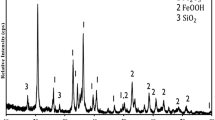
Consideration has been given to problems of chemical activation of a solid product of hydrothermal carbonization (hydrochar) of biomass. Pellets from a mixture of poultry litter and straw subjected to carbonization in a fluidized bed in a medium of superheated water vapor at a temperature of 300°C were impregnated with water solution of ferric nitrate, dried in the air at a temperature of 100°C, and held for 2 h at a temperature of 300°C for degradation of iron(III) nitrate and its transformation into iron oxides. The pellets were activated at a temperature of 700–800°C in a horizontal tube furnace in an inert argon atmosphere. The obtained ferromagnetic sorbents have a rather developed system of micro- and mesopores. Furthermore, a twofold increase in the duration of activation results in an 18% increase of the pore specific surface, and the rise in the temperature of the activation process leads to an increase in this surface by 45%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Liu and F. S. Zhang, Removal of lead from water using biochars prepared from hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass, J. Hazard. Mater., 167, 933–939 (2009).
Z. Liu, F. S. Zhang, and J. Wu, Characterization and application of chars produced from pinewood pyrolysis and hydrothermal treatment, Fuel, 89, 510–514 (2010).
M. Sevilla, A. Fuertes, and R. Mokaya, High-density hydrogen storage in superactivated carbons from hydrothermally carbonized renewable organic materials, Energy Environ. Sci., 4, 1400–1410 (2011).
M. Sevilla and A. B. Fuertes, Sustainable porous carbons with a superior performance for CO2 capture, Energy Environ. Sci., 4, 1765–1771 (2011).
M. Sevilla, J. A. Maciá-Agulló, and A. B. Fuertes, Hydrothermal carbonization of biomass as a route for the sequestration of CO2: chemical and structural properties of the carbonized products, Biomass Bioenergy, 35, 3152–3159 (2011).
M. Sevilla and A. Fuertes, The production of carbon materials by hydrothermal carbonization of cellulose, Carbon, 47, 2281–2289 (2009).
C. Falco, J. Marco-Lozar, D. Salinas-Torres, E. Morallon, D. Cazorla-Amoros, M. Titirici, and D. Lozano-Castello, Tailoring the porosity of chemically activated hydrothermal carbons: Influence of the precursor and hydrothermal carbonization temperature, Carbon, 62, 346–355 (2013).
L. Wang, Y. Guo, B. Zou, C. Rong, X. Ma, Y. Qu, Y. Li, and Z. Wang, High surface area porous carbons prepared from hydrochars by phosphoric acid activation, Bioresour. Technol., 102, 1947–1950 (2011).
Z. Zhang, Y. Qu, Y. Guo, Z. Wang, and X. Wang, A novel route for preparation of high-performance porous carbons from hydrochars by KOH activation, Colloids Surfaces A, 447, 183–187 (2014).
W. Yan, T. C. Acharjee, C. J. Coronella, and V. R. Vásquez, Thermal pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass, Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy, 28, 435–440 (2009).
W. H. Chen, S. C. Ye, and H. K. Sheen, Hydrothermal carbonization of sugarcane bagasse via wet torrefaction in association with microwave heating, Bioresour. Technol., 118, 195–203 (2012).
W. Yan, J. T. Hastings, T. C. Acharjee, C. J. Coronella, and V. R. Vá squez, Mass and energy balances of wet torrefaction of lignocellulosic biomass, Energy Fuels, 24, 4738–4742 (2010).
T. Runge, P. Wipperfurth, and C. Zhang, Improving biomass combustion quality using a liquid hot water treatment, Biofuels, 4, 73–83 (2013).
Q. V. Bach, K. Q. Tran, R. A. Khalil, Q. Skreiberg, and G. Seisenbaeva, Comparative assessment of wet torrefaction, Energy Fuels, 27, 6743–6753 (2013).
W. Yang, T. Shimanouchi, M. Iwamura, Y. Takahashi, R. Mano, K. Takashima, et al., Elevating the fuel properties of Humulus lupulus, Plumeria alba and Calophyllum inophyllum L. through wet torrefaction, Fuel, 146, 88–94 (2015).
Q. V. Bach, K. Q. Tran, R. A. Khalil, Q. Skreiberg, Wet torrefaction of forest residues, Energy Procedia, 61, 1196–1199 (2014).
R. L. Isemin, A. V. Mikhalev, N. S. Muratova, V. S. Kogh-Tatarenko, Yu. S. Teplitskii, E. K. Buchilko, Z. Zh. Greben′kov, and E. A. Pitsukha, Improving the efficiency of biowaste torrefaction, Therm. Eng., 66, No. 7, 521–526 (2019).
G. I. Zhuravskii, Thermolysis of polymeric composite materials, J. Eng. Phys. Thermophys., 92, No. 3, 603–607 (2019).
B. M. Ghanim, D. Sh. Pandey, W. Kwapinski, and J. L. James, Hydrothermal carbonization of poultry litter: Effects of treatment temperature and residence time on yields and chemical properties of hydrochars, Biores. Technol., 236, 373–380 (2016).
Y. Jiang, Q. Xie, Y. Zhang, C. Geng, B. Yu, and J. Chi, Preparation of magnetically separable activates carbon from brown coal with Fe3O4, Int. J. Mining Sci. Technol., 29, 513–519 (2019).
R. S. Shevchenko, N. I. Bogdanovich, L. I. Kuznetsova, and G. V. Dobele, Formation of sorption and magnetic properties of ferromagnetic adsorbents during the pyrolysis of waste wood in the presence of iron (III) hydroxide, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Lesnoi Zh., Nos. 2–3, 142–150 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Inzhenerno-Fizicheskii Zhurnal, Vol. 94, No. 3, pp. 621–625, May–June, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muratova, N.S., Kuz’min, S.N., Milovanov, O.Y. et al. Production of Ferromagnetic Adsorbents from Solid Products of Biowaste Carbonization in a Fluidized Bed in a Medium of Superheated Water Vapor. J Eng Phys Thermophy 94, 602–605 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-021-02334-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-021-02334-5