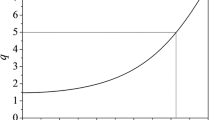
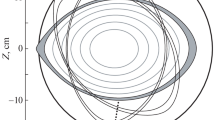
Reduction of core-resonant magnetic fluctuations and improved confinement in the Madison Symmetric Torus reversed-field pinch (MST RFP) have been routinely achieved by applying the surface poloidal electric field. The created inductive poloidal electric field drives current in plasma which leads to the improved confinement. To study the effect we developed a relatively simple 1-D model in cylindrical geometry which assumes poloidal and axial symmetry during the drive. We use resistive magnetohydrodynamics model with realistic plasma parameters and assume that there is a vacuum gap between plasma boundary and conducting wall of the vessel. Evolution of plasma density is taken into account and plasma boundary moves self-consistently with momentum equation. We start from an initial unstable equilibrium and examine stability of plasma configuration at intermediate moments of time during the drive. For this we calculate the growth rates of unstable eigenmodes in the plasma. Our results show that the modifications to the plasma current profile during the drive are stabilizing. The initial stabilization is due to the direct modification of the current profile near the edge. It enhances later in time due to the flattening of λ profile in the core region as plasma and magnetic field compress inward during the drive.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dexter R. N., Kerst D. W., Lovell T. W., Prager S. C., Sprott J. C. (1991) Fusion Technol. 19: 131
Ji H., Almagri A. F., Prager S. C., Sarff J. S. (1994) Phys. Rev. Lett. 73: 668
P. W. Fontana, Ph.D. thesis, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, 1999
Fontana P. W., Den Hartog D. J., Fiksel G., Prager S. C. (2000) Phys. Rev. Lett. 85: 566
Sarff J. S., Hokin S. A., Ji H., Prager S. C., Sovinec C. R. (1994) Phys. Rev. Lett. 72: 3670
Sarff J. S., Lanier N. E., Prager S. C., Stoneking M. R. (1997) Phys. Rev. Lett. 78: 62
Stoneking M. R., Lanier N. E., Prager S. C., Sarff J. S., Sinitsyn D. (1997) Phys. Plasmas 4: 1632
Bartiromo R., Martin P., Martini S., Bolzonella T., Canton A., Innocente P., Marrelli L., Murari A., Pasqualotto R. (1999) Phys. Rev. Lett. 82: 1462
Chapman B. E., Biewer T. M., Chattopadhyay P. K., Chiang C. S., Craig D. J., Crocker N. A., Den Hartog D. J., Fiksel G., Fontana P. W., Prager S. C., Sarff J. S. (2000) Phys. Plasmas 7: 3491
Chapman B. E., Almagri A. F., Anderson J. K., Biewer T. M., Chattopadhyay P. K., Chiang C. S., Craig D., Den Hartog D. J., Fiksel G., Forest C. B., Hansen A. K., Holly D., Lanier N. E., O’Connell R., Prager S. C., Reardon J. C., Sarff J. S., Wyman M. D. (2002) Phys. Plasmas 9: 2061
S. Ortolani and D. Schnack, Magnetohydrodynamics of Plasma Relaxation (World Scientific, 1993)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Svidzinski, V.A., Prager, S.C. On the Physics of Improved Confinement During Pulsed Poloidal Current Drive in MST Reversed-Field Pinch. J Fusion Energ 26, 215–220 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-006-9041-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-006-9041-6