Abstract
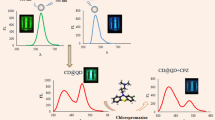
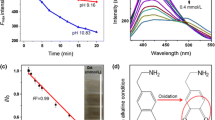
Epirubicin (EPI) is one of the standard anticancer drugs that apply for various cancers treatment. However, the accumulation of EPI in the human body can be highly toxic, and it causes inevitable harm to organs. As a result, the evaluation of low concentrations of this drug in body samples requires sensitive, rapid, and accurate analysis methods. The fluorescence method is an efficient way in comparison of the traditional methods such as liquid chromatography, capillary electrophoresis, and electrochemical methods. Herein, we synthesized a novel fluorescence nanosensor named CMC-CdTe/ZnS based on using quantum dots (QDs). The structure of the prepared nanosensor is confirmed by different analysis methods such as FT-IR, TGA, and TEM. Besides that, the fluorescence intensity response of CMC-CdTe/ZnS QDs in the presence of Epirubicin drug is investigated. Based on obtained results, not only this nanosensor developed, but also the fluorescence quenching was explained by the typical Stern–Volmer equation. The best linear quenching equation for entitled nanosensor in the presence of Epirubicin is F0/F = 0.0346Q + 1.08 (R2 = 0.99), and the detection limit of Epirubicin is around 0.04 × 10−6 mol/L at 25 °C. All of the results display that this method could be reliable and suitable approach for determination of Epirubicin in commercial samples as well.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Medical News Today (2018) Cancer. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/323648. Accessed 6 Jan 2020
WHO (2018) Cancer. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer. Accessed 6 Sept 2020
DeVita VT, Chu E (2008) A history of cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Res 68(21):8643–8653
Compton C (2020) A short history of cancer: how did we get Here? In: Cancer: the enemy from within. Springer, pp 83-107
Rouge-Bugat M-E, Lassoued D, Bacrie J, Boussier N, Delord J-P, Oustric S, Bauvin E, Lapeyre-Mestre M, Bertucci F, Grosclaude P (2015) Supportive care in cancer. Support Care Cancer 23(12):3473–3480
Kamil N, Kamil S, Ahmed SP, Ashraf R, Khurram M, Ali MO (2010) Toxic effects of multiple anticancer drugs on skin. Pak J Pharm Sci 23(1):7–14
Nielsen D, Jensen J, Dombernowsky P, Munck O, Fogh J, Brynjolf I, Havsteen H, Hansen M (1990) Epirubicin cardiotoxicity: a study of 135 patients with advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 8(11):1806–1810
Miyayama S, Yamashiro M, Shibata Y, Hashimoto M, Yoshida M, Tsuji K, Toshima F, Matsui O (2012) Comparison of local control effects of superselective transcatheter arterial chemoembolization using epirubicin plus mitomycin C and miriplatin for hepatocellular carcinoma. Jpn J Radiol 30(3):263–270
Plosker GL, Faulds D (1993) Epirubicin. Drugs 45(5):788–856
Chida T, Miura Y, Cabral H, Nomoto T, Kataoka K, Nishiyama N (2018) Epirubicin-loaded polymeric micelles effectively treat axillary lymph nodes metastasis of breast cancer through selective accumulation and pH-triggered drug release. J Control Release 292:130–140
Sottani C, Rinaldi P, Leoni E, Poggi G, Teragni C, Delmonte A, Minoia C (2008) Simultaneous determination of cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide, doxorubicin, epirubicin and daunorubicin in human urine using high-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry: bioanalytical method validation. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry: An International Journal Devoted to the Rapid Dissemination of Up-to-the-Minute Research in Mass Spectrometry 22 (17):2645–2659
Ali I, Haque A, Wani WA, Saleem K, Al Za'abi M (2013) Analyses of anticancer drugs by capillary electrophoresis: a review. Biomed Chromatogr 27(10):1296–1311
Wang Y, Xie J, Tao L, Tian H, Wang S, Ding H (2014) Simultaneous electrochemical determination of epirubicin and methotrexate in human blood using a disposable electrode modified with nano-au/MWNTs-ZnO composites. Sens Actuators B: Chem 204:360–367
Gong P, Sun L, Wang F, Liu X, Yan Z, Wang M, Zhang L, Tian Z, Liu Z, You J (2019) Highly fluorescent N-doped carbon dots with two-photon emission for ultrasensitive detection of tumor marker and visual monitor anticancer drug loading and delivery. Chem Eng J 356:994–1002
Ong JX, Ang WH (2020) Development of a pre-assembled through-bond energy transfer (TBET) fluorescent probe for Ratiometric sensing of anticancer platinum (ll) complexes. Chem–Asian J 15(9):1449–1455
Mo J, Shen L, Xu Q, Zeng J, Sha J, Hu T, Bi K, Chen Y (2019) An Nd3+-sensitized Upconversion fluorescent sensor for Epirubicin detection. Nanomaterials 9(12):1700
Hu J, Wang R, Fan R, Huang Z, Liu Y, Guo G, Fu H (2020) Enhanced luminescence in Yb3+ doped core-shell upconversion nanoparticles for sensitive doxorubicin detection. J Lumin 217:116812
Mi G, Shi H, Yang M, Wang C, Hao H, Fan J (2020) Efficient detection doxorubicin hydrochloride using CuInSe2@ ZnS quantum dots and Ag nanoparticles. Spectrochim Acta A: Mol Biomol Spectrosc 241:118673
Wei J-R, Chen H-Y, Zhang W, Pan J-X, Dang F-Q, Zhang Z-Q, Zhang J (2017) Ratiometric fluorescence for sensitive and selective detection of mitoxantrone using a MIP@ rQDs@ SiO2 fluorescence probe. Sens Actuators B: Chem 244:31–37
Jiang X, Feng D-Q, Liu G, Fan D, Wang W (2016) A fluorescent switch sensor for detection of anticancer drug and ctDNA based on the glutathione stabilized gold nanoclusters. Sens Actuators B: Che 232:276–282
Vasudevan D, Gaddam RR, Trinchi A, Cole I (2015) Core–shell quantum dots: properties and applications. J Alloys Compd 636:395–404
Bardajee GR, Zamani M, Sharifi M, Mahmoodian H (2020) Preparation of novel fluorescence Nanosensor κC-CdTe/ZnS quantum dots for high accurate detection of Epirubicin. Materials Today communications 101874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101874 (in press)
Zhang LM (2001) New water-soluble cellulosic polymers: a review. Macromol Mater Eng 286(5):267–275
Benchabane A, Bekkour K (2008) Rheological properties of carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) solutions. Colloid Polym Sci 286(10):1173–1180
Elmizadeh H, Soleimani M, Faridbod F, Bardajee GR (2018) Fabrication and optimization of a sensitive tetracycline fluorescent nano-sensor based on oxidized starch polysaccharide biopolymer-capped CdTe/ZnS quantum dots: box–Behnken design. J Photochem Photobiol A: Chem 367:188–199
Roshan KR, Mathai G, Kim J, Tharun J, Park G-A, Park D-W (2012) A biopolymer mediated efficient synthesis of cyclic carbonates from epoxides and carbon dioxide. Green Chem 14(10):2933–2940
Hooshyar Z, Bardajee GR (2017) Fluorescence enhancement of glutathione capped CdTe/ZnS quantum dots by embedding into cationic starch for sensitive detection of rifampicin. Spectrochim Acta A: Mol Biomol Spectrosc 173:144–150
Segets D, Lucas JM, Klupp Taylor RN, Scheele M, Zheng H, Alivisatos AP, Peukert W (2012) Determination of the quantum dot band gap dependence on particle size from optical absorbance and transmission electron microscopy measurements. ACS Nano 6(10):9021–9032
El-Hagary M, Shaaban E, Moustafa S, Gad G (2019) The particle size-dependent optical band gap and magnetic properties of Fe-doped CeO2 nanoparticles. Solid State Sci 91:15–22
Rezanejade Bardajee G, Hooshyar Z, Rezanezhad H, Guerin G, interfaces (2012) Optical properties of water-soluble CdTe quantum dots passivated by a biopolymer based on poly ((2-dimethylaminoethyl) methacrylate) grafted onto κ-carrageenan. ACS appl mater 4(7):3517–3525
Zhang Y, Zhang H, Hollins J, Webb ME, Zhou D (2011) Small-molecule ligands strongly affect the Förster resonance energy transfer between a quantum dot and a fluorescent protein. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13(43):19427–19436
Riaz T, Zeeshan R, Zarif F, Ilyas K, Muhammad N, Safi SZ, Rahim A, Rizvi SA, Rehman IU (2018) FTIR analysis of natural and synthetic collagen. Appl Spectrosc Rev 53(9):703–746
Adegoke O, Khene S, Nyokong T (2013) Fluorescence “switch on” of conjugates of CdTe@ ZnS quantum dots with Al, Ni and Zn tetraamino-phthalocyanines by hydrogen peroxide: characterization and applications as luminescent nanosensors. J Fluoresc 23(5):963–974
Rani MSA, Rudhziah S, Ahmad A, Mohamed NS (2014) Biopolymer electrolyte based on derivatives of cellulose from kenaf bast fiber. Polymers 6(9):2371–2385
Zu F, Yan F, Bai Z, Xu J, Wang Y, Huang Y, Zhou X (2017) The quenching of the fluorescence of carbon dots: a review on mechanisms and applications. Microchim Acta 184(7):1899–1914
Fraiji LK, Hayes DM, Werner T (1992) Static and dynamic fluorescence quenching experiments for the physical chemistry laboratory. J Chem Educ 69(5):424
Funding
The authors are grateful to PNU (Contract Numbe: 46384) and INSF for financial support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ghasem Rezanejade Bardajee: Conceptualization; Data curation; Formal analysis; Funding acquisition; Project administration; Resources; Supervision; Validation; Writing – review & editing.
Mahdieh Sharifi: Methodology; Validation; Investigation; Writing – review & editing.
Hossein Mahmoodian: Methodology; Validation; Investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bardajee, G.R., Sharifi, M. & Mahmoodian, H. Novel CMC-CdTe / ZnS QDs Nanosensor for the Detection of Anticancer Drug Epirubicin. J Fluoresc 31, 651–658 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-021-02687-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-021-02687-3