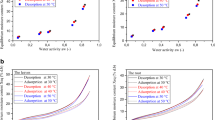
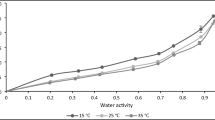
The aim of this work is to determine the sorption isotherms of Launeae nudicaulis, a medicinal plant growing in south-west of Algeria. The equilibrium moisture content was measured, using the static gravimetric method, with the water activity from 6.3 to 89.8% at 30 and 40°C. It was shown that at higher water activities the moisture content increases sharply with the temperature, resulting in crossing of the isotherm curves. Four models were applied for analyzing experimental data (namely, the Peleg, GAB, Henderson–Thompson, and the BET modified ones). The desorption and adsorption data showed the best correlation with the Peleg model. The isosteric sorption heat of water was determined from the equilibrium data at different temperatures. This heat was shown to decrease as the moisture content increases and to be a polynomial function of the moisture content.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Brunauer, The Adsorption of Gases and Vapors, Princenton University Press, Princenton, New York (1945).
M. Daguenet, Les Séchoirs Solaires: Théorie et Pratique, Publication de l′UNESCO, Paris (1985).
D. W. Sun and J. L. Woods, The selection of sorption isotherm equations for wheat based on the fitting of available data, J. Stored Products Res., 30, 27–47 (1994).
D. W. Sun and J. L. Woods, Simulation of the heat and moisture transfer process during drying in deep grain beds, Drying Technol., 15, 2479–2508 (1997).
D. W. Sun and J. L. Woods, Deep bed simulation of the cooling of stored grain with ambient air: A test bed for ventilation control strategies, J. Stored Products Res., 33, 229–312 (1998).
X. D. Chen, A new sorption equilibrium isotherm model, Food Res. Int. J., 30, 755–759 (1997).
N. Arslanand and H. Togrul, Moisture sorption isotherms for crushed chillies, Biosyst. Eng., 90, 47–61 (2005).
M. L. Medeiros, A. I. Bartolomeu Ayrosa, R. N. M. Pitombo, and S. C. Da Silva Lannes, Sorption isotherms of cocoa and cupuassu products, J. Food Eng., 73, 402–406 (2006).
S. R. Baquar, Medicinal and Poisonous Plants of Pakistan, Printas Press, Karachi (1989).
A. Cheriti, N. Belboukhari, and S. J. Hacini, Ethnopharmacological survey and phytochemical screening of some medicinal Asteraceae from Algerian Sahara, PhytoChem. BioSub. J., 7, No. 2 (2013).
S. Rashid, M. Ashraf, S. Bibi, and R. Anjum, Antibacterial and antifungal activites of Launaea nudicaulis (Roxb.) and Launaea resedifolia (Linn.), Pak. J. Bio. Sci., 3, 630–632 (2000).
F. Mansoor and I. Anis, Chemical studies of Launaea nudicaulis Hook.f. extracts with antioxidant and urease inhibitory activities, J. Chem. Soc. Pak., 35, 233–237 (2013).
S. Rashid, M. Ashraf, S. Bibi, and R. Anjum, Insecticidal and cytotoxic activities of Launaea nudicaulis (Roxb.) and Launaea Resedifolia (Linn.), Pak. J. Biol. Sci., 3, 808–809 (2000).
D. Ali, S. M. S. Hussain, A. Malik, and Z. J. Ahmed, Chemical constituents of the Genus Launaea, Chem. Soc. Pak., 25, 341–347 (2003).
M. Saleem, S. Parveen, N. Riaz, M. N. Tahir, M. Ashraf, I. Afzal, M. S. Ali, A. Malikand, and A. Jabbar, New bioactive natural products from Launaea nudicaulis, Phytochem. Lett., 5, 793–799 (2012).
C. Van den Berg and S. Bruin, Water activity and its estimation in food systems: Theoretical aspects, in: L. B. Rockland and G. F. Stewart (Eds.), Water Activity: Influences on Food Quality, Academic Press, New York (1981), pp. 1–61.
Moisture Relationship of Pant-Based Agricultural Products, ASAE Standard D245.5, American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, St. Joseph, Michigan (1995).
D. Ricardo, P. Andrade, M. Roberto Lemus, E. Carmen, and C. Pérez, Models of sorption isotherms for food: Uses and limitations, Vitae: Revista de la Facultad de Química Farmacéutica, 18, 325–334 (2011).
H. Bizot, N. Riou, and J.-L. Multon, Guide pratique pour la détermination des isothermes et de l′activité de l′eau, Sci. Aliments, numéro hors-série (1987).
M. Kouhila, A. Belghit, and M. Daguenet, Approche expérimentale des isothermes de sorption de la menthe en vue d′un séchage par énergie solaire, Rev. Energ. Renouv., 2, 61–68 (1999).
G. Yu, L. Mazza, and D. S. Jayas, Moisture sorption of characteristics of freeze-dried, osmo-dried and osmo-air dried cherries, Trans. ASAE, 42, 141–147 (1999).
S. Brunauer, P. H. Emmett, and E. Teller, Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 60, 309–319 (1938).
M. Kouhila, N. Kechaou, M. Otmani, M. Fliyou, and S. Lahsasni, Experimental study of sorption isotherms and drying kinetics of Moroccan Eucalyptus globulus, Drying Technol., 20, 2027–2039 (2002).
S. Aregba, Effect of temperature on the moisture sorption isotherm of a biscuit containing processed mango (Mangifera indica) kernel flour, J. Food Eng., 48, 121–125 (2002).
M. A. Basunia and T. Abe, Moisture desorption isotherms of medium-grain rough rice, J. Stored Products Res., 37, 205–219 (2001).
A. Belghit, M. Kouhila, and B. C. Boutaleb, Experimental study of drying kinetics by forced convection of aromatic plants, Energy Convers. Manage., 44, 1303–1321 (2000).
N. Ouafi , H. Moghrani, N. Benaouada, N. Yassaa, R. Maachi, and R. Younsi, Moisture sorption isotherms and heat of sorption of Algerian bay leaves, Maderas: Ciencia Tecnol., 17, 759–772 (2015).
S. Lahsasni, M. Kouhila, M. Mahrouz, and N. Kechaou, Experimental study and modelling of adsorption and desorption isotherms of prickly pear peel (Opuntia ficus indica), J. Food Eng., 55, 201–207 (2002).
N. Moshsenin, Physical Properties of Plant and Animal Materials, Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, New York (1986).
S. S. H. Rizvi, Thermodynamics properties of foods in dehydration, in: M. A. Rao, S. S. H. Rizvi, and A. K. Datta (Eds.), Engineering Properties of Food, 3rd edn., CRC Press, New York (2005), pp. 239–326.
R. J. Aguerre, C. Suarez, and P. E. Viollaz, The temperature dependence of isosteric heat of sorption of some cereal grains, Int. J. Food Sci. Technol., 23, 141–145 (1988).
C. Chen, Obtaining the isosteric sorption heat directly by sorption isotherm equations, J. Food Eng., 74, 178–185 (2006).
C. Perez-Alonso, C. I. Beristain, C. Lobato-Calleros, M. E. Rodriguez-Huezo, and E. J. Vernon-Carter, Thermodynamic analysis of the sorption isotherms of pure and blended carbohydrate polymers, J. Food Eng., 77, 753–760 (2006).
M. Vullioud, C. A. Marquez, and A. De Michelis, Equilibrium sorption isotherms and isosteric heat of rose hip fruits (Rosa eglanteria), Int. J. Food Properties, 9, 823–833 (2006).
S. Samapundo, F. Devlieghere, B. De Meulenaer, A. Atukwase, Y. Lamboni, and J. M. Debevere, Sorption isotherms and isosteric heats of sorption of whole yellow dent corn, J. Food Eng., 79, 168–175 (2007).
N. Bahloul, N. Boudhrioua, and N. Kechaou, Moisture desorption–adsorption isotherms and isosteric heats of sorption of Tunisian olive leaves (Olea europaea 294 L.), Ind. Crops Prod., 28, 162–176 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Published in Inzhenerno-Fizicheskii Zhurnal, Vol. 93, No. 4, pp. 846–856, July–August, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fedol, A., Cheriti, A. & Ouahrani, M.R. Study of the Moisture Sorption Isotherms and Isosteric Heat of Sorption of the Medicinal Plant Launeae Nudicaulis from Algerian Sahara. J Eng Phys Thermophy 93, 816–826 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-020-02184-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-020-02184-7