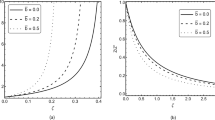
Similarity solutions for the propagation of a spherical shock wave generated by a moving piston in a nonideal gas under the influence of a gravitational field and azimuthal magnetic field with monochromatic radiation are obtained. The gravitational field is due to a central mass at the origin, i.e., the Roche model is valid. The gravitational effect of the gas itself is neglected in comparison with the attraction of the central mass at the origin. We considered that the radiation flux moves through an electrically conducting nonideal gas with constant intensity and energy is absorbed only behind the shock which moves in the direction opposite to the radiation flux. The results are discussed and compared with ones for a perfect gas, as well as for the cases of the influence of the gravitational field and of the absence of this field. The effect of the variations of the Alfven–Mach number, gravitational parameter, adiabatic exponent, and of the parameter of gas nonidealness are discussed in details.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Ro and C. D. Matzner, Shock dynamics in stellar outbursts. I. Shock formation, Astrophys. J., 841, 1–9 (2017).
L. Dessart, E. Livne, and R. Waldman, Shock-heating of stellar envelopes: A possible common mechanism at the origin of explosions and eruptions in massive stars, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 405, 2113–2131 (2010).
L. D. Landau and E. M. Lifshitz, Fluid Mechanics, Pergamon Press, Oxford (1959).
L. Biermann, Zur Deutung der chromosphärischen Turbulenz und des Exzesses der UV-Strahlung der Sonne, Naturwissenschaften, 33, 118–119 (1946).
L. Biermann, Über die Ursache der chromosphärischen Turbulenz und des UV-Exzesses der Sonnenstrahlung, Z. Astrophys., 25, 161–177 (1948).
G. Nath and J. P. Vishwakarma, Similarity solution for the fl ow behind a shock wave in a non-ideal gas with heat conduction and radiation heat flux in magnetogasdynamics, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat., 19, 1347–1365 (2014).
E. N. Parker, Interplanetary Dynamical Processes, Interscience, New York (1963).
M. N. Director and E. K. Dabora, Predictions of variable energy blast waves, AIAA J., 15, 1315–1321 (1977).
M. H. Rogers, Similarity flows behind strong shock waves, Q. J. Mech. Appl. Math., 11, 411–422 (1958).
E. K. Dabora, Variable energy blast waves, AIAA J., 10, 1384–1386 (1972).
J. S. Shang, Recent research in magneto-aerodynamics, Prog. Aerosp. Sci., 21, 1–20 (2001).
R. M. Lock and A. J. Mestel, Annular self-similar solution in ideal gas magnetogasdynamics, J. Fluid Mech., 74, 531–554 (2008).
L. Hartmann, Accretion Processes in Star Formation, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1998).
B. Balick and A. Frank, Shapes and shaping of planetary nebulae, Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys., 40, 439–486 (2002).
S. I. Anisimov and O. M. Spiner, Motion of an almost ideal gas in the presence of a strong point explosion, J. Appl. Math. Mech., 36, 883–887 (1972).
C. C. Wu and P. H. Roberts, Shock wave propagation in a sonoluminescing gas bubble, Phys. Rev. Lett., 70, 3424–3427 (1993).
P. H. Roberts and C. C. Wu, Structure and stability of a spherical implosion, Phys. Lett. A, 213, 59–64 (1996).
M. P. Ranga Rao and N. K. Purohit, Self-similar piston problem in non-ideal gas, Int. J. Eng. Sci., 14, 91–97 (1976).
J. P. Vishwakarma and G. Nath, Similarity solutions for the flow behind an exponential shock in a non-ideal gas, Meccanica, 42, 331–339 (2007).
G. Nath, Propagation of a cylindrical shock wave in a rotational axisymmetric isothermal flow of a non-ideal gas in magnetogasdynamics, Ain Shams Eng. J., 3, 393–401 (2012).
G. Nath, Self-similar solution of cylindrical shock wave propagation in a rotational axisymmetric mixture of a non-ideal gas and small solid particles, Meccanica, 47, 1797–1814 (2012).
G. Nath, Similarity solutions for unsteady flow behind an exponential shock in an axisymmetric rotating non-ideal gas, Meccanica, 50, 1701–1715 (2015).
L. I. Sedov, Similarity and Dimensional Methods in Mechanics, Academic Press, New York (1959).
R. E. Marshak, Effect of radiation on shock wave behaviour, Phys. Fluids, 1, 24–29 (1958).
L. A. Elliott, Similarity methods in radiation hydrodynamics, Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. A, 258, 287–301 (1960).
K. C. Wang, Piston problems with thermal radiation, J. Fluid Mech., 20, 447–555 (1964).
J. B. Helliwell, Self-similar piston problem with radiative heat transfer, J. Fluid Mech., 37, 497–512 (1969).
J. R. Nicastro, Similarity analysis of radiative gas dynamics with spherical symmetry, Phys. Fluids, 13, 2000–2006 (1970).
G. Deb-Ray and J. B. Bhowmick, Similarity solutions for expansions in stars, Ind. J. Pure Appl. Math., 7, 96–103 (1976).
V. M. Khudyakov, The self-similar problem of the motion of a gas under the action of monochromatic radiation, Soviet Phys. Dokl. (Trans. Am. Inst. Phys.), 28, 853–855 (1983).
A. N. Zheltukhin, A family of exact solutions of the equations of the one-dimensional motion of a gas under the influence of monochromatic radiation, J. Appl. Math. Mech., 52, 262–263 (1988).
O. Nath and H. S. Takhar, Propagation of cylindrical shock waves under the action of monochromatic radiation, Astrophys. Space Sci., 166, 35–39 (1990).
O. Nath and H. S. Takhar, Spherical MHD shock waves under the action of monochromatic radiation, Astrophys. Space Sci., 202, 355–362 (1993).
O. Nath, A study of self-similar cylindrical MHD shock waves in monochromatic radiation, Astrophys. Space Sci., 155, 163–167 (1989).
O. Nath, Propagation of cylindrical shock waves in a rotating atmosphere under the action of monochromatic radiation, Il Nuovo Cimento D, 20, 1845–1852 (1998).
J. P. Vishwakarma and V. K. Pandey, Self-similar flow under the action of monochromatic radiation behind a cylindrical MHD shock in a non-ideal gas, Appl. Math., 2, 28–33 (2012).
P. Carrus, P. Fox, F. Hass, and Z. Kopal, The propagation of shock waves in a stellar model with continuous density distribution, Astrophys. J., 113, 496–518 (1951).
M. H. Rogers, Analytic solutions for blast wave problem with an atmosphere of varying density, Astrophys. J., 152, 478–493 (1957).
S. N. Ojha, H. S. Takhar, and O. Nath, Dynamical behaviors of an unstable magnetic star, J. MHD Plasma Res., 8, 1–14 (1998).
J. B. Singh, A self-similar flow in a generalized Roche mode with increasing energy, Astrophys. Space Sci., 88, 269–275 (1988).
J. P. Vishwakarma and G. Nath, Spherical shock wave generated by a moving piston in mixture of a non-ideal gas and small solid particles under a gravitational field, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat., 17, 2382–2393 (2012).
G. Nath, Self-similar flow behind a spherical shock wave in a non-ideal dusty gas under the gravitational field: Isothermal flow, Adv. Space Res., 52, 1304–1313 ( 2013).
D. Summers, An idealized model of a magnetohydrodynamic spherical blast wave applied to a flare produced shock in the solar wind, Astron. Astophys., 45, 151–158 (1975).
P. Rosenau, Equatorial propagation of axisymmetric magnetohydrodynamic shocks. II, Phys. Fluids, 20, 1097–1103 (1977).
Ya. B. Zel'dovich and Yu. P. Raizer, Physics of Shock Waves and High Temperature Hydrodynamic Phenomena, Vol. II, Academic Press, New York (1967).
P. Rosenau and S. Frankenthal, Equatorial propagation of axisymmetric magnetohydrodynamic shocks, Phys. Fluids, 19, 1889–1899 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Inzhenerno-Fizicheskii Zhurnal, Vol. 93, No. 4, pp. 943–955, July–August, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nath, G. Spherical Shock Generated by a Moving Piston in a Nonideal Gas under Gravitation Field with Monochromatic Radiation and Magnetic Field. J Eng Phys Thermophy 93, 911–923 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-020-02193-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-020-02193-6