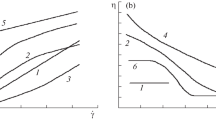
An exact solution of rheology equations, which is possible for a layered two-phase material simplest of structure, is used as a tool for testing concepts and rheological equations obtained on the basis of the existing structural models of disperse systems and for ranking the models by the extent to which the excluded-volume effect is taken account of in them. Consideration has been given to the features of flow of layered systems in which the dispersed phase is a continuous impermeable medium, an elastic material, and a coagulation structure permeable to a dispersion medium. In the context of the model of flow of layered systems, the authors interpret the flow regime observed experimentally, the so-called “stress plateau,” which is characteristic of liquid crystalline structures and polymer melts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Reiner, Rheology, Springer-Verlag, Berlin–Güttingen–Heidelberg (1958).
V. N. Matveenko and E. A. Kirsanov, Non-Newtonian Flow of Disperse, Polymer, and Liquid Crystalline Systems. Structural Approach [in Russian], Tekhnosfera, Moscow (2016).
T. F. Tadros, Rheology of Dispersions: Principles and Applications, Wiley-VCH Verlag & Co., Weinheim, Germany (2010).
H. L. Frisch and R. Simha, Viscosity of colloidal dispersions and solutions containing macromolecules, in: F. R. Eirich (Ed.), Rheology: Theory and Applications, Vol. 1, Academic Press, New York (1956).
J. V. Robinson, The viscosity of suspensions of spheres, J. Phys. Chem., 53, No. 7, 1042–1056 (1949).
V. Vand, Viscosity of solutions and suspensions. I. Theory, J. Phys. Chem., 52, No. 2, 277–299 (1948).
H. C. Brinkman, The viscosity of concentrated suspensions and solutions, J. Chem. Phys., 20, No. 4, 571 (1952).
M. Mooney, The viscosity of a concentrated suspension of spherical particles, J. Colloid Sci., 6, No. 2, 162–170 (1951).
E. E. Bibik and E. A. Popova, Fractal model of a coagulating suspension, Zh. Prikl. Khim., 73, Issue 1, 19–23 (2000).
E. E. Bibik, Kinetics of structuring and separation of phases of a disperse system in a gravity field, Zh. Prikl. Khim., 70, Issue 8, 1258–1262 (1997).
E. E. Bibik, Fractal aggregates, rheological and magnetic properties of magnetic liquids, Sixth Int. Conf. on Magnetic Fluids, July 20–24, 1992, Paris (1992), Programme and Abstracts, P3/48, pp. 392–393.
E. E. Bibik, N. S. Gamov, and N. M. Gribanov, Fractal aggregates and rheological properties of ferromagnetic fluids, V All-Union Conf. on the Physics of Magnetic Fluids, September 18–20, 1990, Abstracts of Papers, Perm (1990), pp. 28–30.
E. E. Bibik and V. E. Skobochkin, Friction torque in a rotating field and the magnetorheological effect in colloidal ferromagnetics, J. Eng. Phys. Thermophys., 22, No. 4, 474–478 (1972).
E. E. Bibik, Physics, chemistry, and technology of disperse systems (colloidal chemistry), in: New Reference Book of a Chemist and a Technologist. Volume: Electrode Processes. Chemical Kinetics and Diffusion. Colloidal Chemistry [in Russian], ANONPO “Professional,” St. Petersburg (2004), pp. 547–830.
M. Youssry, L. Coppola, I. Nicotera, and C. Morán, Swollen and collapsed lyotropic lamellar rheology, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 321, 459–467 (2008).
K. Mortensen, Structural studies of lamellar surfactant systems under shear, Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci., 6, 140–145 (2001).
W. Richtering, Rheology and shear induced structures in surfactant solutions, Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci., 6, 446–450 (2001).
L. Porcar, G. G. Warr, W. A. Hamilton, and P. D. Butler, Shear-induced collapse in a lyotropic lamellar phase, Phys. Rev. Lett., 95, 078302 (2005).
S. Fujii, S. Komura, and C.-Y. D. Lu, Structural rheology of the smectic phase, Materials, 7, 5146–5168 (2014).
J. Zipfel, P. Lindner, M. Tsianou, P. Alexandridis, and W. Richtering, Shear-induced formation of multilamellar vesicles (“Onions”) in block copolymers, Langmuir, 15, No. 8, 2599–2602 (1999).
P. Versluis, J. C. van de Pas, and J. Mellema, Microstructure and rheology of lamellar liquid crystalline phases, Langmuir, 13, 5732–5738 (1997).
J. Zhao, Z. N. Wang, X. L. Wei, F. Liu, W. Zhou, X. L. Tang, and T. H. Wu, Phase behavior and rheological properties of the lamellar liquid crystals formed in dodecyl polyoxyethylene-polyoxypropylene ether/water system, Indian J. Chem., 50A, 641–649 (2011).
O. Henrich, K. Stratford, D. Marenduzzo, P. V. Coveney, and M. E. Cates, Rheology of lamellar liquid crystals in two and three dimensions: A simulation study, Soft Matter, 8, 3817–3831 (2012).
M. G. Berni, C. J. Lawrence, and D. Machin, A review of the rheology of the lamellar phase in surfactant systems, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 98, 217–243 (2002).
J. P. Rothstein, Strong flows of viscoelastic wormlike micelle solutions, Rheology Rev., 1–46 (2008).
E. Cappelaere, J. F. Berret, J. P. Decruppe, R. Cressely, and P. Lindner, Rheology, birefringence, and small-angle neutron scattering in a charged micellar system: Evidence of a shear-induced phase transition, Phys. Rev. E, 56, No. 2, 1869–1878 (1997).
V. N. Matveenko and E. A. Kirsanov, Viscosity and structure of disperse systems, Vestn. Moskovsk. Univ., Ser. 2. Khimiya, 52, No. 4, 243–276 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Inzhenerno-Fizicheskii Zhurnal, Vol. 93, No. 4, pp. 870–881, July–August, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bibik, E.E., Sivtsov, E.V. & Rodinova, V.D. Excluded Volume in Microrheological Models of Structured Suspensions. J Eng Phys Thermophy 93, 839–849 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-020-02186-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-020-02186-5