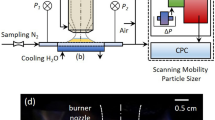
We have investigated the influence of an electric field in the form of a gas discharge on the flame pattern, the radiographic parameters of soot particles, and the yield of fullerenes and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. It has been shown that an external electric field permits controlling the processes proceeding in the flame, as well as the soot formation, and even increasing the soot yield under certain conditions. It has been established that the height of the soot packet L c and the interplanar spacing d 002 remain unchanged with increasing voltage, which is confirmed by the absence of graphitization under the action of the electric field. It has been revealed that negative polarity has a stronger effect on the increase in the yield of fullerenes with increasing voltage applied compared to positive polarity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. B. Olson and H. F. Calcote, Ions in fuel-rich and sooting acetylene and benzene flames, 18th Symp. (Int.) on Combustion, The Combust. Inst., Pittsburgh (1981), pp. 458–464.
D. G. Kell, R. J. Gill, D. B. Olson, and H. F. Calcote, Ionization and soot formation in premixed flames, 20th Symp. (Int.) on Combustion, The Combust. Inst., Pittsburgh (1984), pp. 1129–1137.
J. Lawton and F. Vainberg (V. A. Popov Ed.), Electrical Aspects of Combustion [Russian translation], Énergiya, Moscow (1976).
E. M. Stepanov and B. G. D’yachkov, Ionization in a Flame and Electric Field [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1968).
N. I. Kidin, V. B. Librovich, and G. M. Makhviladze, Electrical Properties of Laminar Flames [in Russian], Preprint No. 51 of the Institute for the Problems of Mechanics, Academy of Sciences of the USSR, Moscow (1975).
Z. A. Mansurov, A. A. Merkulov, V. T. Popov, B. K. Tuleutaev, and N. S. Almazov, Formation of ultrafine soot by methane combustion in an electric field, Khim. Tverd. Topl., No. 3, 83–86 (1994).
Z. A. Mansurov, Cool sooting flames of hydrocarbons, Therm. Sci., 10, No. 3, 269–280 (2001).
A. V. Krestinin, M. B. Kislov, A. V. Raevskii, O. I. Kolesova, and L. N. Stestik, On the formation mechanism of soot particles, Kinet. Katal., 41, No. 1, 102–111 (2000).
S. Masahiro, A. Toshihiro, and A. Masataka, Control of soot emitted from acetylene diffusion flames by applying an electric field, Combust. Flame, 119, No. 3, 356–366 (1999).
Z. A. Mansurov, B. K. Tuleutaev, V. T. Popov, Yu. M. Korolev, and A. A. Merkulov, Soot formation by lowtemperature combustion, Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva, 27, No. 1, 42–45 (1991).
N. G. Prikhod’ko, B. T. Lesbaev, T. T. Mashan, and Z. A. Mansurov, Formation of fullerens in hydrocarbon flames under the influence of electric field, Vestn. KazNU, Ser. Khim., No. 4 (36), 444–448 (2004).
Z. A. Mansurov, N. G. Prikhodko, T. T. Mashan, and B. T. Lesbaev, Study of soot formation at combustion of hydrocarbons at low pressure, Proc. 7th APISCEU, Hongkong, CD, A1-141 (2004).
P. Hebgen, A. Goel, J. B. Howard, L. C. Rainey, and J. B. Sande, Synthesis of fullerenes and fullerenic nanostructures in a low-pressure benzene/oxygen diffusion flame, Proc. Combust. Inst., 28, 1397–1404 (2000).
F. Goel, P. Hebgen, J. Sande, and J. Howard, Combustion synthesis of fullerenes and fullerenic nanostructures, Carbon, 40, 177–182 (2002).
M. Hammida, A. Fonseca, P. A. Thiry, and J. B. Nagy, Hydrocarbon combustion: a better technique for largescale production of fullerenes, in: Proc. 18th Int. Colloq. on the Dynamics of Explosions and Reactive Systems, Seattle, Washington (2001), pp. 403–407.
N. G. Prikhod’ko, B. T. Lesbaev, T. T. Mashan, and Z. A. Mansurov, Soot formation by combustion of a benzene-oxygen mixture in an electric field at a pressure of 40 Torr, Goren. Plazmokhim., 2, No. 1, 59–71 (2004).
Yu. P. Raizer, The Physics of Gas Discharge [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1987).
N. G. Prikhod’ko, B. T. Lesbaev, B. M. Tasov, and Z. A. Mansurov, Structural and radiographic characteristics of soot formed by combustion in an electric field at a low pressure, Goren. Plazmokhim., 3, 1, 41–52 (2005).
L. S. Zazhigaev, A. A. Kish’yan, and Yu. I. Romanikov, Methods of Planning and Processing Results of a Physical Experiment [in Russian], Atomizdat, Moscow (1978).
J. Warnats, U. Maas, and R. Dibble (P. A. Vlasov Ed.), Combustion. Physical and Chemical Aspects, Modeling, Experiments, Pollutant Formation [Russian translation], Fizmatlit, Moscow (2003).
K. H. Homann and H. G. Wagner, Some aspects of soot formation, in: J. Ray Bawen (Ed.), Dynamics of Exothermicity, (Combust. Sci. Technol. Book Series; Vol. 2). Carbon and Breach Publishers (1996), pp. 151–184.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Inzhenerno-Fizicheskii Zhurnal, Vol. 83, No. 1, pp. 154–161, January–February, 2010.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prikhod’ko, N.G. Influence of the electric field on the soot formation in the flame at a low pressure. J Eng Phys Thermophy 83, 171–178 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-010-0332-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-010-0332-4