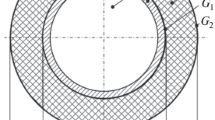
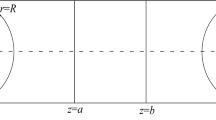
The paper presents the technique of computing flow and heat transfer of water in a pipeline whose initial temperature is lower than the freezing point of water. A feature of the method is the possibility of calculating the process from the moment of pouring water into a pipe on the inner surface of whose wall a layer of ice is being formed. The system of equations describing the process involves nonstationary energy equations for the water flow, ice layer, and for the pipe wall. It is solved for each section of the pipeline passed by water in a small time interval in the process of filling the pipe and further flow. The Beginning computer program has been created and implemented in the Visual Basic language for numerical analysis of the process. The calculations made with the aid of this program allow one to estimate the possibility of appearance of an ice plug in the pipeline at the given temperature, water flow rate, pipeline diameter, and conditions of external heat transfer of water flow in the pipeline.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. A. Bogoslovskii, Ice Regime of the Pipelines of Hydroelectric Power Stations [in Russian], Gosénergoizdat, Moscow–Leningrad (1950).
D. A. Nusupbekova, Thermal Regime of Above-Ground Pipelines in Winter Conditions [in Russian], Nauka KazSSR, Alma-Ata (1988).
V. M. Zhidkikh and Yu. A. Popov, Ice Regime of Pipelines [in Russian], Énergiya, Leningrad (1979).
B. A. Krasovitskii, Thermal and hydraulic conditions in a pipeline carrying a liquid, J. Eng. Phys. Thermophys., 35, Issue 1, 849–853 (1978).
T. Hirata and H. Matsuzawa, A study of ice-formation phenomena on freezing of flowing water in a pipe, Trans. ASME, J. Heat Transf., No. 3, 154–161 (1988).
R. D. Zerkle and J. E. Sunderland, The effect of liquid solidification in a tube upon laminar-flow heat transfer and pressure drop, Trans. ASME, J. Heat Transf., No. 2, 1–11 (1968).
Chul Cho and N. N. Ozisik, Transient freezing of liquids in turbulent flow inside tubes, Trans. ASME, J. Heat Transf., No. 3, 99–102 (1979).
N. N. Ozisik, Transient freezing of liquids in forced flow inside circular tubes, Trans. ASME, J. Heat Transf., 91, Nos. 3–4, 385–390 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Inzhenerno-Fizicheskii Zhurnal, Vol. 89, No. 4, pp. 805–811, July–August, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kitanin, É.L., Smirnov, Y.A. & Lebedev, M.E. Development of Flow and Heat Transfer During Filling a Pipeline with Water at the Pipe Wall Temperature Below the Freezing Point. J Eng Phys Thermophy 89, 808–814 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-016-1440-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-016-1440-6