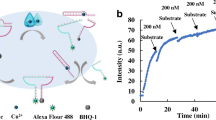
Abstract
A label -free DNAzyme amplified biosensor is found to be highly selective and sensitive towards fluorescent detection of Pb2+ ions in aqueous media. The DNAzyme complex has designed by the hybridization of the enzyme and substrate strand. In the presence of Pb2+, the DNAzyme activated and cleaved the substrate strand of RNA site (rA) into two oligonucleotide fragments. Further, the free fragment was hybridized with a complementary strand on the surface of MBs. After magnetic separation, SYBER Green I was added and readily intercalate with the dsDNA to gives a bright fluorescence signal with intensity directly proportional to the concentration of Pb2+ions. A detection limit of 5 nM in Pb2+ the detection range 0 to 500 nM was obtained. This label- free fluorescent biosensor has been successfully applied to the determination of environmental water samples. Then results open up the possibility for real-time quantitative detection of Pb2+ with convenient potential applications in the biological and environmental field.

Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Panich S, Wilson KA, Nuttall P, Wood CK, Albrecht T, Edel EB (2004) Label–free Pb(II) whispering gallery mode sensing using self-assembled glutathione-modified gold nanoparticles on an optical micro cavity. Anal Chem 86(23):6299–6306
Nolan EM, Lippard SJ (2009) Small – molecule fluorescent sensors for investigating zinc metallonuerochemistry. Acc Chem Res 42(1):193–203
Xiang Y, Tong A, Lu Y (2009) Abasic site-containing DNAzyme and aptamer for label-free fluorescent detection of Pb2+ and adenosine with high sensitivity, selectivity and tunable dynamic range. J Am Chem Soc 131(42):15352–15357
Xiang Y, Lu Y (2014) DNA as sensors and imaging agents for metal ions. Inorg Chem 53:1925–1942
Li F, Yang L, Chen M, Li P, Tang B (2012) A selective amperometric sensing platform for lead based on target-induced strand release. Analyst 138:461–466
He QW, Miller EW, Wong AP, Chang CJ (2006) A sensitive fluorescent sensor for detecting lead in living cells. J Am Chem Soc 128:9316–9317
Schneider E, Clark DS (2013) Cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes and the development of CYP biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 39:1–13
Godwin HA (2001) The biological chemistry of Lead. Curr Opin Chem Biol 5:223–227
Needleman H (2004) Lead poisoning. Annu Rev Med 55:209–222
Ratte HT (1999) Bioaccumulation and toxicity of silver compounds: review. Environ Toxicol Chem 18(1):89–108
BIS (1981) Tolerance limits for industrial effluents prescribed by bureau of indian standards, IS 2490(Part I) New Delhi
Yang X, Xu J, Tang X, Liu H, Tian D (2010) A novel electrochemical DNAzyme sensor for the amplified detection of Pb2+ ions. Chem Commun 46:3107–3109
Wuertz S, Bishop S, Wilderer PA (2003) Biofilms in waste-water treatment: an interdisciplinary approach. IWA, London
Teixerira CR, Andradea TFN, Oliveirac FM, Corazzac MZ, Azevedo LFM, Segatellid MG (2011) Synthesis and application of imprinted polyvinylimidazole-silica hybride copolymer for Pb2+ determination by flow-injection thermospray flame furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 703:145–151
Silva MVL, Frescura VL, Curtius A (2000) Determination of trace elements in water samples by ultrasonic nebulization inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry after cloud point extraction. Spectrochimi A J Acta Part B 55:803–813
Elfering H, Anderson JT, Poll KG (1998) Determination of organic soils and waters by hydride generation inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. Analyst 123:669–674
Wu J, Boyle EA (1997) Low blank pre-concentration technique for the determination of lead, copper and cadmium in small-volume seawater samples by isotope dilution ICPMS. Anal Chem 69:2464–2470
Chan MS, Huang SD (2000) Direct determination of copper in seawater using transversely heated graphite furnace atomic adsorption spectrometer with Zeeman-effect background corrector. Talanta 51:373–380
Santosa SJ, Tanaka S, Yamanaka K (1997) Sequential determination of trace metals in sea water by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry after electrochemical vaporization of their dithiocarbamate complexes in methyl isobutyl ketone. Environ Monit Assess 44:515–528
Rea RW, Keeler GJ (1998) Microwave digestion and analysis of foliage for total mercury by cold vapour atomic fluorescence spectroscopy. Biogeochemistry 40:115–123
Al-Assaf KH, Tyson JF, Uden PC (2009) Determination of four arsenic species in soil by sequential extraction and high performance liquid chromatography with post-column hydride generation and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry detection. J Anal Atom Spectrom 24:379–384
Miao X, Ling L, Shuai (2011) Ultraaensitive detection of lead(II) with DNAzyme and gold nanoparticles probes by using a dynamic light scattering technique. Chem Commun 47:4192–4194
Tang S, Tong P, Li H, Tang J, Zhang L (2013) A novel label-free electrochemical sensor for Hg2+ based on the catalytic formation of metal nanoparticle. Biosens Bioelectron 42:608–611
Xu H, Xu P, Gao S, Zhang L, Fan C, Zuo X (2013) Highly sensitive recognition of Pb2+ using Pb2+ triggered exonuclease aided DNA recycling. Biosens Bioelectron 43:520–523
Seeling G, Yurke B, Winfree E (2006) Catalyzed relaxation of a metastable DNA fuel. J Am Chem Soc 128:12211–12220
Li J, Cao Z, Lu Y (2000) Functional nucleic acid sensors. Chem Rev 109(5):1948–1998
Li J, Lu Y (2000) A highly sensitive and selective catalytic DNA biosensor for lead ions. J Am Chem Soc 122:10466–10467
Liu J, Lu Y (2012) Metal ion dependent DNAzymes and their applications as biosensors. Met Ions Life Sci 10:217
Zhu, X, Lin Z, Chen L, Qiu B, Chen G (2009) A sensitive and specific electro-chemiluminescnt sensor for lead based DNAzyme. Chem Commun 6050–6052
Gao A, Tang CX, He XW, Yin XB (2013) Electrochemilumiscent lead biosensor based on GR-5 lead-dependent DNAzyme for Ru(phen)3 2+ intercalation and lead recognition. Analyst 138:263
Wu Y, Cai Z, Wu G, Rong M, Jiang Y, Yang CJ, Chen X (2014) A novel signal-on DNAzyme –based electrochemiluminescencesensor. Sensors Actuators B 191: 60–66
Wang Y, Irudayaraj J (2011) A SERS DNAzyme biosensor for lead ion detection. Chem Commun 47:4394–4396
Wang FL, Wu Z, Lu YX, Wang J, Jiang JH, Yu RQ (2010) A label free DNAzyme sensor for lead (II) detection by quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Anal. Biochem 405: 168–173
Zhang LB, Han BY, Li T, Wang EK (2011) Label-free DNAzyme-based fluorescing molecular switch for sensitive and selective detection of lead. Chem Commun 47:3099–3101
Wang J, Liu B (2008) Highly sensitive and selective detection of Hg2+ in aqueous solution with mercury –specific DNA and Syber Green I. Chem Commun 4759–4761
Chen YY, Chang HT, Shiang YC, Hung YL (2009) Colorimetric assay for lead ions based on the leaching of gold nanoparticles. Anal Chem 81:9433–9439
Liu JW, Lu Y (2004) Accelerated color change of gold nanoparticles assembled by DNAzymes for simple and fast colorimetric Pb2+ detection. J Am Chem Soc 126:12298–12305
Chen G, Chen J, Wu W, Fang F, Chen L, Liu Q, Wang L, Xing X, Zeng L (2013) A enzyme-free and label-free assay for copper(II) ion detection based on self-assembled DNA concatamers and Syber Green I. Analyst 138:4737–4740
Fu T, Zhao XH, Bai HR, Zhao ZL, Hu R, Kong RM, Zhang XB, Tan W, Yu RQ (2013) A superquenched DNAzyme-perylene complex: a convenient, universal and low-background strategy for fluorescence catalytic biosensors. Chem Commun 49:6644
Li CL, Liu KT, Lin YW, Chang HT (2011) Fluorescence detection of lead(II) ions through their induced catalytic activity of DNAzymes. Anal Chem 83:225–230
Nagaraj N, Liu J, Sterling S, Wu J, Lu Y (2009) DNAzyme catalytic beacon sensors that resist temperature-dependent variations. Chem Commun 27:4103–4105
Liu J, Lu Y (2003) Improving fluorescent DNAzyme biosensors by combining inter - and intramolecular quenchers. Anal Chem 75:66–6672
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ravikumar, A., Panneerselvam, P., Radhakrishnan, K. et al. DNAzyme Based Amplified Biosensor on Ultrasensitive Fluorescence Detection of Pb (II) Ions from Aqueous System. J Fluoresc 27, 2101–2109 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-017-2149-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-017-2149-4