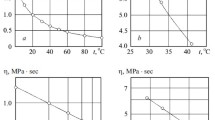
The role of rheological properties of a liquid dispersion medium, in particular, its dynamic viscosity determined by the temperature of the medium, in its magnetophoretic separation was investigated. The temperature dependences of the viscosity of a water and other liquids as well as their phenomenological approximations by logarithmic, exponential, and power functions in the working temperature ranges of these liquids are presented. The definition of the efficiency of separation of a liquid dispersion medium with the use of magnetic filters by one of the indicated functions (a logarithmic one) and its testing by the corresponding experimental temperature dependence obtained for a low-concentration aqueous suspension, whose continuous medium is a water or an industrial condensate and disperse phase is formed by particles of a synthetic magnetite or ferroparticles, are considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Chen, D. Bockenfeld, D. Rempfer, M. D. Kaminski, X. Liu, and A. J. Rosengart, Preliminary 3-D analysis of a high gradient magnetic separator for biomedical applications, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 320, 279–284 (2008).
D. Norrgran, Magnetic filtration: producing fine high-purity feedstocks, Filtr. Separ., 45, No. 6, 15–17 (2008).
Y. Liu, H. Peng, and M. Hu, Removing iron by magnetic separation from a potash feldspar ore, J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed., 28, Issue 2, 362–366 (2013).
Jay D. Wheaton and Steven W. Day, Feasibility of capturing circulating tumor cells with a magnetized device, Proc. ASME 2013 Conf. on Frontiers in Medical Devices: Applications of Computer Modeling and Simulation (FMD2013), 11–13 September, 2013.
N. A. Ebner, C. S. G. Gomes, T. J. Hobley, O. R. T. Thomas, and M. Franzreb, Filter capacity predictions for the capture of magnetic microparticles by high-gradient magnetic separation, IEEE Trans. Magn., 43, No. 5, 1941–1949 (2007).
D. Ito, K. Nishimura, and O. Miura, Removal and recycle of phosphate from treated water of sewage plants with zirconium ferrite adsorbent by high gradient magnetic separation, J. Phys.: Conf, Ser., 156, p. 012033 (2009).
B. Liu, Y. Jia, M. Ma, H. Liu, S. Li, Y. Deng, L. Zhang, Z. Lu, W. Wang, and N. He, High throughput SNP detection system based on magnetic nanoparticles separation, J. Biomed. Nanotech., 9, No. 2, 247–256 (2013).
G. Mariani, M. Fabbri, F. Negrini, and P. L. Ribani, High-gradient magnetic separation of pollutant from wastewaters using permanent magnets, Separ. Purif. Technol., 72, 147–155 (2010).
S. K. Baik, D. W. Ha, R. K. Ko, and J. M. Kwon, Magnetic field analysis of high gradient magnetic separator via finite element analysis, Phys. C, 480, 111–117 (2012).
J. W. Haverkort, S. Kenjereš, and C. R. Kleijn, Magnetic particle motion in a Poiseuille flow, Phys. Rev. E, 80, p. 016302 (2009).
A. V. Sandulyak, Purification of Liquids and Gases with the Use of Magnetic Filters [in Russian], Khimiya, Moscow (1988).
T. H. Wu, J. H. Mao, J. T. Wang, J. Y. Wu, and Y. B. Xie, A new on-line visual ferrograph. Tribol. Trans., 52, 623–631 (2009).
B. É. Kashevskii, S. É. Kashevskii, I. V. Prokhorov, and A. M. Zholud’, Investigation of the process of diamagnetic particle separation in a high-gradient ordered-structure magnetic field, J. Eng. Phys. Thermophys., 84, Issue 3, 483–489 (2011).
J. Ravnik and M. Hriberšek, High gradient magnetic particle separation in viscous flows by 3D BEM, Comput. Mech., 51, Issue 4, 465–474 (2013).
Saud A. Khashan and Edward P. Furlani, Effects of particle–fluid coupling on particle transport and capture in a magnetophoretic microsystem, Microfluid. Nanofluid., 12, Issue 1–4, 565–580 (2012).
D. Kirby, J. Siegrist, G. Kijanka, L. Zavattoni, O. Sheils, J. O'Leary, R. Burger, and J. Ducrée, Centrifugomagnetophoretic particle separation, Microfluid. Nanofluid., 13, Issue 6, 899–908 (2012).
T. Baier, K. S. Drese, J. Kim, S. Mohanty, F. Rampf, and F. Schönfeld, Modelling immunomagnetic cell capture in CFD, Proc. Sixth Int. ASME Conf. on Nanochannels, Microchannels, and Minichannels (ICNMM2008), 23–25 June 2008, Darmstadt, Germany.
X. Wu and H. Wu, A numerical study on separation characteristics of magnetic particles in magnetophoretic chip microchannels, Proc. 2nd ASME Int. Conf. on Micro/Nanoscale Heat and Mass Transfer (MNHMT2009), 18–21 December 2009, Shanghai, China.
P. Babinec, A. Krafčík, M. Babincová, and J. Rosenecker, Dynamics of magnetic particles in cylindrical Halbach array: implications for magnetic cell separation and drug targeting, Med. Biol. Eng. Comput., 48, 745–753 (2010).
X. Wu, H. Wu, and D. Hu, High-efficiency magnetophoretic separation based on synergy of magnetic force field and flow field in microchannels, Sci. China Technol. Sci., 54, No. 12, 3311–3319 (2011).
X. Wu, H. Wu, and Y. Hu, Enhancement of separation efficiency on continuous magnetophoresis by utilizing L/T-shaped microchannels, Microfluid. Nanofluid., 11, Issue 1, 11–24 (2011).
Yu. A. Taran, A. V. Kozlov, and A. L. Taran, Influence of the deposits formed in the pores of a filtration partition on the filtration process, Tonkie Khim. Tekhnol., 14, No. 2, 15–22 (2019).
D. A. Sandulyak, V. V. Sleptsov, A. A. Sandulyak, A. V. Sandulyak, V. A. Ershova, and A. V. Doroshenko, Filtration magnetophoresis process: An approah to choosing a speed regime, Proc. Int. Conf. on Recent Advances in Mechanics, Mechatronics, and Civil, Chemical and Industrial Engineering, July 2015, Zakynthos Island, Greece, pp. 72–76.
A. V. Sandulyak and A. A. Sandulyak, Role of the temperature of water in its magnetophorestic purification. Modified purification equation, Proc. 49th Int. Sci. Tekh. Conf. AAI (FISITA), MGTU, Moscow (2005), Part 2, pp. 54–60.
O. Yu. Korkhov, A. V. Sandulyak, and V. A. Dubchak, Efficiency of the magnetic filtration of condensates at different temperatures, Prom. Énerg., No. 2, No. 2, 51–52 (1989).
A. A. Sandulyak, V. A. Ershova, and A. V. Sandulyak, Temperature dependences of the efficiency and the limiting rate of the magnetophoretic purification of liquids, Énergosberezhenie Vodopodgotovka, No. 5, (49), 45–48 (2007).
A. G. Kasatkin, Basic Processes and Apparatus of Chemical Technology [in Russian], Khimiya, Moscow (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Inzhenerno-Fizicheskii Zhurnal, Vol. 94, No. 4, pp. 945–952, July–August, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sandulyak, A.V., Sandulyak, D.A., Polismakova, M.N. et al. Role of Viscosity and Temperature Factors in the Magnetophoresis of Dispersed Phase of Different Liquid Media. J Eng Phys Thermophy 94, 919–926 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-021-02368-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-021-02368-9