, it is expected that chiral carbon quantum dots will have broad commercial prospects in future applications.











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
Not applicable.
References
Petitjean M (2020) Chirality in metric spaces. Optim Lett 14:329–338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-017-1189-7
Zhao D, Xu M, Dai K, Liu H, Jiao Y, Xiao X (2023) The preparation of chiral carbon dots and the study on their antibacterial abilities. Mater Chem Phys 295:127144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.127144
Hou X, Song J, Wu Q, Lv H (2021) Chiral carbon quantum dots as fluorescent probe for rapid chiral recognition of isoleucine enantiomers. Anal Chim Acta 1184 (2021) 339012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.339012
Milton FP, Govan J, Mukhina MV, Gun'ko YK (2015) The chiral nano-world: chiroptically active quantum nanostructures. Nanoscale Horiz 1:14–26. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NH00072F
Wang S, Li R, Zhang C, Li Y, Li B, Yang Y (2013) Formation and asymmetric catalysis of C- and 8-shaped titania tubes. Mater Lett 106:71–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2013.05.009
Shahshahanipour M, Rezaei B, Ensafi AA, Etemadifar Z (2019) An ancient plant for the synthesis of a novel carbon dot and its applications as an antibacterial agent and probe for sensing of an anti-cancer drug. Mater Sci Eng C 98:826–833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.01.041
Hallaji Z, Bagheri Z, Ranjbar B (2023) One-Step Solvothermal Synthesis of Red Chiral Carbon Dots for Multioptical Detection of Water in Organic Solvents. ACS Appl Nano Mater 6:3202–3210. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.2c04466
Das P, Ganguly S, Saha A, Noked M, Margel S, Gedanken A (2021) Carbon-Dots-Initiated Photopolymerization: An In Situ Synthetic Approach for MXene/Poly(norepinephrine)/Copper Hybrid and its Application for Mitigating Water Pollution. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13:31038–31050. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c08111
Fang Q, Dong Y, Chen Y, Lu C-H, Chi Y, Yang H-H, Yu T (2017) Luminescence origin of carbon based dots obtained from citric acid and amino group-containing molecules. Carbon 118:319–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2017.03.061
Malishev R, Arad E, Bhunia SK, Shaham-Niv S, Kolusheva S, Gazit E, Jelinek R (2018) Chiral modulation of amyloid beta fibrillation and cytotoxicity by enantiomeric carbon dots. Chem Commun 54:7762–7765. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8CC03235A
Dong Y, Wang R, Li H, Shao J, Chi Y, Lin X, Chen G (2012) Polyamine-functionalized carbon quantum dots for chemical sensing. Carbon 50:2810–2815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2012.02.046
Rajendran S, Zichri SB, Usha Vipinachandran V, Jelinek R, Bhunia SK (2021) Bhunia, Triphenylphosphonium-Derived Bright Green Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Mitochondrial Targeting and Rapid Selective Detection of Tetracycline. ChemNanoMat 7:545–552. https://doi.org/10.1002/cnma.202100125
Qiao Z-A, Wang Y, Gao Y, Li H, Dai T, Liu Y, Huo Q (2009) Commercially activated carbon as the source for producing multicolor photoluminescent carbon dots by chemical oxidation. Chem Commun 46:8812–8814. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC02724C
Wang Y, Li X, Zhao S, Wang B, Song X, Xiao J, Lan M (2022) Synthesis strategies, luminescence mechanisms, and biomedical applications of near-infrared fluorescent carbon dots. Coord Chem Rev 470:214703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2022.214703
Kumar J, Thomas KG, Liz-Marzán LM (2016) Nanoscale chirality in metal and semiconductor nanoparticles. Chem Commun 52:12555–12569. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC05613J
Lim SY, Shen W, Gao Z (2014) Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem Soc Rev 44:362–381. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00269E
Arad E, Bhunia SK, Jopp J, Kolusheva S, Rapaport H, Jelinek R (2018) Lysine-Derived Carbon Dots for Chiral Inhibition of Prion Peptide Fibril Assembly. Adv Ther 1:1800006. https://doi.org/10.1002/adtp.201800006
Li H, Kong W, Liu J, Liu N, Huang H, Liu Y, Kang Z (2015) Fluorescent N-doped carbon dots for both cellular imaging and highly-sensitive catechol detection. Carbon 91:66–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2015.04.032
Ghosal K, Ghosh A (2019) Carbon dots: The next generation platform for biomedical applications. Materi Sci Eng C 96:887–903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2018.11.060
Zhang Y, Hu L, Sun Y, Zhu C, Li R, Liu N, Huang H, Liu Y, Huang C, Kang Z (2016) One-step synthesis of chiral carbon quantum dots and their enantioselective recognition. RSC Adv 6:59956–59960. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA12420H
Wang C, Wu E, Wu X, Xu X, Zhang G, Pu L (2015) Enantioselective Fluorescent Recognition in the Fluorous Phase: Enhanced Reactivity and Expanded Chiral Recognition. J Am Chem Soc 137:3747–3750. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja512569m
Wei Y, Chen L, Wang J, Liu X, Yang Y, Yu S (2019) Investigation on the chirality mechanism of chiral carbon quantum dots derived from tryptophan. RSC Adv 9:3208–3214. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA09649J
Milton FP, Govan J, Mukhina MV, Gun'ko YK (2016) The chiral nano-world: chiroptically active quantum nanostructures. Nanoscale Horiz 1:14–26. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NH00072F
Tao S, Feng T, Zheng C, Zhu S, Yang B (2019) Carbonized Polymer Dots: A Brand New Perspective to Recognize Luminescent Carbon-Based Nanomaterials. J Phys Chem Lett 10:5182–5188. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.9b01384
Rao X, Yuan M, Jiang H, Li L, Liu Z (2019) A universal strategy to obtain chiroptical carbon quantum dots through the optically active surface passivation procedure. New J Chem 43:13735–13740. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NJ03434J
Ru Y, Ai L, Jia T, Liu X, Lu S, Tang Z, Yang B (2020) Recent advances in chiral carbonized polymer dots: From synthesis and properties to applications. Nano Today 34:100953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2020.100953
Sun D, Ban R, Zhang P-H, Wu G-H, Zhang J-R, Zhu J-J (2013) Hair fiber as a precursor for synthesizing of sulfur- and nitrogen-co-doped carbon dots with tunable luminescence properties. Carbon 64:424–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2013.07.095
Chen W, Bian A, Agarwal A, Liu L, Shen H, Wang L, Xu C, Kotov NA (2009) Nanoparticle Superstructures Made by Polymerase Chain Reaction: Collective Interactions of Nanoparticles and a New Principle for Chiral Materials. Nano Lett 9:2153–2159. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl900726s
Wang R-Y, Wang H, Wu X, Ji Y, Wang P, Qu Y, Chung T-S (2011) Chiral assembly of gold nanorods with collective plasmonic circular dichroism response. Soft Matter 7:8370–8375. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1SM05590A
Vázquez-Nakagawa M, Rodríguez-Pérez L, Herranz MA, Martín N (2016) Chirality transfer from graphene quantum dots. Chem Commun 52:665–668. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CC08890A
Li RS, Gao PF, Zhang HZ, Zheng LL, Li CM, Wang J, Li YF, Liu F, Li N, Huang CZ (2017) Chiral nanoprobes for targeting and long-term imaging of the Golgi apparatus. Chem Sci 8:6829–6835. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC01316G
Copur F, Bekar N, Zor E, Alpaydin S, Bingol H (2019) Nanopaper-based photoluminescent enantioselective sensing of L-Lysine by L-Cysteine modified carbon quantum dots. Sens Actuators B Chem 279:305–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.10.026
Yan X, Zhao H, Zhang K, Zhang Z, Chen Y, Feng L (2023) Chiral Carbon Dots: Synthesis and Applications in Circularly Polarized Luminescence, Biosensing and Biology. ChemPlusChem 88:e202200428. https://doi.org/10.1002/cplu.202200428
Visheratina A, Hesami L, Wilson AK, Baalbaki N, Noginova N, Noginov MA, Kotov NA (2022) Hydrothermal synthesis of chiral carbon dots. Chirality 34:1503–1514. https://doi.org/10.1002/chir.23509
Li F, Li Y, Yang X, Han X, Jiao Y, Wei T, Yang D, Xu H, Nie G (2018) Highly Fluorescent Chiral N-S-Doped Carbon Dots from Cysteine: Affecting Cellular Energy Metabolism. Angew Chem Int Ed 57:2377–2382. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201712453
Yang Y, Wang Q, Li G, Guo W, Yang Z, Liu H, Deng X (2023) Cysteine-Derived Chiral Carbon Quantum Dots: A Fibrinolytic Activity Regulator for Plasmin to Target the Human Islet Amyloid Polypeptide for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 15:2617–2629. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c17975
Gao P, Xie Z, Zheng M (2020) Chiral carbon dots-based nanosensors for Sn(II) detection and lysine enantiomers recognition. Sens Actuators B Chem 319:128265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128265
Ostadhossein F, Vulugundam G, Misra SK, Srivastava I, Pan D (2018) Chirality Inversion on the Carbon Dot Surface via Covalent Surface Conjugation of Cyclic α-Amino Acid Capping Agents. Bioconjugate Chem 29:3913–3922. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.8b00736
Ming H, Ma Z, Liu Y, Pan K, Yu H, Wang F, Kang Z (2012) Large scale electrochemical synthesis of high quality carbon nanodots and their photocatalytic property. Dalton Trans 41:9526–9531. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2DT30985H
Zhang M, Wang H, Wang B, Ma Y, Huang H, Liu Y, Shao M, Yao B, Kang Z (2019) Maltase Decorated by Chiral Carbon Dots with Inhibited Enzyme Activity for Glucose Level Control. Small 15:1901512. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201901512
Hu L, Li H, Liu C, Song Y, Zhang M, Huang H, Liu Y, Kang Z (2018) Chiral evolution of carbon dots and the tuning of laccase activity. Nanoscale 10:2333–2340. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NR08335A
Li L, Zhang D, Deng J, Kang Q, Liu Z, Fang J, Gou Y (2020) Review—Progress of Research on the preparation of graphene oxide via electrochemical approaches. J Electrochem Soc 167:155519. https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/abbbc0
Chekini M, Prince E, Zhao L, Mundoor H, Smalyukh II, Kumacheva E (2020) Chiral Carbon Dots Synthesized on Cellulose Nanocrystals. Adv Opt Mater 8:1901911. https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.201901911
Xiong R, Yu S, Smith MJ, Zhou J, Krecker M, Zhang L, Nepal D, Bunning TJ, Tsukruk VV (2019) Self-Assembly of Emissive Nanocellulose/Quantum Dot Nanostructures for Chiral Fluorescent Materials. ACS Nano 13:9074–9081. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b03305
Liu X, Lu J, Chen J, Zhang M, Chen Y, Xing F, Feng L (2020) Chiral Self-Assembly of Porphyrins Induced by Chiral Carbon Dots. Front Chem 8:670. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.00670
Vázquez-Nakagawa M, Rodríguez-Pérez L, Herranz MA, Martín N (2015) Chirality transfer from graphene quantum dots. Chem Commun 52:665–668. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CC08890A
Yuan M, Guo Y, Wei J, Li J, Long T, Liu Z (2017) Optically active blue-emitting carbon dots to specifically target the Golgi apparatus. RSC Adv 7:49931–49936. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA09271G
Ru Y, Sui L, Song H, Liu X, Tang Z, Zang S, Yang B, Lu S (2021) Rational Design of Multicolor-Emitting Chiral Carbonized Polymer Dots for Full-Color and White Circularly Polarized Luminescence. Angew Chem Int Ed 60:14091–14099. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202103336
Ru Y, Zhang B, Yong X, Sui L, Yu J, Song H, Lu S (2023) Full-Color Circularly Polarized Luminescence of CsPbX 3 Nanocrystals Triggered by Chiral Carbon Dots. Adv Mater 35:2207265. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202207265
Zhou S, Bian J, Chen P, Xie M, Chao J, Hu W, Lu Y, Zhang W (2022) Polarization-dispersive imaging spectrometer for scattering circular dichroism spectroscopy of single chiral nanostructures. Light Sci Appl 11:64. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-022-00755-2
Yang S, Li Y, Chen L, Wang H, Shang L, He P, Dong H, Wang G, Ding G (n.d) (2023) Fabrication of Carbon-Based Quantum Dots via a “Bottom-Up” Approach: Topology, Chirality, and Free Radical Processes in “Building Blocks,” Small 2205957. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202205957
Döring A, Ushakova E, Rogach AL (2022) Chiral carbon dots: synthesis, optical properties, and emerging applications. Light Sci Appl 11:75. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-022-00764-1
Gogoi A, Mazumder N, Konwer S, Ranawat H, Chen N-T, Zhuo G-Y (2019) Enantiomeric Recognition and Separation by Chiral Nanoparticles. Molecules 24:1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061007
Wei YY, Chen L, Zhang X, Du JL, Li Q, Luo J, Liu XG, Yang YZ, Yu SP, Gao YD (2022) Orange-emissive carbon quantum dots for ligand-directed Golgi apparatus-targeting and in vivo imaging. Biomater Sci 10:4345–4355. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2BM00429A
Zhang M, Hu L, Wang H, Song Y, Liu Y, Li H, Shao M, Huang H, Kang Z (2018) One-step hydrothermal synthesis of chiral carbon dots and their effects on mung bean plant growth. Nanoscale 10:12734–12742. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NR01644E
Zhou L, Zheng D, Wu B, Zhu Y, Zhu L (2020) Gel Systems Doped with Chiral Carbon Dots for Optical Combination. ACS Appl Nano Mater 3:946–952. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.9b01677
Funding
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (21375117) and a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiang Li and Xiashi Zhu wrote the main manuscript text; Xiang Li and Yujian Sun prepared figures. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., YujuanSun & Zhu, X. Preparation of Chiral Carbon Quantum Dots and its Application. J Fluoresc 34, 1–13 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-023-03262-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-023-03262-8