Abstract
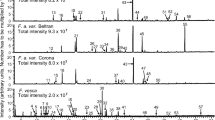
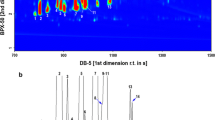
Induced responses by Norway spruce (Picea abies) seedlings to feeding damage by two mite species were studied by analyzing the volatiles emitted during infestation. Four specimens of a Norway spruce (Picea abies L.) clone were infested with mites of Nalepella sp., another four with Oligonychus ununguis, and four were kept mite-free as controls. After a year of infestation, spruce volatiles were collected, analyzed, and identified using SPME-GC-MS. In addition, enantiomers of chiral limonene and linalool were separated by two-dimensional GC. Methyl salicylate (MeSA), (-)-linalool, (E)-β-farnesene, and (E,E)-α-farnesene were the main volatiles induced by both species of mites, albeit in different proportions. The ability of the main compounds emitted by the mite-infested spruces to attract or repel the pine weevil, Hylobius abietis (L.), was tested. (E)-β-farnesene was found to be attractive in the absence of spruce odor, whereas methyl salicylate had a deterrent effect in combination with attractive spruce odor. The other tested compounds had no significant effects on the behavior of the weevils.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arimura, G.-I., Ozawa, R., Shimoda, T., Nishioka, T., Boland, W., and Takabayashi, J. 2000a. Herbivory-induced volatiles elicit defence genes in lima bean leaves. Nature 406:512-515.
Arimura, G.-I., Tashiro, K., Kuhara, S., Nishioka, T., Ozawa, R., and Takabayashi, J. 2000b. Gene responses in bean leaves induced by herbivory and by herbivory-induced volatiles. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 277:305–310.
Arimura, G.-I., Ozawa, R., Horiuchi, J.-I., Nishoika, T., and Takabayashi, J. 2001. Plant-plant interactions mediated by volatiles emitted from plants infested by spider mites. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 29:1049–1061.
Arimura, G.-I., Ozawa, R., Kugimiya, S., Takabayashi, J., and Bohlmann, J. 2004. Herbivore-induced defence response in a model legume. Two-spotted spider mites induce emission of (E)-β-ocimene and transcript accumulation of (E)-β-ocimene synthase in Lotus japonicus. Plant Physiol. 135:1976–1983.
Asaro, C., Sullivan, B. T., Dalusky, M. J., and Berisford, C. W. 2004. Volatiles associated with preferred and nonpreferred hosts of the Nantucket pine tip moth, Rhyacionia frustrana. J. Chem. Ecol. 30:977–990.
Bichão, H., Borg-Karlson, A.-K., Araujo, J., and Mustaparta, H. 2003. Identification of plant odours activating receptor neurones in the weevil Pissodes notatus F. (Coleoptera, Curculionidae). J. Comp. Physiol. 189:203–212.
Borg-Karlson, A.-K., Lindström, M., Norin, T., Persson, M., and Valterova, I. 1993. Enantiomeric composition of monoterpene hydrocarbons in different tissues of Norway spruce, Picea abies (L.) Karst. A multi-dimensional gas chromatography study. Acta Chem. Scand. 47:138–144.
Borg-Karlson, A.-K., Nordlander, G., Mudalige, A., Nordenhem, H., and Unelius, C. R. 2006. Antifeedants in the feces of the pine weevil Hylobius abietis: identification and biological activity. J. Chem. Ecol. 32: 943–957.
Bouwmeester, H. J., Verstappen, F. W. A., Posthumus, M. A., and Dicke, M. 1999. Spider mite-induced (3S)-(E)-nerolidol synthase activity in cucumber and lima bean. The first dedicated step in acyclic C11-homoterpene biosynthesis1. Plant Physiol. 121:173–180.
Byers, J. A. 1992. Attraction of bark beetles, Tomicus piniperda, Hylurgops palliates, and Trypodendron domesticum and other insects to short-chain alcohols and monoterpenes. J. Chem. Ecol. 18:2385–2402.
Byers, J. A, Zhang, Q-H., and Birgersson, G. 2000. Strategies of a bark beetle, Pityogenes bidentatus, in an olfactory landscape. Naturwissenschaften 87:503–507.
Campbell, M., and Ellis, B. E. 1992. Fungal elicitor-mediated responses in pine cell cultures. I. Induction of phenylpropanoid metabolism. Planta 186:409–417.
Cvikrová, M., Mala, J., Hrubcova, M., and Eder, J. 2006. Soluble and cell wall-bound phenolics and lignin in Ascocalyx abietina infected Norway spruce. Plant Science 170:563–570.
Davies, N. W. 1990. Gas chromatographic retention indices of monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes on methyl silicone and Carbowax 20M phases. J. Chromatogr. 503:1–24.
De Boer, J. G., and Dicke, M. 2004. The role of methyl salicylate in prey searching behaviour of the pedatory mite Phytoseiulus persimilis. J. Chem. Ecol. 30:255–271.
Delphia, C. M., Mescher, M. C., and De Moraes, C. M. 2007. Induction of plant volatiles by herbivores with different feeding habits and the effects of induced defences on host-plant selection by thrips. J. Chem. Ecol. 33:997–1012.
Dicke, M., Van Beek, T. A., Posthumus, M. A., Ben Dom, N., Van Bokhoven, H., and De Groot, A. E. 1990. Isolation and identification of volatile kairomone that affects acarine predator-prey interactions. J. Chem. Ecol. 16:381–396.
Dudareva, N., and Pichersky, E. 2000. Biochemical and molecular genetic aspects of floral scents. Plant Physiol. 122:627–633.
Dudareva, N., Raguso, R. A., Wang, J., Ross, J. R., and Pichersky, E. 1998. Floral scent production in Clarkia breweri. III. Enzymatic synthesis and emission of benzenoid esters. Plant Physiol. 116:599–604.
Dudareva, N., Murfitt, L. M., Mann, C. J., Gorenstein, N., Kolosova, N., Kish, C. M., Bonham, C., and Wood, K. 2000. Developmental regulation of methyl benzoate biosynthesis and emission in snapdragon flowers. Plant Cell 12:949–961.
Dudareva, N., Negre, F., Nagegowda, D. A., and Orlova, I. 2006. Plant volatiles: recent advances and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 25:417–440.
Ehnström, B., Petersen, B., Löyttyniemi, K., and Tvermyr, S. 1974. Insect pests in forests of the Nordic countries 1967–1971. Ann. Entomol. Fenn. 40:37–47.
Fatouros, N. E., Van Loon, J. J. A., Hordijk, K. A., Smid, H. M., and Dicke, M. 2005. Herbivore-induced plant volatiles mediate in-flight host discrimination by parasitoids. J. Chem. Ecol. 31:2033–2047.
Gang, D. R., Wang, J., Dudareva, N., Nam, K. H., Simon, J. E., Lewinsohn, E., and Pichersky, E. 2001. An investigation of the storage and biosynthesis of phenylpropenes in sweet basil. Plant Physiol. 125:539–555.
Gilman, E. F., and Watson, D. G. 1994. Picea abies Norway spruce. Environmental Horticulture Department, Fact Sheet ST-448. <http://hort.ufl.edu/trees/PICABIA.pdf>.
Grodzki, W. 1997. Changes in the occurrence of bark beetles on Norway spruce in a forest decline area in the Sudety Mountains in Poland. USDA Forest Service General Technical Report NE-236 <http://iufro-archive.boku.ac.at/wu70307/valproc/grodzk.pdf>.
Guterman, I., Masci, T., Chen, X., Negre, F., and Pichersky, E. 2006. Generation of phenylpropanoid pathway-derived volatiles in transgenic plants: rose alcohol acetyltransferase produces phenylethyl acetate and benzyl acetate in petunia flowers. Plant Mol. Biol. 60:555–563.
Heiden, A. C., Kobel, K., Langebartels, C., Schuh-Thomas, G., and Wildt, J. 2003. Emissions of oxygenated volatile organic compounds from plants. Part I: Emission from lipoxygenase activity. J. Atmos. Chem. 45:143–172.
Hiraoka, H., Mori, N., Okabe, K., Nishida, R., and Kuwahara, Y. 2003. Chemical ecology of astigmatid mites LXIX. Neryl formate [3.7-dimethyl-(Z)-2.6-octadienyl formate] as the alarm pheromone of an acarid mite, Histiogaster rotundud Woodring (Acari: Acaridae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 38:379–385.
Huber, D. P. W., Gries, R., Borden, J. H., and Pierce, H. D. 2000. A survey of antennal responses by five species of coniferophagous bark beetles (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) to bark volatiles of six species of angiosperm trees. Chemoecology 10:103–113.
Janssen, A. 1999. Plants with spider-mite prey attract more predatory mites than clean plants under greenhouse conditions. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 90:191–198.
Jeppson, L. R., Keifer, H. H., and Baker, E. W. 1975. Mites injurious to economic plants. University of California Press, Berkeley and Los Angeles.
Jourdes, M., Cardenas, C. L., Laskar, D. D., Moinuddin, S. G. A., Davin, L. B., and Lewis, N. G. 2007. Plant cell walls are enfeebled when attempting to preserve native lignin configuration with poly-p-hydroxycinnamaldehydes: evolutionary implications. Phytochemistry 68:1932–1956.
Kännaste, A., Vongvanich, N., and Borg-Karlson, A.-K. 2008. Infestation by a Nalepella species induces emissions of α- and β-farnesenes, (-)-linalool and aromatic compounds in Norway spruce clones of different susceptibility to the large pine weevil. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2:31–41.
Kielkiewicz, M., PUCHALSKA, E., and Czajkowska, B. 2005. Changes in biochemical composition of needles of ornamental dwarf spruce (Picea glauca ‘Conica’) induced by spruce spider mite (Oligonychus ununguis Jacobi, Acari: Tetranychidae) feeding. Acta Physiol. Plant. 27:463–471.
Koeduka, T., Fridman, E., Gang, D. R., Vassāo, D. G., Jackson, B. L., Kish, C. M., Orlova, I., Spassova, S. M., Lewis, N. G., Noel, J. P., Baiga, T. J., Dudareva, N., and Pichersky, E. 2006. Eugenol and isoeugenol, characteristic aromatic constituents of spices, and biosynthesized via reduction of a coniferyl alcohol ester. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103:10128–10133.
Legrand, S., Nordlander, G., Nordenhem, H., Borg-Karlson, A.-K., and Unelius, C. R. 2004. Hydroxy-methoxybenzoic methyl esters: synthesis and antifeedant activity on the pine weevil, Hylobius abietis. Z. Naturforsch. B 59:829–835.
Lehman, R. D. 1982. Mites (Acari) of Pennsylvania conifers. Trans. Amer. Entomol. Soc. 108:181–286.
Löyttyniemi, K. 1973. On the biology of Nalepella haarlovi Boczek va. Picea abietis Löyttyniemi (Acarina, Eriophyidae). Commun. Inst. For. Fenn. 73:1–16.
Martin, D. M., Fäldt, J., and Bohlmann, J. 2004. Functional characterization of nine Norway Spruce TPS genes and evolution of gymnosperm terpene synthases of the TPS-d subfamily. Plant Physiol. 135:1908–1927.
Miller, D. R., Crowe, C. M., Asaro, C., and Debarr, G. L. 2003. Dose and enantiospesific responses of white pine cone beetles, Conophthorus coniperda, to α-pinene in an eastern white pine seed orchard. J. Chem. Ecol. 29:437–451.
Morita, A., Mori, N., Nishida, R., Hirai, N., and Kuwahara, Y. 2004. Neral (the alarm pheromone) biosynthesis via the mevalonate pathway, evidenced by D-glucose-1- 13C feeding in Carpoglyphus lactis and 13C incorporation into other opisthonotal gland exudates. J. Pestic. Sci. 29:27–32.
Mumm, R., and Hilker, M. 2005. The significance of background odour for an egg parasitoid to detect plants with host eggs. Chem. Senses 30:337–343.
Mumm, R., Tiemann, T., Varama, M., and Hilker, M. 2005. Choosy egg parasitoids: specificity of oviposition-induced volatiles exploited by an egg parasitoid of pine sawflies. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 115:217–225.
Musser, R. O., Farmer, E., Peiffer, M., Williams, S. A., and Felton, G. W. 2006. Ablation of catepillar labial salivary glands: technique for determining the role of salvia in insect-plant interactions. J. Chem. Ecol. 32:981–992.
Nishimura, K., Shimizu, N., Mori, N., and Kuwahara, Y. 2002. Chemical ecology of astigmatid mites. LXIV The alarm pheromone neral functions as an attractant in Schwiebea elongate (Banks) (Acari: Acaridae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 37:13–18.
Nordlander, G. 1990. Limonene inhibits attraction to α-pinene in the pine weevils Hylobius abietis and H. pinastri. J. Chem. Ecol. 16:1307–1320.
Nordlander, G. 1991. Host finding in the pine weevil Hylobius abietis: effects of conifer volatiles and added limonene. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 59 :229–237.
Pare, P. W., and Tumlinson, J. H. 1999. Plant volatiles as a defense against insect herbivores. Plant Physiol. 121:325–331.
Park, S.-W., Kaimoyo, E., Kumar, D., Mosher, S., and Klessig, D. F. 2007. Methyl salicylate is a critical signal for plant systemic acquired resistance. Science 318:113–116.
Pettersson, E. M., Sullivan, B. T., Anderson, P., Berisford, C. W., and Birgersson, G. 2000. Odor perception in the bark beetle parasitoid Roptrocerus xylophagorum exposed to host associated volatiles. J. Chem. Ecol. 26:2507–2525.
Puchalska, E. 2006. The influence of Oligonychus ununguis Jacobi (Acari: Tetranychidae) on phytosynthetic activity and needle damage of Picea glauca ‘Conica’. Biological Lett. 43:353–360.
Ruther, J. 2000. Retention index database for identification of general green leaf volatiles in plants by coupled capillary gas chromatography-mass-spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 890:313–319.
Schultz, T. P. 1987. Role of the p-hydroxyl group in the nitrobenzene oxidation of hydroxybenzyl alcohols. J. Org. Chem. 52:279–281.
Shulaev, V., Silverman, P., and Raskin, I. 1997. Airborne signaling by methyl salicylate in plant pathogen resistance. Nature 385:718–721.
Takabayashi, J., Dicke, M., and Posthumus, M. A. 1991. Variation in composition of predator-attracting allelochemicals emitted by herbivore-infested plants: relative influence of plant and herbivore. Chemoecology 2:1–6.
Takabayashi, J., Dicke, M., and Posthumus, M. A. 1994. Volatile herbivore-induces terpenoids in plant-mite interactions: variation caused by biotic and abiotic factors. J. Chem. Ecol. 20:1329–1354.
Thiery, D., and Marion-Poll, F. 1998. Electroantennogram responses of Douglas-fir seed chalcids to plant volatiles. J. Insect Physiol. 44:483–490.
Tominaga, Y., Yamamoto, M., Kuwahara, Y., and Sugawara, R. 1984. Behavioural responses of the pinewood nematode to terpenes. Agric. Biol. Chem 48:519–520.
Van Den Boom, C. E. M., Van Beek, T. A., Posthumus, M. A., De Groot, A., and Dicke, M. 2004. Qualitative and quantitative variation among volatile profiles induced by Tetranychus urticae feeding of plant from various families. J. Chem. Ecol. 30:69–89.
Weissbecker, B., Van Loon, J. J. A., and Dicke, M. 1999. Electroantennogram responses of a predator, Perillus bioculatus, and its prey, Leptinotarsa decemlineata, to plant volatiles. J. Chem. Ecol. 25:2313–2325.
Wibe, A., Borg-Karlson, A-K., Norin, T., and Mustaparta, H. 1997. Identification of plant volatiles activating single receptor neurons in the pine weevil (Hylobius abietis). J. Comp. Physiol. 180:585–595.
Xugen, S., and Luqin, Q. 2006. Effect of volatiles from plants on the selectivity of Tetranychus viennensis for different host plants. Front. For. China 1:105–108.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Mariusz Lewandowski who identified (using photos) one of the mites as belonging to the genus Nalepella. The photos are present at the Department of Chemistry, Ecological Chemistry group, KTH. We are also grateful to Lars Lundqvist for identifying the spinning mite Oligonychus ununguis. This study was financially supported by FORMAS (Swedish Research Council for Environment, Agricultural Sciences and Spatial Planning), the Carl Trygger Foundation and an Archimedes stipend from Estonia to Astrid Kännaste.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kännaste, A., Nordenhem, H., Nordlander, G. et al. Volatiles from a Mite-Infested Spruce Clone and Their Effects on Pine Weevil Behavior. J Chem Ecol 35, 1262–1271 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-009-9708-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-009-9708-3