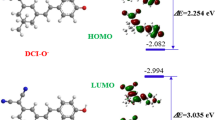
Abstract
Although hydrogen sulfide (H2S) has been known as a toxic gas with unpleasant rotten egg smell, the correlation between H2S and physiological processes has attracted scientists to develop brand new methods to monitor such a gaseous molecule in vitro and in vivo. Herein, we described a couple of coumarin-based fluorescent probes (1a and 1b) that can be activated by reduction of azide to amine in the presence of H2S. It should be emphasized that probe 1b demonstrated high selectivity and sensitivity for H2S over other relevant reactive sulfur species in vitro, as well as identified exogenous H2S in living cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li L, Bhatia M, Zhu YZ, Zhu YC, Ramnath RD, Wang ZJ, Anuar FBM, Whiteman M, Salto-Tellez M, Moore PK (2005) Hydrogen sulfide is a novel mediator of lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in the mouse. FASEB J 19(9):1196
Li L, Bhatia M, Moore PK (2006) Hydrogen sulphide–a novel mediator of inflammation? Curr Opin Pharmacol 6(2):125–129
Yang G, Wu L, Jiang B, Yang W, Qi J, Cao K, Meng Q, Mustafa AK, Mu W, Zhang S (2008) H2S as a physiologic vasorelaxant: hypertension in mice with deletion of cystathionine γ-lyase. Science 322(5901):587
Kulkarni KH, Monjok EM, Zeyssig R, Kouamou G, Bongmba ON, Opere CA, Njie YF, Ohia SE (2009) Effect of hydrogen sulfide on sympathetic neurotransmission and catecholamine levels in isolated porcine iris-ciliary body. Neurochem Res 34(3):400–406
Kimura Y, Dargusch R, Schubert D, Kimura H (2006) Hydrogen sulfide protects HT22 neuronal cells from oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 8(3–4):661–670
Wu L, Yang W, Jia X, Yang G, Duridanova D, Cao K, Wang R (2008) Pancreatic islet overproduction of H2S and suppressed insulin release in Zucker diabetic rats. Lab Invest 89(1):59–67
Rose P, Moore PK, Ming SH, Nam OC, Armstrong JS, Whiteman M (2005) Hydrogen sulfide protects colon cancer cells from chemopreventative agent beta-phenylethyl isothiocyanate induced apoptosis. World J Gastroenterol 11(26):3990
Hu LF, Lu M, Wu ZY, Wong PTH, Bian JS (2009) Hydrogen sulfide inhibits rotenone-induced apoptosis via preservation of mitochondrial function. Mol Pharmacol 75(1):27
Kabil O, Banerjee R (2010) Redox biochemistry of hydrogen sulfide. J Biol Chem 285(29):21903–21907. doi:10.1074/jbc.R110.128363
Wang R (2003) The gasotransmitter role of hydrogen sulfide. Antioxid Redox Signal 5(4):493–501
Łowicka E, Bełtowski J (2007) Hydrogen sulfide (H2S)-the third gas of interest for pharmacologists. Pharmacological Reports: PR 59(1):4–24
Moore PK (2011) Hydrogen sulfide and cell signaling. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 51(1)
Culotta E, Koshland DE Jr (1992) Molecule of the year. NO news is good news. Science 258:1862–1865
Morita T, Perrella MA, Lee ME, Kourembanas S (1995) Smooth muscle cell-derived carbon monoxide is a regulator of vascular cGMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci 92(5):1475
Cline JD (1969) Spectrophotometric determination of hydrogen sulfide in natural waters. Limnol Oceanogr 14(3):454–458
Sen A, Albarella JD, Carey JR, Kim P, McNamara WB III (2008) Low-cost colorimetric sensor for the quantitative detection of gaseous hydrogen sulfide. Sensors and Actuators B Chem 134(1):234–237
Schiavon G, Zotti G, Toniolo R, Bontempelli G (1995) Electrochemical detection of trace hydrogen sulfide in gaseous samples by porous silver electrodes supported on ion-exchange membranes (solid polymer electrolytes). Anal Chem 67(2):318–323
Lawrence NS, Davis J, Jiang L, Jones TGJ, Davies SN, Compton RG (2000) The electrochemical analog of the methylene blue reaction: a novel amperometric approach to the detection of hydrogen sulfide. Electroanalysis 12(18):1453–1460
Cord-Ruwisch R (1985) A quick method for the determination of dissolved and precipitated sulfides in cultures of sulfate-reducing bacteria. J Microbiol Methods 4(1):33–36
Radford-Knoery J, Cutter GA (1993) Determination of carbonyl sulfide and hydrogen sulfide species in natural waters using specialized collection procedures and gas chromatography with flame photometric detection. Anal Chem 65(8):976–982
Liu C, Pan J, Li S, Zhao Y, Wu LY, Berkman CE, Whorton AR, Xian M (2011) Capture and visualization of hydrogen sulfide by a fluorescent probe. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 50(44):10327–10329. doi:10.1002/anie.201104305
Sasakura K, Hanaoka K, Shibuya N, Mikami Y, Kimura Y, Komatsu T, Ueno T, Terai T, Kimura H, Nagano T (2011) Development of a highly selective fluorescence probe for hydrogen sulfide. J Am Chem Soc 133(45):18003–18005. doi:10.1021/ja207851s
Lippert AR, New EJ, Chang CJ (2011) Reaction-based fluorescent probes for selective imaging of hydrogen sulfide in living cells. J Am Chem Soc 133(26):10078–10080. doi:10.1021/ja203661j
Peng H, Cheng Y, Dai C, King AL, Predmore BL, Lefer DJ, Wang B (2011) A fluorescent probe for fast and quantitative detection of hydrogen sulfide in blood. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 50(41):9672–9675. doi:10.1002/anie.201104236
Xuan W, Sheng C, Cao Y, He W, Wang W (2012) Fluorescent probes for the detection of hydrogen sulfide in biological systems. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. doi:10.1002/anie.201107025
Sivakumar K, Xie F, Cash BM, Long S, Barnhill HN, Wang Q (2004) A fluorogenic 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reaction of 3-azidocoumarins and acetylenes†. Org Lett 6(24):4603–4606. doi:10.1021/ol047955x
Liu X, Cole JM, Waddell PG, Lin TC, Radia J, Zeidler A (2012) Molecular origins of optoelectronic properties in coumarin dyes: toward designer solar cell and laser applications. J Phys Chem A 116(1):727–737. doi:10.1021/jp209925y
Acknowledgments
The present work was supported by grants from Shandong Natural Science Foundation (No. JQ201019) and Independent Innovation Foundation of Shandong University, IIFSDU (No. 2010JQ005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Sun, W., Yu, X. et al. Coumarin-based Fluorescent Probes for H2S Detection. J Fluoresc 23, 181–186 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-012-1131-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-012-1131-4