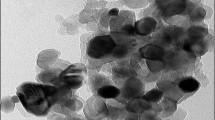
This paper assesses the heat transfer performance of nanofluids containing a core–shell structure of SiO2 –TiO2 nanoparticles of low concentration in a mixture of water and ethylene glycol (EG) in a commercially available heat exchanger. For heat transfer analysis, 0–0.025% of SiO2 –TiO2 nanoparticles were employed in a finned-tube cross-flow heat exchanger (automobile radiator kit). The obtained results indicate that SiO2 –TiO2 particles have an amorphous structure and make it possible to increase the thermal conductivity as the nanoparticle fraction increases up to 0.04%. The nanofluid characteristics (Reynolds, Nusselt, and Prandtl numbers) increase, leading to an increase in the convection coefficient. As the thermal conductivity and the convection coefficient increase, the total heat transfer improves. Finally, the heat transfer effectiveness increases linearly by 21% with 0.025% mass fraction of SiO2 –TiO2 in a water/EG-based fluid.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. M. Arsana, K. Budhikardjono, A. Susianto, and A. Altway, Modelling of the single staggered wire and tube heat exchanger, Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res., 11, No. 8, 5591–5599 (2016).
I. M. Arsana, K. Budhikardjono, A. Susianto, and A. Altway, Optimization of the single staggered wire and tube heat exchanger, MATEC Web Conf., 58, 01017 (2016).
E. Ebrahimnia-Bajestan, M. C. Moghadam, H. Niazmand, W. Daungthongsuk, and S. Wongwises, Experimental and numerical investigation of nanofluids heat transfer characteristics for application in solar heat exchangers, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 92, 1041–1052 (2016).
R. Davarnejad and M. Kheiri, Numerical comparison of turbulent heat transfer and flow characteristics of SiO2/water nanofluid within helically corrugated tubes and plain tube, Int. J. Eng., Trans. B Appl., 28, No. 10, 1408–1414 (2015).
W. Duangthongsuk and S. Wongwises, Measurement of temperature-dependent thermal conductivity and viscosity of TiO2–water nanofluids, Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci., 33, 706–714 (2009).
R. Barzegarian, M. K. Moraveji, and A. Aloueyan, Experimental investigation on heat transfer characteristics and pressure drop of BPHE (brazed plate heat exchanger) using TiO2–water nanofluid, Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci., 74, 11–18 (2016).
W. H. Azmi, K. A. Hamid, R. Mamat, K. V. Sharma, and M. S. Mohamad, Effects of working temperature on thermo-physical properties and forced convection heat transfer of TiO2 nanofluids in water–ethylene glycol mixture, Appl. Therm. Eng., 106, 1190–1199 (2016).
M. C. S. Reddy and V. V. Rao, Experimental studies on thermal conductivity of blends of ethylene glycol–water-based TiO2 nanofluid, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf., 46, 31–36 (2013).
B. A. Bhanvase, M. R. Sarode, L. A. Putterwar, K. A. Abdullah, M. P. Deosarkar, and S. H. Sonawane, Intensification of convective heat transfer in water/ethylene glycol based nanofluids containing TiO2 nanoparticles, Chem. Eng. Process., 82, 123–131 (2014).
K. A. Hamid, W. H. Azmi, R. Mamat, and K. V. Sharma, Experimental investigation on heat transfer performance of TiO2 nanofluids in water–ethylene glycol mixture, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf., 73, 16–24 (2016).
R. Davarnejad and R. M. Ardehali, Modeling of TiO2–water nanofluid effect on heat transfer and pressure drop, Int. J. Eng., Trans. B Appl., 27, No. 2, 195–202 (2014).
M. Pirhayati, M. A. Akhavan-Behabadi, and M. Khayat, Convective heat transfer of oil based nanofluid flow inside a circular tube, Int. J. Eng., Trans. B Appl., 27, No. 2, 341–348 (2014).
M. Asefi, H. Molavi, M. Shariaty-Niassar, J. B. Darband, N. Nemati, M. Yavari, and M. Akbari, An investigation on stability, electrical and thermal characteristics of transformer insulting oil nanofluids, Int. J. Eng., Trans. B Appl., 29, No. 10, 1332–1340 (2016).
M. Ebrahimi, M. Farhadi, K. Sedighi, and S. Akbarzade, Experimental investigation of force convection heat transfer in a car radiator filled with SiO2–water nanofluid, Int. J. Eng., Trans. B Appl., 27, No. 2, 333–340 (2014).
K. A. Hamid, W. H. Azmi, M. F. Nabil, and R. Mamat, Experimental investigation of nanoparticle mixture ratios on TiO2–SiO2 nanofluids heat transfer performance under turbulent flow, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 118, 617–627 (2018).
M. F. Nabil, W. H. Azmi, K. A. Hamid, and R. Mamat, Experimental investigation of heat transfer and friction factor of TiO2–SiO2 nanofluids in water:ethylene glycol mixture, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 124, 1361–1369 (2018).
K. A. Hamid, W. H. Azmi, and R. M. K. V. Sharma, Heat transfer performance of TiO2–SiO2 nanofluids in a tube with wire coil inserts, Appl. Therm. Eng., 152, 275–286 (2019).
J.-W. Lee, S. Kong, W.-S. Kim, and J. Kim, Preparation and characterization of SiO2/TiO2 core–shell particles with controlled shell thickness, Mater. Chem. Phys., 106, 39–44 (2007).
M. C. S. Reddy and V. V. Rao, Experimental investigation of heat transfer coefficient and friction factor of ethylene glycol–water based TiO2 nanofluid in double pipe heat exchanger with and without helical coil inserts, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf., 50, 68–76 (2014).
R. A. Wahyuono, Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells (DSSC) Fabrication with TiO2 and ZnO Nanoparticles for High Conversion Efficiency, Master Thesis-ITS, Surabaya, Indonesia (2013).
M. M. Rusu, R. A. Wahyuono, C. I. Fort, A. Dellith, J. Dellith, A. Ignaszak, A. Vulpoi, V. Danciu, B. Dietzek, and L. Baia, Impact of drying procedure on the morphology and structure of TiO2 xerogels and the performance of dyesensitized solar cells, J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol., 81, No. 3, 693–703 (2017).
W. H. Azmi, K. V. Sharma, P. K. Sarma, R. Mamat, and G. Najafi , Heat transfer and friction factor of water based TiO2 and SiO2 nanofluids under turbulent flow in a tube, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf., 59, 30–38 (2014).
M. N. F. Mohamad, W. A. W. Hamzah, K. A. Hamid, and R. Mamat, Heat transfer performance of TiO2–SiO2 nanofluid in water–ethylene glycol mixture, J. Mech. Eng., 5, No. 1, 39–48 (2018).
S. K. Eiamsa-ard, K. Kiatkittipong, and W. Jedsadaratanachai, Heat transfer enhancement of TiO2/water nanofluid in a heat exchanger tube equipped with overlapped dual twisted-tapes, Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol., 18, 336–350 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Inzhenerno-Fizicheskii Zhurnal, Vol. 94, No. 2, pp. 439–446, March–April, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arsana, I.M., Muhimmah, L.C., Nugroho, G. et al. Enhanced Heat Transfer Effectiveness Using Low Concentration SiO2–TiO2 Core–Shell Nanofluid in a Water/Ethylene Glycol Mixture. J Eng Phys Thermophy 94, 423–430 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-021-02312-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-021-02312-x