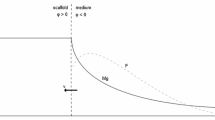
The paper aims to develop a mathematical model for the investigation of degradation of a porous matrix of polylactic acid implanted in a bone tissue based on the study of kinetics of hydrolytic degradation of the matrix due to the action of a body fluid and diffusion of lactic acid released as a result of a chemical reaction. The numerical solution of nonstationary nonlinear equation of lactic acid diffusion through the host tissue obtained by the finite difference method allows one to establish a relationship between the lactic acid density in the bone tissue with time and the density during the implanted matrix degradation as well as the density profile of lactic acid in the bone tissue as a function of the kinetic reaction parameters for different porosities. The validation of the model is verified using the available experimental data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. A. Paz Estévez and A. Pla Pérez, Adjustable degradability and biocompatibility of porous matrices for bone tissue engineering, in: Proc. X Int. Convention Integrative Innovative University, Matanzas, 23–25 March 2021, Matanzas, Cuba (2021); http://www.umcc.cu/eventoCIUM-2021; ISBN: 978-959-16-45470.
A. González, M. Rivas Santana, R. Quiza Sardiñas, E. A. Paz Estévez, and A. Pla Pérez, Modeling of porous scaffolds based on the triple-periodic structures P and G, Orange J., No. 3, 30–41 (2021); https://doi.org/10.46502/issn.2710-995X/2021.5.04.
L. F. Ardila, H. A. Estupiñán, C. Vásquez, and D. Y. Peña, Study of hydrolytic biodegradation of biopolymer/ceramic coatings by EQCM, Revista Ing., No. 35, 41–46 (2011).
R. A. Auras, L. T. Lim, S. E. M. Selke, and H. Tsuji, Polylactic Acid: Synthesis, Structures, Properties, Processing, and Application, John Wiley & Sons, New Jersey (2010).
M. A. Elsawy, K. H. Kim, J. W. Park, and A. Deep, Hydrolytic degradation of polylactic acid composites, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., 79, 1346–1352 (2017).
A. Zargar, K. Mohammad, H. Fathi, M. Manshaei, and S. M. Razavi, In-vivo evaluation of a partially resorbable poly L-lactic acid/braided bioactive glass fibers reinforced composite for load bearing fracture fixation, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med., 31, No. 7 (2020); https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-020-06394-6.
V. Mittal, Characterization Techniques for Polymer Nanocomposites, John Wiley & Sons, Weinheim (2012).
A. Shah, F. Hasan, A. Hameed, and S. Ahmed, Biological degradation of plastics, Biotechnol. Adv., 26, 246–265 (2008); https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2007.12.005.
V. Jašo, G. Glenn, A. Klamczynski, and Z. S. Petrović, Biodegradability study of polylactic acid/thermoplastic polyurethane blends, Polym. Test., 47, 1–3 (2015).
A. Atala, R. Lanza, R. Nerem, and J. Thomson (Eds.), Principles of Regenerative Medicine, Academic Press (2011).
Technical Report·of Karaganda Medical University, Kazakhstan (February 2021); https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.26688.87047.2021.
I. Sandonis, Porous Scaffolds, Doctor's Thesis, University of the Basque Country, Spain (2015).
M. A. Sadovoi, P. M. Larionov, A. G. Samokhin, and O. M. Rozhnova, Cellular matrices (scaffolds) for bone regeneration purposes: The current state of the problem, Khirurgiya Pozvonochnika, No. 2, 79–86 (2014).
M. F. Shockley and A. H. Muliana, Modeling temporal and spatial changes during hydrolytic degradation and erosion in biodegradable polymers, Polym. Degrad. Stab. (2020); https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2020.109298.
S. Bose, M. Roy, and A. Bandyopadhyay, Recent advances in bone tissue engineering scaffolds, Trends Biotechnol., 30, No. 10, 546–554 (2013).
I. A. Khlusov, K. V. Zaitsev, O. B. Zhukova, A. A. Gostyukhina, N. G. Abdulkina, A. A. Zaitsev, I. V. Kulagina, S. I. Tverdokhlebov, E. N. Bolbasov, and K. S. Stankevich, The dynamics of in vitro degradation of non-woven polylactide matrices in model biological liquid, Bull. Sib. Med., 12, No. 6, 73–81 (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Inzhenerno-Fizicheskii Zhurnal, Vol. 95, No. 6, pp. 1644–1652, November–December, 2022.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Estévez, E.A.P., Mesa, R.F. & Pavlyukevich, N.V. Nonstationary Diffusion in Hydrolytic Degradation of a Porous Polymeric Matrix. J Eng Phys Thermophy 95, 1615–1623 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-022-02630-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-022-02630-8