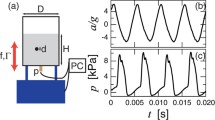
A comparison has been made between the results of numerical calculations of the vibrofluidization process of relatively large dolomite and fi ne glass particles by a granular gas hydrodynamic model and the corresponding experimental data. Good agreement is observed between the numerical calculations and the experimental data in the case of vibrofluidization of relatively thin layers of the above materials. On the basis of the obtained results, the field of use of the granular gas hydrodynamic model for describing the vibrofluidization process has been determined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. G. Loktionova, Dynamics of Vibrational Technological Processes and Machines for Processing Inhomogeneous Granular Media, Doctoral Dissertation (in Engineering), Kursk (2008).
V. G. Lyul’ko, K. K. Shugai, A. V. Lyul′ko, and S. A. Malofeeva, Development of the thermodynamic technology in a vibrating bed of powder microcomposites, Vestn. DGTU, 8, No. 1 (36), 13–30 (2008).
É. É. Lavendel (Ed.), Vibrations in Engineering, Handbook in 6 vols., Vol. 4, Vibrational Processes and Machines [in Russian], Mashinostroenie, Moscow (1981).
I. I. Blekhman, Vibrational Mechanics [in Russian], Fizmatlit, Moscow (1994).
A. S. Bodrova, Kinetic Theory of Nonequilibrium Processes in Systems of Dissipative Particles, Candidate′s Dissertation (in Physics and Mathematics), MGU, Moscow (2010).
T. W. Martin, J. M. Huntley, and R. D. Wildman, Hydrodynamic model for a vibrofluidized granular bed, J. Fluid Mech., 535, 325–345 (2005).
R. D. Wildman, T. W. Martin, J. M. Huntley, et al., Experimental investigation and kinetic-theory-based model of a rapid granular shear fl ow, J. Fluid Mech., 602, 63–79 (2008).
H. Iddir and H. Arastoopour, Modeling of multitype particle flow using the kinetic theory approach, AIChE J., 51, No. 6, 1620–1632 (2005).
D. Gidaspow, Multiphase Flow and Fluidization: Continuum and Kinetic Theory Descriptions, Academic Press, Boston (1994).
Haitao Xu, Collisional Granular Flows with and without Gas Interactions in Microgravity, Ph.D Thesis, Cornell University (2003).
N. S. Orlova, Comparison of calculations by a two-liquid vibrofluidized bed model with experimental data, Inzh.-Fiz. Zh., 85, No. 6, 1202–1207 (2012).
A. A. Revo, N. S. Orlova, G. I. Sverdlik, and E. S. Kamenetskii, Investigation of the mathematical “large particle gas” model for the vibrofluidization process, Tr. Molod. Uchen., No. 3, 11–16 (2010).
G. I. Sverdlik, A. A. Revo, E. S. Kamenetskii, and N. S. Orlova, Comparison of the results of experiments and mathematical modeling of a vibrofluidized bed, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved. Sev.-Kavk. Reg., Tekh. Nauki, No.1, 24–27 (2011).
F. H. Harlow and A. A. Amsden, Numerical calculation of multiphase flow, J. Comput. Phys., 17, 19–52 (1975).
N. S. Orlova, Testing of two vibrofluidized bed models, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved. Sev.-Kavk. Reg., Tekh. Nauki, No. 2, 42–45 (2012).
W. Kroll, Über das Verhalten von Schuttguf in lotrecht schwingenden Gefaben, Forschung, Bd. 20, Heft 1, 2–15 (1954).
G. I. Sverdlik, A. A. Revo, and E. S. Kamenetskii, Characteristic features of the slipping of a loose material from an inclined vibrating shelf, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved. Sev.-Kavk. Reg., Tekh. Nauki, No. 4, 151–152 (2008).
N. I. Gel’perin and V. G. Ainshtein, Fluidization [in Russian], Znanie, Moscow (1968).
Y. Tatemoto, Y. Mawatari, and K. Noda, Numerical simulation of cohesive particle motion in vibrated fluidized bed, Chem. Eng. Sci., 60, 5010–5021 (2005).
A. Goldshtein, M. Shapiro, L. Moldavsky, and M. Fichman, Mechanics of collisional motion of granular materials, Part 2. Wave propagation through vibrofluidized granular layers, J. Fluid Mech., 287, 349–382 (1995).
R. V. Daleffe, M. C. Ferreira, and J. T. Freire, Analysis of the effect of particle size distribution on the fluid dynamic behavior and segregation patterns of fluidized, vibrated and vibrofluidized beds, Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng., 2, 3–11 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Inzhenerno-Fizicheskii Zhurnal, Vol. 87, No. 2, pp. 429–435, March–April, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orlova, N.S. Comparison of the Results of Experimental Investigations of a Vibrofluidized Bed with Calculations by a Granular Gas Hydrodynamic Model. J Eng Phys Thermophy 87, 443–449 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-014-1030-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-014-1030-4