Abstract
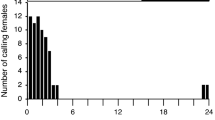
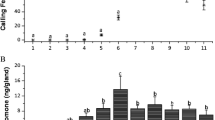
Behavioral analysis revealed that S-(+)-isopiperitenone [(S)-3-methyl-6-isopropenyl-2-cyclohexen-1-one], previously identified as an alarm pheromone, is also the female sex pheromone of Tyrophagus similis (Astigmata: Acaridae), showing maximum male attraction at a dose of 0.1 female equivalent. Although the antipode, R-(−)-isopiperitenone, was not detectable in the mite extract, this synthetic optical isomer (80% e.e.) also induced activity at a dose of 100 ng, a response indicative of S-(+)-isopiperitenone being the active compound. The average content was determined to be 38.5 ng per female and 19.8 ng per male. This is the first example of an astigmatid mite species possessing a compound that functions as an alarm as well as a sex pheromone.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi, K. 2000. Introduction of practical statics. Shinohara-syuppan shinnsha, Tokyo. (in Japanese)
Howard, R. W., Kuwahara, Y., Suzuki, H., and Suzuki, T. 1988. Pheromone study on acarid mites. XII. Characterization of the hydrocarbons and external gland morphology of the opisthonotal glands of six species of mites (Acari: Astigmata). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 23:58–66.
Kuwahara, Y. 2004. Chemical ecology in astigmatid mites, pp. 76–109, in R. T. Cardè and J. G. Millar (eds.), Advances in Insect Chemical Ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Kuwahara, Y., Fukami, H., Ishii, S., Matsumoto, K., and Wada, Y. 1980a. Pheromone study on acarid mite III. Citral: isolation and identification from four species of acarid mite, and its possible role. Jpn. J. Sanit. Zool. 31:49–52.
Kuwahara, Y., Matsumoto, K., and Wada, Y. 1980b. Pheromone study on acarid mite IV. Citral: composition and function as an alarm pheromone and its secretory gland in four species of acarid mites. Jpn. J. Sanit. Zool. 31:73–80.
Kuwahara, Y., My-Yen, L. T., Tominaga, Y., Matsumoto, K., and Wada, Y. 1982. 1,3,5,7-Tetramethyldecyl formate, lardolure: aggregation pheromone of the acarid mite, Lardoglyphus konoi (Sasa et Asanuma)(Acarina: Acaridae). Agric. Biol. Chem. 46:2283–2291.
Kuwahara, Y., Akimoto, K., Leal, W. S., Nakao, H., and Suzuki, T. 1987. Isopiperitenone: a new alarm pheromone of the acarid mite, Tyrophagus similis (Acarina, Acaridae). Agric. Biol. Chem. 51:3441–3442.
Kuwahara, Y., Asami, N., Morr, M., Matsuyama, S., and Suzuki, T. 1994. Chemical ecology of astigmatid mites XXXVIII. Aggregation pheromone and kairomone activity of lardolure and its analogues against Lardoglyphus konoi and Carpoglyphus lactis. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 29:253–257.
Kuwahara, Y., Ibi, T., Nakatani, Y., Ryouno, A., Mori, N., Sakata, T., Okabe, K., Tagami, K., and Kurosa, K. 2001. Chemical ecology of astigmatid mites LIX. Neral, the alarm pheromone of Schwiebea elongata (Acari: Acaridae). J. Acarol. Soc. Jpn. 10:19–25.
Leal, W. S., Kuwahara, Y., Suzuki, T., and Kurosa, K. 1989. β-Acaridial, the sex pheromone of the acarid mite Caloglyphus polyphyllae. Pheromone study of acarid mites, XXI. Naturwissenschaften 76:332–333.
Maruno, G., Mori, N., Nishida, R., and Kuwahara, Y. 2006. Chemical ecology of astigmatid Mites LXXXII. β-Acaridial as a female sex pheromone of the mold mite Tyrophagus putrescentiae. Jpn. J. Environ. Entomol. Zool. 16:167–173.
Mizoguchi, A., Mori, N., Nishida, R., and Kuwahara, Y. 2003. α-Acaridial a female sex pheromone from an alarm pheromone emitting mite Rhizoglyphus robini. J. Chem. Ecol. 29:1681–1690.
Mizoguchi, A., Murakami, K., Shimizu, N., Mori, N., Nishida, R., and Kuwahara, Y. 2005. S-Isorobinal as the female sex pheromone from an alarm pheromone emitting mite Rhizoglyphus setosus. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 36:107–117.
Mori, K. and Kuwahara, S. 1986a. Stereochemistry of lardolure, the aggregation pheromone of the acarid mite, Lardoglyphus konoi. Tetrahedron 42:5545–5550.
Mori, K. and Kuwahara, S. 1986b. Synthesis of both the enantiomers of lardolure, the aggregation pheromone of the acarid mite, Lardoglyphus konoi. Tetrahedron 42:5539–5544.
Mori, N. and Kuwahara, Y. 2000. Comparative studies of the ability of males to discriminate both sexes in Caloglyphus spp. J. Chem. Ecol. 26:1299–1309.
Mori, N., Kuwahara, Y., Kurosa, K., Nishida, R., and Fukushima, T. 1995. Chemical ecology of astigmatid mites XLI. n-Undecane: The sex pheromone of the acarid mite Caloglyphus rodriguezi Samsinak (Acarina: Acaridae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 30:415–423.
Mori, N., Kuwahara, Y., and Kurosa, K. 1996. Chemical ecology of astigmatid mites XLV. (2R,3R)-Epoxyneral, sex pheromone of the acarid mite, Caloglyphus sp. (Acarina: Acaridae). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 4:415–423.
Mori, N., Kuwahara, Y., and Kurosa, K. 1998. Rosefuran: a sex pheromone of the acarid mite Caloglyphus sp. J. Chem. Ecol. 24:1771–1779.
Nakao, H. and Kurosa, K. 1988. Description of four species of acarid mites newly recorded from Japan, with reference to the damage caused to crops (Acari, Astigmata). Jpn. J. Ent. Zool. 32:135–42 (in Japanese).
Nishimura, K., Shimizu, N., Mori, N., and Kuwahara, Y. 2002. Chemical ecology of astigmatid mites LXIV. The alarm pheromone neral functions as an attractant in Schwiebea elongata (Banks) (Acari: Acaridae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 37:13–18.
Sakata, T., Shimano, S., and Kuwahara, Y. 2003. Chemical ecology of oribatid mites III. Chemical composition of oil gland exudate from two oribatid mites, Trhypochthoniellus sp. and Trhypochthonius japonicus (Acari: Trhypochthoniidae). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 29:279–291.
Shimizu, N., Mori, N., and Kuwahara, Y. 2001. Aggregation pheromone activity of the female sex pheromone, β-acaridial, in Caloglyphus polyphyllae (Acari: Acaridae). Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 65:1724–1728.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported partly by a Grant-in-aid for Scientific Research (no. 22380068) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan and by Development Works for Practical Technology driving novel Policies for Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (no. 22005) from the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maruno, G., Mori, N. & Kuwahara, Y. Chemical Ecology of Astigmatid Mites LXXXVII. S-(+)-Isopiperitenone: Re-identification of the Alarm Pheromone as the Female Sex Pheromone in Tyrophagus similis (Acari: Acaridae). J Chem Ecol 38, 36–41 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-012-0059-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-012-0059-0