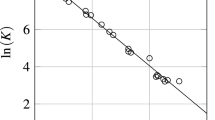
The authors have proposed a method to model the thermodynamic equilibrium of the two-phase multicomponent system “solution–vapor” by solving a system of ordinary differential equations following from the principles of nonequilibrium thermodynamics and statistical physics. Calculation of the thermodynamics of liquid and vapor phases was based on the equation of state. During the solution of the system of ordinary differential equations, the authors determined the molar volumes of the solution and the vapor, the molar composition of the phases, and the pressures of the onset of boiling of the solution and condensation of the vapor. The proposed method is fundamentally different from the popular empirical Rachford–Rice method. Results of calculating with this method have been presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. S. Glebov and G. A. Kliger, Molecular-mass distribution of Fischer–Tropsch synthesis products, Usp. Khim., 2, No. 1, 192–202 (1994).
I. V. Derevich, V. S. Ermolaev, N. V. Zol’nikova, and V. Z. Mordkovich, Thermodynamics of formation of solid paraffins in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis products, Teor. Osn. Khim. Tekhnol., 47, No. 3, 243–252 (2013).
H. H. Rachford and J. D. Rice, Procedure for use of electronic digital computers in calculating flash vaporization hydrocarbon equilibrium, J. Pet. Technol., 4, No. 1, 19–23 (1952).
M. L. Michelsen, The isothermal flash problem. Part I. Stability, Fluid Phase Equilib., 9, No. 1, 1–19 (1982).
M. L. Michelsen, The isothermal flash problem. Part II. Phase-split calculation, Fluid Phase Equilib., 9, No. 2, 21–40 (1982).
D. V. Nichita and C. F. Leibovici, Improved solution windows for the resolution of the Rachford–Rice equation, Fluid Phase Equilib., 452, No. 25, 69–73 (2017).
R. Juanes, A robust negative flash based on a parameterization of the tie-line field, Fluid Phase Equilib., 267, No. 1, 6–17 (2008).
D. V. Nichita and S. Gomez, Efficient and reliable mixture critical points calculation by global optimization, Fluid Phase Equilib., 291, No. 2, 125–140 (2010).
H. A. Zhang, Review on global optimization methods for phase equilibrium modeling and calculations, Open Thermodyn. J., 5, No. 1, 71–92 (2011).
Y. S. Wei and R. J. Sadus, Equations of state for the calculation of fluid-phase equilibria, Exp. Thermodyn., 46, No. 1, 169–196 (2000).
D.-Y. Peng and D. B. Robinson, A new two-constant equation of state, Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam., 15, No. 1, 59–64 (1976).
F. L. Román, A. Mulero, and F. Cuadros, Simple modifications of the van der Waals and Dieterici equations of state: vapor–liquid equilibrium properties, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 6, No. 23, 5402–5409 (2004).
J. S. Lopez-Echeverry, S. Reif-Acherman, and E. Araujo-Lopez, Peng–Robinson equation of state: 40 years through cubics, Fluid Phase Equilib., 447, 39–71 (2017).
A. Anderko, Cubic and generalized Van der Waals equations, Exp. Thermodyn., 5, 75–126 (2000).
S. B. Kiselev and D. G. Friend, Cubic crossover equation of state for mixtures, Fluid Phase Equilib., 162, Nos. 1–2, 51–82 (1999).
B. I. Lee and M. G. Kesler, A generalized thermodynamic correlation based on three-parameter corresponding states, AIChE J., 21, No. 3, 510–527 (1975).
N. F. Carnahan and K. E. Starling, Equation of state for nonattracting spheres, J. Chem. Phys., 51, 635–636 (1969).
M. Khanpour and G. A. Parsafar, A simple method of generating equations of state for hard sphere fluid, Chem. Phys., 333, Nos. 2–3, 208–213 (2007).
A. A. Migdal, Equation of state near a critical point, Sov. Phys. JETP, 35, No. 4, 816–822 (1972).
Dong NguyenHuynh, A modified group-contribution PC-SAFT equation of state for prediction of phase equilibria, Fluid Phase Equilib., 430, 33–46 (2016).
R. T. Jacobsen, S. G. Penoncello, and E. W. Lemmon, Equations of state for fluids and fluid mixtures, Exp. Thermodyn., 5, 849–881 (2000).
L. Sun, S. B. Kiselev, and J. F. Ely, Multiparameter crossover equation of state: Generalized algorithm and application to carbon dioxide, Fluid Phase Equilib., 233, No. 2, 204–219 (2005).
P. P. Bezverkhii, V. G. Martynets, and É. V. Matizen, Nonparametric scale equation of state for fluids with account of symmetry, Zh. Éksp. Teor. Fiz., 136, No. 2 (8), 311–317 (2009).
M. L. Michelsen, A simple method for calculation of approximate phase boundaries, Fluid Phase Equilib., 98, 1–11 (1994).
T. K. S. Ritschel and J. B. Jørgensen, Computation of Phase Equilibrium and Phase Envelopes, DTU Compute-Technical Report-2017, Technical University of Denmark (2017).
H. Sun, A. Raghavan, K. Haugen, and S. Chempath, An improved isenthalpic flash algorithm based on maximization of entropy, Fluid Phase Equilib., 438, 18–28 (2017).
G. Venkatarathnam, Density marching method for calculating phase envelopes. 2. Three-phase envelopes, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 53, No. 9, 3723–3730 (2014).
M. Castier, Solution of the isochoric-isoenergetic flash problem by direct entropy maximization, Fluid Phase Equilib., 276, No 1, 7–17 (2009).
A. Firoozabadi and H. Pan, Fast and robust algorithm for compositional modeling: Part I. Stability analysis testing, SPE J., 7, No. 1, 78–89 (2002).
D. V. Nichita, New unconstrained minimization methods for robust flash calculations at temperature, volume and moles specifications, Fluid Phase Equilib., 466, 31–47 (2018).
L. D. Landau and E. M. Lifshits, Theoretical Physics. Part 1. Statistical Physics [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1976).
I. Gyarmati, Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics [Russian translation], Mir, Moscow (1974).
S. M. Walas, Phase Equilibria in Chemical Engineering. Part 1 [Russian translation], Mir, Moscow (1989).
S. M. Walas, Phase Equilibria in Chemical Engineering. Part 2 [Russian translation], Mir, Moscow (1989).
V. B. Kogan and V. V. Fridman, Equilibrium Between a Liquid and a Vapor [in Russian], Book 2, Nauka, Moscow–Leningrad (1966).
V. I. Klyatskin, Dynamics of Stochastic Systems [in Russian], Fizmatlit, Moscow (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Inzhenerno-Fizicheskii Zhurnal, Vol. 93, No. 2, pp. 259–273, March–April, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Derevich, I.V., Panova, A.A. Calculation of the Thermodynamic Equilibrium of a Multicomponent Two-Phase System Based on Minimization of the Gibbs Potential. J Eng Phys Thermophy 93, 247–260 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-020-02115-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-020-02115-6