Abstract
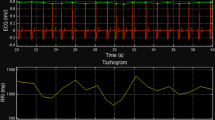
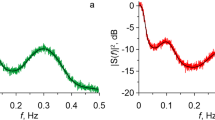
To evaluate the impact of different ECG sampling frequencies on parameters of spectral and baroreflex analysis. Spectral and baroreflex analyses were performed in the EUROBAVAR data set (46 recordings of 23 persons) using the original ECG sampling frequency of 500 Hz and – simulated – sampling frequencies of 200 and 100 Hz. For this analysis, the technique of trigonometric regressive spectral (TRS) analysis was used. In the standing position, there were no statistically significant differences in baroreflex sensitivity and frequency bands ranging from VLF to HF using 100 Hz instead of the original 500 Hz. Only the UHF band (>0.40 Hz) was significantly different. In the supine position, similar results could be described for 100 Hz, although there were slight, but significant (P < 0.05) changes in baroreflex sensitivity of around 1 ms/mmHg at the simulated 100 Hz. Using a simulated 200 Hz instead of a 500 Hz sampling frequency had no significant impact on the spectral and baroreflex parameters. The probability to demonstrate an impact of different ECG sampling frequencies was higher in people with pathologically decreased variability of RR intervals. In most of the cases, it is sufficient for spectral and baroreflex analysis by TRS to use data with an ECG sampling frequency of 100 Hz in comparison to 500 Hz. Only if there is a pathologically decreased variability of RR intervals in patients, spectral and baroreflex parameters could be significantly influenced by lower ECG sampling frequencies of up to 100 Hz, but only to a minor degree.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akselrod S, Gordon D, Madwed JB, Snidman NC, Shannon DC, Cohen RJ. Hemodynamic regulation: investigation by spectral analysis. Am J Physiol 1985; 49: H867–H875
Pagani M, Lombardi F, Guzzetti S, Rimoldi O, Furlan R, Pizzinelli P, Sandrone G, Malfatto G, Dell’Orto S, Piccaluga E, Turiel M, Baselli G, Cerutti S, Malliani A. Power spectral analysis of heart rate and arterial pressure variabilities as a marker of sympatho-vagal interaction in man and conscious dog. Circ Res 1986; 59: 178–193
Parati G, Saul JP, Rienzo MD, Manchia G. Spectral analysis of blood pressure and heart rate variability in evaluating cardiovascular regulation: a critical appraisal. Hypertension 1995; 25: 1276–1286
Parati G, Rizzoni D, Omboni S, Bernardi L, Mormino P, Rienzo MD. The analysis of blood pressure and heart rate variability: methodological aspects and interpretation of results. High Blood Press 1995; 4: 186–203
Pomeranz B, Macaulay RJB, Caudill MA, Kutz I, Adam D, Gordon D, Kilborn KM, Barger AC, Shannon DC, Cohen RJ, Benson H. Assessment of autonomic function in humans by heart rate spectral analysis. Am J Physiol 1985; 248: H151–H153
Berntson GG, Bigger JT, Eckberg DL, Grossman P, Kaufmann PG, Malik M, Nagaraja HN, Porges SW, Saul JP, Stone PH, van der Molen MW. Heart rate variability: origins, methods and interpretive caveats. Psychophysiology 1997; 34: 623–648
Patzak A, Mrowka R, Springer S, Eckard T, Ipsiroglu OS, Erler T, Hofmann S, Gramse V. Heart rate variability in the paediatric sleep laboratory – recommendations for measurement and analysis. Somnologie 2002; 6: 39–50
Patzak A, Mrowka R, Springer S, Eckard T, Ipsiroglu OS, Erler T, Hofmann S. Heart rate variability – physiology, methods of registration and application in pediatric sleep laboratory. Wien Klin Wochenschr 2000; 112(5): 234–250
Riniolo T, Porges SW. Inferential and descriptive influences on measures of respiratory sinus arrhythmia: sampling rate, R-wave trigger accuracy, and variance estimates. Psychophysiology 1997; 34: 613–621
Task Force of the ESC/ASPE. Heart rate variability. Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Eur Heart J 1996; 17: 354–381
Constant I, Laude D, Murat I, Elghozi JL. Pulse rate variability is not a surrogate for heart rate variability. Clin Sci (Lond) 97(4): 391–397, 1999
Breuer H-WM, Skyschally A, Wehr M, Schulz R, Heusch G. Poor reproducibility of parameters of heart rate variations. Z Kardiol 1992; 81: 475–481
Clifford GD, Tarassenko L. Quantifying errors in spectral estimates of HRV due to beat replacement and resampling. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 2005; 52: 630–638
Pelzer M, Hafner D, Arnold G, Schipke JD. Minimal interval length for safe determination of brief heart rate variability. Z Kardiol 1995; 84: 986–994
Sing D, Vinod K, Saxena SC. Sampling frequency of the RR interval time series for spectral analysis of heart rate variability. J Med Eng Technol 2004; 28: 263–272
Toledo E, Pinhas I, Aravot D, Akselrod S. Very high frequency oscillations in the heart rate and blood pressure of heart transplant patients. Med Biol Eng Comput 2003; 41(4): 432–438
van Steenis HG, Toulen JHM, Mulder LJM. Heart rate variability spectra based on non-equidistant sampling: the spectrum of counts and the instantaneous heart rate spectrum. Med Eng Phys 1994; 16: 355–362
Mitov IP, Daskalov IK. Comparison of heart rate variability spectra using generic relationships of their input signals. Med Biol Eng Comput 1998; 36: 573–580
Laude D, Elghozi JL, Girard A, Bellard E, Bouhaddi M, Castiglioni P, Cerutti C, Cividjian A, Di Rienzo M, Fortrat JO, Janssen BJA, Karemaker JM, Leftheriotis G, Parati G, Persson PB, Porta A, Quintin L, Regnard J, Ruediger H, Stauss HM. Correlation and differences between the various techniques used to estimate spontaneous baroreflex sensitivity—The EuroBaVar study. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2004; 286: R226–R231
Hejjel L, Roth E. What is the adequate sampling interval of the ECG signal for heart rate variability analysis in the time domain? Physiol Meas 2004; 25: 1405–1411
Laguna P, Moody GB, Mark RG. Power spectral density of unevenly sampled data by least-square analysis: performance and application to heart rate signals. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 1998; 45: 698–715
Ruediger H, Klinghammer L, Scheuch K. The trigonometric regressive spectral analysis, a method for mapping of beat-to-beat recorded cardiovascular parameters on to frequency domain in comparison with Fourier transformation. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 1999; 58: 1–15
Garcia-Gonzalez MA, Fernandez-Chimeno M, Ramos-Castro J. Bias and uncertainty in heart rate variability spectral indices due to the finite ECG sampling frequency. Physiol Meas 2004; 25: 489–504
Merri M, Farden DC, Mottley JG, Titlebaum EL. Sampling frequency of the electrocardiogram for spectral analysis of the heart rate variability. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 1990; 37: 99–106
Ruediger H, Henke S, Paditz E, Ziemssen T, Suess M, Suess F. Assessment of accuracy of ECG signal sampling for spectral analysis of beat-to-beat recorded R-R intervals in a sleep laboratory. Somnologie 2006; 10: 53–60
Thong T, Li KH, McNames J, Aboy M, Goldstein B. Accuracy of ultra-short heart rate variability measures. Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE EMBS Conference, Cancun, Mexico, Sept 17–21, 2003; 2424–2427.
Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. The Lancet 1986; 1: 307–310
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ziemssen T, Gasch J, Ruediger H. Influence of ECG sampling frequency on spectral analysis of RR intervals and baroreflex sensitivity using the EUROBAVAR data set.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ziemssen, T., Gasch, J. & Ruediger, H. Influence of ECG Sampling Frequency on Spectral Analysis of RR Intervals and Baroreflex Sensitivity Using the EUROBAVAR Data set. J Clin Monit Comput 22, 159–168 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-008-9117-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-008-9117-0