Abstract
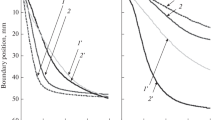
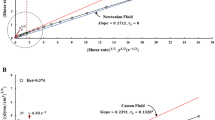
The rheological properties of the blood of donors and patients have been experimentally investigated on a rotational viscosimeter in the process of plasmapheresis at a temperature of 30°C and rates of shear ranging from 1.7 to 54.2 sec−1. The efficiency of the plasmapheresis was increased when it was performed in combination with an extracorporeal autohemomagnetotherapy. The action of the plasmapheresis and the combined action of the plasmapheresis and the extracorporeal autohemomagnetotherapy on the rheological properties of blood were compared.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. A. Nasonova and N. V. Bunchuk, Rheumatic Diseases [in Russian], Meditsina, Moscow (1997).
N. F. Soroka and V. E. Yagur, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Problems of Diagnostics and Therapy [in Russian], Belarus’, Minsk (2000).
V. V. Kirkovskii, N. P. Mit’kovskaya, F. N. Laban’, et al., Plasmapheresis and UV Irradiation of Blood in Complex Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Methodological Recommendations [in Russian], State Medical Institute, Belorussian Center of Extra-and Intracorporeal Methods of Homeostasis Correction, Minsk (2000).
V. V. Kirkovskii, V. A. Mansurov, N. P. Mit’kovskaya, and Yu. A. Mukharskaya, Influence of a variable magnetic field on the rheological properties of blood in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, Inzh.-Fiz. Zh., 76, No. 3, 199–203 (2003).
S. S. Bessmel’tsev, K. M. Abdulkadyrov, and Yu. L. Katsadze, Use of a magnetized autoblood in therapy of myelomatosis, Éfferentnaya Terapiya, 5, No. 1, 34–40 (1998).
N. Bordyushkov, I. A. Goroshinskaya, and E. M. Frantsiyants, Structural-functional changes in the erythrocyte and lymphocyte membranes under the action of a variable magnetic field, Vopr. Med. Khim., 46, No. 1, 72–80 (2000).
V. V. Lednev, Possible mechanism for the influence of weak magnetic fields on biological systems, Bioelectromagnetics, 12, 71–75 (1991).
R. Seze, C. Bouthet, and S. Tuffet, Effects of time-varying uniform magnetic fields on natural killer cell activity and antibody response in mice, Bioelectromagnetics, 14, 405–412 (1993).
J. A. Sirs, The flow of human blood through capillary tubes, J. Physiol., 442, 569–583 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
__________
Translated from Inzhenerno-Fizicheskii Zhurnal, Vol. 78, No. 5, pp. 24–26, September–October, 2005.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vilanskaya, S.V. Rheological properties of blood in the process of plasmapheresis. J Eng Phys Thermophys 78, 859–861 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-006-0004-6
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-006-0004-6