Abstract
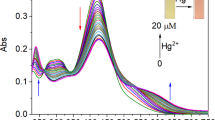
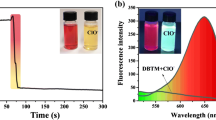
A Nile blue-based chemodosimeter was newly synthesized. It can detect Hg2+ in aqueous solution based on desulfurization reaction. Upon its addition into aqueous Hg2+ ion solution, it exhibited a considerable blue-shift in its absorption and obvious fluorescence quenching. The detection mechanism was proved by mass spectrometry analysis and Gaussian calculations. Detection at an emission of 685 nm was extremely sensitive, with a detection limit of 2.5 × 10−9 mol/L. The fluorescent images in living cells and zebrafish demonstrate its potential for studying the accumulation of mercury species in organism.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen X et al (2010) Fluorescent and colorimetric probes for detection of thiols. Chem Soc Rev 39(6):2120–2135
Feng X et al (2010) Water-soluble fluorescent conjugated polymers and their interactions with biomacromolecules for sensitive biosensors. Chem Soc Rev 39(7):2411–2419
Xu Z, Yoon J, Spring DR (2010) Fluorescent chemosensors for Zn2+. Chem Soc Rev 39(6):1996–2006
Vernet P (1991) Heavy metals in the environment. Elsevier, New York
Charlet L et al (2012) Neurodegenerative diseases and exposure to the environmental metals Mn, Pb, and Hg. Coord Chem Rev 256(19–20):2147–2163
Fitzgerald WF, Lamborg CH, Hammerschmidt CR (2007) Marine biogeochemical cycling of mercury. Chem Rev 107(2):641–662
Wade CR et al (2010) Fluoride Ion complexation and sensing using organoboron compounds. Chem Rev 110(7):3958–3984
Keum D, Kim S, Kim Y (2014) A fluorescence turn-on sensor for the detection of palladium ions that operates through in situ generation of palladium nanoparticles. Chem Commun 50(10):1268–1270
Guo Z et al (2014) Recent progress in the development of near-infrared fluorescent probes for bioimaging applications. Chem Soc Rev 43(1):16–29
Zhang X, Xiao Y, Qian X (2008) A ratiometric fluorescent probe based on FRET for imaging Hg2+ ions in living cells. Angew Chem Int Ed 47(42):8025–8029
Wang GK et al (2014) A pyrene derivative for Hg2+-selective fluorescent sensing and its application in in vivo imaging. Chem Asian J 9(3):744–748
Meng Q et al (2011) A hybrid mesoporous material functionalized by 1,8-naphthalimide-base receptor and the application as chemosensor and absorbent for Hg2+ in water. Talanta 84(1):53–59
Du J et al (2012) Fluorescent chemodosimeters using “mild” chemical events for the detection of small anions and cations in biological and environmental media. Chem Soc Rev 41(12):4511–4535
Yang Y et al (2013) Luminescent chemodosimeters for bioimaing. Chem Rev 113:192–270
Hirano T et al (2000) Highly zinc-selective fluorescent sensor molecules suitable for biological applications. J Am Chem Soc 122(49):12399–12400
Wang J et al (2005) A pH-resistant Zn(ii) sensor derived from 4-aminonaphthalimide: design, synthesis and intracellular applications. J Mater Chem 15(27–28):2836–2839
Zhang W et al (2009) A highly sensitive acidic pH fluorescent probe and its application to HepG2 cells. Analyst 134(2):367–371
Yuan L, Lin W, Feng Y (2011) A rational approach to tuning the pKa values of rhodamines for living cell fluorescence imaging. Org Biomol Chem 9(6):1723–1726
Duke RM et al (2010) Colorimetric and fluorescent anion sensors: an overview of recent developments in the use of 1,8-naphthalimide-based chemosensors. Chem Soc Rev 39(10):3936–3953
Fan J et al (2014) Fluorescence imaging lysosomal changes during cell division and apoptosis observed using Nile blue based near-infrared emission. Chem Commun 50(7):882–884
Zhu B et al (2011) A 4-hydroxynaphthalimide-derived ratiometric fluorescent chemodosimeter for imaging palladium in living cells. Chem Commun 47(30):8656–8658
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheesseman JR, Scalmani G, Barone V, Mennucci B, Petersson GA, Nakatsuji H, Caricato M, Li X, Hratchian HP, Izmaylov AF, Bloino J, Zheng G, Sonnenberg JL, Hada M, Ehara M, Toyota K, Fukuda R, Hasegawa J, Ishida M, Nakajima T, Honda Y, Kitao O, Nakai H, Vreven T, Montgomery JA Jr, Peralta JE, Ogliaro F, Bearpark M, Heyd JJ, Brothers E, Kudin KN, Staroverov VN, Kobayashi R, Normand J, Raghavachari K, Rendell A, Burant JC, Iyengar SS, Tomasi J, Cossi M, Rega N, Millam JM, Klene M, Knox JE, Cross JB, Bakken V, Adamo C, Jaramillo J, Gomperts R, Stratmann RE, Yazyev O, Austin AJ, Cammi R, Pomelli C, Ochetershk JW, Martin RL, Morokuma K, Zakrzewshi VG, Voth GA, Salvador P, Dannenberg JJ, Dapprich S, Daniels AD, Farkas O, Foresman JB, Ortiz JV, Cioslowski J, Fox DJ (2009) The gaussian 09 package refer to gaussian 09, revision a.02. Gaussian, Inc, Inc., Wallingford CT
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Public science and technology research funds projects of ocean (201505021–2, 201005023–4), and Youth science funds project of ocean (2013560).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 220 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, M., Yin, J., Li, Y. et al. Development of a Nile-Blue Based Chemodosimeter for Hg2+ in Aqueous Solution and its Application in Biological Imaging. J Fluoresc 25, 403–408 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-015-1527-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-015-1527-z