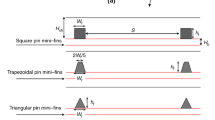
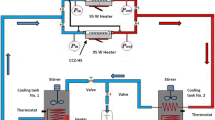
The nanofluid jet impingement heat transfer characteristics in a rectangular mini-fin heat sink are studied. The heat sink is fabricated from aluminum by a wire electrical discharge machine. The nanofluid is a mixture of deionized water and nanoscale TiO2 particles with a volume nanoparticle concentration of 0.2%. The results obtained for nanofluid jet impingement cooling in the rectangular mini-fin heat sink are compared with those found in the water jet impingement cooling. The effects of the inlet temperature of the nanofluid, its Reynolds number, and the heat flux on the heat transfer characteristics of the rectangular mini-fin heat sink are considered. It is found that the average heat transfer rates for the nanofluid as coolant are higher than those for deionized water.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
X. F. Peng and G. P. Peterson, Convective heat transfer and flow friction for water flow in microchannel structures, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 39, No. 2, 2599–2608 (1996).
T. M. Adams, S. l. Abdel-Khalik, S. M. Jeter, and Z. H. Qureshis, An experimental investigation of singlephase forced convection in microchannels, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 41, No. 8, 851–857 (1996).
C. Gillot, A. Bricard, and C. Schaeffer, Single- and two-phase heat exchangers for power electronic components, Int. J. Thermal Sci., 39, No. 2, 826–832 (2000).
W. Qu and I. Mudawar, Experimental and numerical study of pressure drop and heat transfer in a single-phase microchannel heat sink, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 45, No. 3, 2549–2565 (2002).
G. Hetsroni, A. Mosyak, Z. Segal, and G. Ziskind, A uniform temperature heat sink for cooling of electronic devices, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 45, No. 1, 3275–3286 (2002).
B. Agostini, B. Watel, A. Bontemps, and B. Thonon, Friction factor and heat transfer coefficient of R134a liquid flow in mini-channels, Appl. Thermal Eng., 22, No. 5, 1821–1834 (2002).
B. Agostini, B. Watel, A. Bontemps, and B. Thonon, Liquid flow friction factor and heat transfer coefficient in small channels: an experimental investigation, Exp. Thermal Fluid Sci., 28, No. 2, 97–103 (2004).
W. Owhaib and B. Palm, Experimental investigation of single-phase convective heat transfer in circular microchannels, Exp. Thermal Fluid Sci., 28, No. 6, 105–110 (2004).
J. Yue, G. Chen, and Q. Yuan, Pressure drops of single and two-phase flows through T-type microchannel mixers, Chem. Eng. J., 102, No. 4, 11–24 (2004).
F. F. Abdelall, G. Hahn, S. M. Ghiasian, S. I. Abdel-Khalik, S. S. Jeter, M. Yoda, and D. L. Sadowski, Pressure drop caused by abrupt flow area changes in small channels, Exp. Thermal Fluid Sci., 29, No. 8, 425–434 (2005).
P. S. Lee, S. V. Garimella, and D. Liu, Investigation of heat transfer in rectangular microchannels, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 48, No. 2, 1688–1704 (2005).
H. Y. Zhang, D. Pinjala, T. N. Wong, K. C. Toh, and Y. K. Joshi, Single phase liquid cooled microchannel heat sink for electronic packages, Appl. Thermal Eng., 25, No. 5, 1472–1487 (2005).
S. Shen, J. L. Xu, J. J. Zhou, and Y. Chen, Flow and heat transfer in microchannels with rough wall surface, Energy Convers. Manag., 47, No. 6, 1311–1325 (2006).
T. P. Brackbill, Effect of triangular roughness elements on pressure drop in microchannels and minichannels, in: Proc. ICNMM 2006, Fourth Int. Conf. on Nanochannels, Microchannels, and Minichannels’, June 19–21, 2006, Limerick, Ireland (2006).
M. E. Steinke and S. G. Kandlikar, Single phase liquid friction factors in microchannels, Int. J. Thermal Sci., 45, No. 1, 1073–1083 (2006).
P. Hrnjak and X. Tu, Single phase pressure drop in microchannels, Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow, 28, No. 7, 2–14 (2007).
X. L. Xie, Z. J. Liu, Y. L. He, and W. Q. Tao, Numerical study of laminar heat transfer and pressure drop characteristics in a water-cooled minichannel heat sink, Appl. Thermal Eng., 29, No. 5, 64–74 (2009).
S. Geedipalli, A. K. Datta, and V. Rakesh, Heat transfer in a combination microwave–jet impingement oven, Food Bioprod. Process., 86, No. 2, 53–63 (2008).
M. K. Sung and I. Mudawar, Single-phase and two-phase heat transfer characteristics of low temperature hybrid micro-channel/micro-jet impingement cooling module, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 51, No. 3, 3882–3895 (2008).
M. F. Koseoglu and S. Baskaya, The effect of flow field and turbulence on heat transfer characteristics of confined circular and elliptic impinging jets, Int. J. Thermal Sci., 47, No. 8, 1332–1346 (2008).
M. F. Koseoglu and S. Baskaya, Experimental and numerical investigation of natural convection effects on confined impinging jet heat transfer, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 52, No. 1, 1326–1336 (2009).
V. Katti and S. V. Prabhu, Heat transfer enhancement on a flat surface with axisymmetric detached ribs by normal impingement of circular air jet, Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow, 29, No. 2, 1279–1294 (2008).
P. R. Kanna and M. K. Das, Heat transfer study of two-dimensional laminar incompressible offset jet flows, Int. J. Thermal Sci., 47, No. 1, 1620–1629 (2008).
M. Goodro, J. Park, P. Ligrani, M. Fox, and H. K. Moon, Effects of hole spacing on spatially-resolved jet array impingement heat transfer, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 51, No. 4, 6243–6253 (2008).
T. M. Jeng, S. C. Tzeng, and H. R. Liao, Flow visualizations and heat transfer measurements for a rotating pin-fin heat sink with a circular impinging jet, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 52, No. 4, 2119–2131 (2009).
C. T. Nguyen, N. Galanis, G. Polidori, S. Fohanno, C. V. Popa, and A. L. Bechec, An experimental study of a confined and submerged impinging jet heat transfer using Al2O3–water nanofluids, Int. J. Thermal Sci., 48, No. 7, 401–411 (2009).
M. A. R. Sharif and A. Banerjee, Numerical analysis of heat transfer due to confined slot-jet impingement on a moving plate, Appl. Thermal Eng., 29, No. 1, 532–540 (2009).
B. P. Whelan and A. J. Robinson, Nozzle geometry effects in liquid jet array impingement, Appl. Thermal Eng., 29, No. 9, 2211–2221 (2009).
J. Koo and C. Kleinstreuer, Laminar nanofluid flow in microheat-sinks, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 48, No. 1, 2652–2661 (2005).
R. Chein and G. Huang, Analysis of microchannel heat sink performance using nanofluids, Appl. Thermal Eng., 25, No. 3, 3104–3114 (2005).
S. P. Jang and S. U. S. Choi, Cooling performance of a microchannel heat sink with nanofluids, Appl. Thermal Eng., 26, No. 6, 2457–2463 (2006).
S. W. Kang, W. C. Wei, S. H. Tsai, and S. Y. Yang, Experimental investigation of silver nanofluid on heat pipe thermal performance, Appl. Thermal Eng., 26, No. 2, 2377–2382 (2006).
R. Chein and J. Chuang, Experimental microchannel heat sink performance studies using nanofluids, Int. J. Thermal Sci., 46, No. 5, 57–66 (2007).
J. Lee and I. Mudawar, Assessment of the effectiveness of nanofluids for single-phase and two-phase heat transfer in micro-channels, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 50, No. 2, 452–463 (2007).
C. T. Nguyen, G. Roy, C. Gauthier, and N. Galanis, Heat transfer enhancement using Al2O3–water nanofluids for an electronic liquid cooling system, Appl. Thermal Eng., 27, No. 3, 1501–1506 (2007).
C. H. Chen, Forced convection heat transfer in microchannel heat sinks, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 50, No. 1, 2182–2189 (2007).
T. H. Tsai and R. Chein, Performance analysis of nanofluid-cooled microchannel heat sinks, Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow, 28, No. 1, 1013–1026 (2007).
C. Kleinstreuer, J. Li, and J. Koo, Microfluidics of nanodrug delivery, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 51, No. 9, 5590–5597 (2008).
J. Li and C. Kleinstreuer, Thermal performance of nanofluid flow in microchannels, Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow, 29, No. 6, 1221–1232 (2008).
W. Duangtongsuk and S. Wongwises, Effect of thermophysical properties models on the predicting of the convective heat transfer coefficient for low concentration nanofluid, Int. Comm. Heat Mass Transfer, 35, No. 10, 1320–1326 (2008).
W. Duangtongsuk and S. Wongwises, Heat transfer enhancement and pressure drop characteristics of TiO2–water nanofluid in a double-tube counter flow heat exchanger, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 52, No. 7, 2059–2067 (2009).
W. Duangtongsuk and S. Wongwises, An experimental study on the heat transfer performance and pressure drop of TiO2–water nanofluids flowing under a turbulent flow regime, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 53, No. 13, 334–344 (2010).
H. W. Coleman and W. G. Steele, Experimental and Uncertainty Analysis for Engineers, John Wiley & Sons, New York (1989).
B. C. Pak and Y. I. Cho, Hydrodynamic and heat transfer study of dispersed fluids with submicron metallic oxide particles, Exp. Heat Transfer, 11, No. 1, 151–170 (1998).
Y. Xuan and W. Roetzel, Conceptions of heat transfer correlation of nanofluids, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 43, No. 2, 3701–3707 (2000).
D. A. Drew and S. L. Passman, Theory of Multicomponent Fluids, Springer, Berlin (1999).
W. Yu and S. U. S. Choi, The role of interfacial layers in the enhanced thermal conductivity of nanofluids: a renovated Maxwell model, J. Nanoparticle Res., 5, 167–171 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Inzhenerno-Fizicheskii Zhurnal, Vol. 85, No. 6, pp. 1324–1331, November–December, 2012.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naphon, P., Nakharintr, L. Nanofluid jet impingement heat transfer characteristics in the rectangular mini-fin heat sink. J Eng Phys Thermophy 85, 1432–1440 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-012-0793-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-012-0793-8