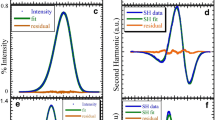
We previously applied the electrochromic modulation of excited-state intramolecular proton-transfer (ESIPT) reaction for the design of novel 3-hydroxyflavone (3-HF) derivatives as fluorescent probes for measuring the dipole potential, ΨD, in lipid bilayers (Klymchenko et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2003, 100, 11219). In the present work, this method was revisited to take into account the influence of the bilayer hydration on the emission ratiometric response of 3-HF probes. For this reason, it was necessary to deconvolute the whole fluorescence spectra into three bands corresponding to the non H-bonded forms, normal N* and tautomer T* forms, both participating to the ESIPT reaction, and to the H-bonded H–N* form, excluded from this reaction. This allowed us to determine the pure N*/T* intensity ratio, without any contribution from the H–N* form emission depending essentially on the bilayer hydration. This new approach allowed us to confirm the correlation we obtained between the response of 3-HF probes on dipole potential modifications and the corresponding response of the reference fluorescent probe di-8-ANEPPS, thus further confirming the potency of 3-HF probes as excellent emission ratiometric probes to measure dipole potential in lipid membranes.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
P. O'Shea (2003). Intermolecular interactions with/within cell membranes and the trinity of membrane potentials: Kinetics and imaging. Biochem. Soc. Transactions 31, 990–996.
R. J. Clarke (2001). The dipole potential of phospholipid membranes and methods for its detection. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 89–90, 263–281.
J. C. Franklin and D. S. Cafiso (1993). Internal electrostatic potentials in bilayers measuring and controlling dipole potentials in lipid vesicles. Biophys. J. 65, 289–299.
R. J. Mashl, H. L. Scott, S. Subramaniam, and E. Jakobsson (2001). Molecular simulation of dioleoylphosphatidylcholine lipid bilayers at different level of hydration. Biophys. J. 81, 3005–3015.
M. R. Moncelli, L. Becucci, F. T. Buoninsegni, and R. Guidelli (1998). Surface dipole potential at the interface between water and self-assembled monolayers of phosphatidylserine and phosphatidic acid. Biophys. J. 74, 2388–2397.
L. Becucci, M. R. Moncelli, R. Herrero, and R. Guidelli (2000). Dipole potentials of monolayers of phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylserine and phosphatidic acid on mercury. Langmuir 16, 7694–7700.
R. Herrero, M. R. Moncelli, R. Guidelli, M. Carlà, A. Arcangeli, and M. Olivotto (2000). Hybrid polar compounds produce a positive shift in the surface dipole potential of self-assembled phospholipids monolayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1466, 278–288.
U. Peterson, D. A. Mannock, R. N. A. H. Lewis, P. Pohl, R. N. McElhaney, and E. P. Pohl (2002). Origin of membrane dipole potential. Contribution of the phospholipids fatty acid chains. Chem. Phys. Lipids 117, 19–27.
E. Gross, R. Bedlack Jr., and L. M. Loew (1994). Dual-wavelength ratiometric fluorescence measurement of the membrane dipole potential. Biophys. J. 67, 208–216
A. Zouni, R. J. Clarke, and J. F. Holzwarth (1994). Kinetics of the solubilization of styryl dye aggregates by lipid vesicles. J. Phys. Chem. 98, 1732–1738.
R. Cseh and R. Benz (1998). The adsorption of phloretin to lipid monolayers and bilayers cannot be explained by Langmuir adsorption isotherms alone. Biophys. J. 74, 1399–1408.
S. A. Simon, T. J. McIntosh, A. D. Magid, and D. Needham (1992). Modulation of the interbilayer hydration pressure by the addition of dipoles at the hydrocarbon/water interface. Biophys. J. 61, 786–799.
G. R. Bright, G. W. Fisher, J. Rogowska, and D. L. Taylor (1989). Fluorescence ratio imaging microscopy. Methods Cell Biol. 30, 157–192.
R. B. Silver (1998). Ratio imaging: Practical considerations for measuring intracellular calcium and pH in living tissue. Methods Cell Biol. 56, 237–251.
A. S. Klymchenko and A. P. Demchenko (2002). Electrochromic odulation of excited-state intramolecular proton transfer: the new principle in design of fluorescence sensors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 12372–12379.
A. S. Klymchenko and A. P. Demchenko (2002). Multiparametric probing of intermolecular interactions with fluorescent dye exhibiting excited state intramolecular proton transfer. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 5, 461–468.
A. S. Klymchenko, G. Duportail, Y. Mély, and A. P. Demchenko (2003). Ultrasensitive two-color fluorescence probes for dipole potential in phospholipids membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 11219–11224.
A. S. Klymchenko, G. Duportail, A. P. Demchenko, and Y. Mély (2004). Bimodal distribution and fluorescence response of environment-sensitive probes in lipid bilayers. Biophys. J. 86, 2929–2941.
A. S. Klymchenko, Y. Mély, A. P. Demchenko, and G. Duportail. (2004). Simultaneous probing of hydration and polarity of lipid bilayers with 3-hydroxyflavone fluorescent dyes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1665, 6–19.
G. L. Jendrasiak, R. L. Smith, and T. J. McIntosh (1997). The effect of phloretin on the hydration of egg phosphatidylcholine multilayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1329, 159–168.
K. Gawrish, D. Ruston, J. Zimmerberg, V. A. Parsegian, R. P. Rand, and N. Fuller (1992). Membrane dipole potentials, hydration forces, and the ordering of water at membrane surfaces. Biophys. J. 61, 1213–1223.
A. S. Klymchenko, G. Duportail, T. Oztürk, V. G. Pivovarenko, Y. Mély, and A. P. Demchenko (2002). Novel two-band ratiometric fluorescence probes with different location and orientation in phospholipids membranes. Chem. Biol. 9, 1199–1208.
V. V. Shynkar, A. S. Klymchenko, G. Duportail, A. P. Demchenko, and Y. Mély (2005). Two-color fluorescent probes for imaging the dipole potential of cell plasma membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1712, 128–136.
M. J. Hope, M. B. Bally, G. Webb, and P. R. Cullis (1985). Production of large unilamellar vesicles by a rapid extrusion procedure. Characterization of size distribution, trapped volume and ability to maintain a membrane potential. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 812, 55–65.
A. O. Doroshenko, L. B. Sychevskaya, A. V. Grygorovych, and V. G. Pivovarenko (2002). Fluorescence probing of cell membranes with azacrown substituted ketocyanine dyes. J. Fluorescence 12, 455–464.
D. B. Siano and D. E. Metzler (1969). Band shapes of the electronic spectra of complex molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 51, 1856–1861.
M. Langner and K. Kubica (1999). The electrostatics of lipid surfaces. Chem. Phys. Lipids 101, 3–35.
H. M. Shapiro (1994). Cell membrane potential analysis. Methods Cell Biol. 41, 121–133.
C. Xu and L. M. Loew (2003). Activation of phospholipase C increases intramembrane electric fields in NTE-115 neuroblastoma cells. Biophys. J. 84, 4144–4156.
R. J. Clarke and D. J. Kane (1997). Optical detection of membrane dipole potential: avoidance of fluidity and dye-induced effects. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1323, 223–239.
A. S. Verkman (1980). The quenching of an intramembrane fluorescent probe. A method to study the binding and permeation of phloretin through bilayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 599, 370–379.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by CNRS and Université Louis Pasteur. GM is a fellow from Agence Universitaire de la Francophonie. VVS was a student from Collège Doctoral Européen and was supported by the Région Alsace. ASK was a fellow from the European project TriOH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
M`Baye, G., Shynkar, V.V., Klymchenko, A.S. et al. Membrane Dipole Potential as Measured by Ratiometric 3-Hydroxyflavone Fluorescence Probes: Accounting for Hydration Effects. J Fluoresc 16, 35–42 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-005-0022-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-005-0022-3