Abstract
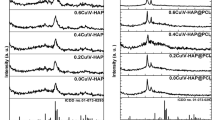
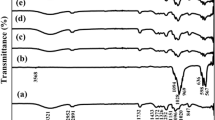
Developing wound dressing biomaterials is crucial to maintaining an appropriate health care system. Electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) encapsulated with co-doped hydroxyapatite (HAP) with [silver (Ag)/magnesium (Mg)] ions have been fabricated with a variation in Ag+ ions contributions. Besides, Ag/Mg-HAP powder forms have been investigated upon their structure. Their lattice parameters were investigated, including a-axis, and plunged slightly from 9.487 ± 0.03 to 9.467 ± 0.07 Å for the lowest and the highest additional Ag+ ions. Furthermore, the average surface roughness value increased from 16.0 nm to 25.9 nm for the lowest and the highest doped Ag+ for powdered phases, while it increased from 106.5 to 174.6 nm for the scaffold ones. The produced scaffolds were formed in random fibers distribution with diameters ranged from 3.4–7.8 to be 1.9–5.1 µm for the lowest and the highest ionic substitution. Moreover, the antibacterial effectiveness has been evaluated and showed that the inhibition zone grew from 14.8 ± 3.1 mm and 13.5 ± 4.2 mm to be 19.3 ± 3.8 mm and 17.6 ± 2.9 mm for the 0.4Ag/Mg-HAP@PVA and 0.8Ag/Mg-HAP@PVA against E. coli and S. aureus, respectively. Furthermore, the attachment of human fibroblasts cells has been tested in vitro and depicted that the cells could proliferate and grow adhesively through the scaffolds, which may support these platforms or substitutes to be examined for clinical applications.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Zou, R. Xie, E. Hu, P. Qian, B. Lu, G. Lan, and F. Lu (2020). Protein-reduced gold nanoparticles mixed with gentamicin sulfate and loaded into konjac/gelatin sponge heal wounds and kill drug-resistant bacteria. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 148, 921–931.
H. D. Zomer, T. da Silva Jeremias, B. Ratner, and A. G. Trentin (2020). Mesenchymal stromal cells from dermal and adipose tissues induce macrophage polarization to a pro-repair phenotype and improve skin wound healing. Cytotherapy. 22, 247–260.
P. Zou, W.-H. Lee, Z. Gao, D. Qin, Y. Wang, J. Liu, T. Sun, and Y. Gao (2020). Wound dressing from polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan electrospun fiber membrane loaded with OH-CATH30 nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 232, 115786.
H. A. Radwan, R. A. Ismail, S. A. Abdelaal, B. A. Al Jahdaly, A. Almahri, M. K. Ahmed, and K. Shoueir (2021). Electrospun polycaprolactone nanofibrous webs containing Cu–Magnetite/Graphene oxide for cell viability, antibacterial performance, and dye decolorization from aqueous solutions. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05363-7.
A. A. Menazea, M. M. Eid, and M. K. Ahmed (2020). Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of antimicrobial activity of novel Chitosan/Tigecycline composite. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 147, 194–199.
M. M. Sayed, H. M. Mousa, M. R. El-Aassar, N. M. El-Deeb, N. M. Ghazaly, M. M. Dewidar, and A. Abdal-hay (2019). Enhancing mechanical and biodegradation properties of polyvinyl alcohol/silk fibroin nanofibers composite patches for cardiac tissue engineering. Mater. Lett. 255, 126510.
A. Abdal-hay, M. Taha, H. M. Mousa, M. Bartnikowski, M. L. Hassan, M. Dewidar, and S. Ivanovski (2019). Engineering of electrically-conductive poly (ε-caprolactone)/multi-walled carbon nanotubes composite nanofibers for tissue engineering applications. Ceram. Int. 45, 15736–15740.
A. A. Hassan, H. A. Radwan, S. A. Abdelaal, N. S. Al-Radadi, M. K. Ahmed, K. R. Shoueir, and M. A. Hady (2021). Polycaprolactone based electrospun matrices loaded with Ag/hydroxyapatite as wound dressings: Morphology, cell adhesion, and antibacterial activity. Int. J. Pharm. 593, 120143.
S. Abolghasemzade, M. Pourmadadi, H. Rashedi, F. Yazdian, S. Kianbakht, and M. Navaei-Nigjeh (2021). PVA based nanofiber containing CQDs modified with silica NPs and silk fibroin accelerates wound healing in a rat model. J. Mater. Chem. B. 9, 658–676.
Y. Agarwal, P. S. Rajinikanth, S. Ranjan, U. Tiwari, J. Balasubramnaiam, P. Pandey, D. K. Arya, S. Anand, and P. Deepak (2021). Curcumin loaded polycaprolactone-/polyvinyl alcohol-silk fibroin based electrospun nanofibrous mat for rapid healing of diabetic wound: An in-vitro and in-vivo studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 176, 376–386.
M. I. Wuriantika, J. Utomo, M. Nurhuda, and D. Santjojo (2021). Nanostructure, porosity and tensile strength of PVA/Hydroxyapatite composite nanofiber for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Today Proc. 44, 3203–3206.
M. A. Norouzi, M. Montazer, T. Harifi, and P. Karimi (2021). Flower buds like PVA/ZnO composite nanofibers assembly: Antibacterial, in vivo wound healing, cytotoxicity and histological studies. Polym. Test. 93, 106914.
M. Keshvardoostchokami, S. S. Majidi, P. Huo, R. Ramachandran, M. Chen, and B. Liu (2021). Electrospun nanofibers of natural and synthetic polymers as artificial extracellular matrix for tissue engineering. Nanomaterials. 11, 21.
K. R. Shoueir, A. M. Atta, A. A. Sarhan, and M. A. Akl (2017). Synthesis of monodisperse core shell PVA@P(AMPS-co-NIPAm) nanogels structured for pre-concentration of Fe(III) ions. Environ. Technol. 38, 967–978.
R. R. Fouad, H. A. Aljohani, and K. R. Shoueir (2016). Biocompatible poly(vinyl alcohol) nanoparticle-based binary blends for oil spill control. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 112, 42–52.
A. M. Atta, G. A. El-Mahdy, H. A. Al-Lohedan, and K. R. Shoueir (2015). Electrochemical behavior of smart N-isopropyl acrylamide copolymer nanogel on steel for corrosion protection in acidic solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 10, 870–882.
J. Yun, J. S. Im, Y.-S. Lee, and H.-I. Kim (2011). Electro-responsive transdermal drug delivery behavior of PVA/PAA/MWCNT nanofibers. Eur. Polym. J. 47, 1893–1902.
T. M. Tamer, M. M. Sabet, A. M. Omer, E. Abbas, A. I. Eid, M. S. Mohy-Eldin, and M. A. Hassan (2021). Hemostatic and antibacterial PVA/Kaolin composite sponges loaded with penicillin–streptomycin for wound dressing applications. Sci. Rep. 11, 1–15.
S. Sultana, M. S. Hossain, M. Mahmud, M. Bin Mobarak, M. H. Kabir, N. Sharmin, and S. Ahmed (2021). UV-assisted synthesis of hydroxyapatite from eggshells at ambient temperature: cytotoxicity, drug delivery and bioactivity. RSC Adv. 11, 3686–3694.
K. Szyszka, J. Rewak-Soroczynska, A. Dorotkiewicz-Jach, K. A. Ledwa, A. Piecuch, M. Giersig, Z. Drulis-Kawa, and R. J. Wiglusz (2020). Structural modification of nanohydroxyapatite Ca10 (PO4) 6 (OH) 2 related to Eu3+ and Sr2+ ions doping and its spectroscopic and antimicrobial properties. J. Inorg. Biochem. 203, 110884.
M. K. Ahmed, S. F. Mansour, R. Al-Wafi, S. I. El-dek, and V. Uskoković (2019). Tuning the mechanical, microstructural, and cell adhesion properties of electrospun ε-polycaprolactone microfibers by doping selenium-containing carbonated hydroxyapatite as a reinforcing agent with magnesium ions. J. Mater. Sci. 54, 14524–14544.
M. K. Ahmed, S. F. Mansour, R. Al-Wafi, and A. Anter (2020). Composition and design of nanofibrous scaffolds of Mg/Se-hydroxyapatite/graphene oxide@ ε-polycaprolactone for wound healing applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 7472–7485.
K. Shoueir, M. K. Ahmed, S. A. A. Gaber, and M. El-Kemary (2020). Thallium and selenite doped carbonated hydroxyapatite: microstructural features and anticancer activity assessment against human lung carcinoma. Ceram. Int. 46, 5201–5212.
A. A. Menazea, S. A. Abdelbadie, and M. K. Ahmed (2020). Manipulation of AgNPs coated on selenium/carbonated hydroxyapatite/ε-polycaprolactone nano-fibrous via pulsed laser deposition for wound healing applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 508, 145299.
M. K. Ahmed, S. F. Mansour, M. S. Mostafa, R. Darwesh, and S. I. El-dek (2019). Structural, mechanical and thermal features of Bi and Sr co-substituted hydroxyapatite. J. Mater. Sci. 54, 1977–1991.
S. F. Mansour, S. I. El-Dek, S. V. Dorozhkin, and M. K. Ahmed (2017). Physico-mechanical properties of Mg and Ag doped hydroxyapatite/chitosan biocomposites. New J. Chem. 41, 13773–13783.
M. T. Elsayed, A. A. Hassan, S. A. Abdelaal, M. M. Taher, M. K. Ahmed, and K. R. Shoueir (2020). Morphological, antibacterial, and cell attachment of cellulose acetate nanofibers containing modified hydroxyapatite for wound healing utilizations. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9 (6), 13927–13936.
S. F. Mansour, S. I. El-dek, and M. K. Ahmed (2017). Tailoring the structure of biphasic calcium phosphate via synthesis procedure. Mater. Res. Express. 4, 125015.
S. C. Veerla, J. Kim, H. Sohn, and S. Y. Yang (2019). Controlled nanoparticle synthesis of Ag/Fe co-doped hydroxyapatite system for cancer cell treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 98, 311–323.
C. S. Ciobanu, F. Massuyeau, L. V. Constantin, and D. Predoi (2011). Structural and physical properties of antibacterial Ag-doped nano-hydroxyapatite synthesized at 100 C. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 6, 1–8.
C. Shi, J. Gao, M. Wang, J. Fu, D. Wang, and Y. Zhu (2015). Ultra-trace silver-doped hydroxyapatite with non-cytotoxicity and effective antibacterial activity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 55, 497–505.
S. Kamonwannasit, C. M. Futalan, P. Khemthong, T. Butburee, A. Karaphun, and P. Phatai (2020). Synthesis of copper-silver doped hydroxyapatite via ultrasonic coupled sol-gel techniques: structural and antibacterial studies. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 96, 452–463.
B. A. Al Jahdaly, N. S. Al-Radadi, G. M. G. Eldin, A. Almahri, M. K. Ahmed, K. Shoueir, and I. Janowska (2021). Selenium nanoparticles synthesized using an eco-friendly method: Dye decolorization from aqueous solutions, cell viability, antioxidant, and antibacterial effectiveness. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 11, 85–87.
F. Liu, X. Wang, T. Chen, N. Zhang, Q. Wei, J. Tian, Y. Wang, C. Ma, and Y. Lu (2020). Hydroxyapatite/silver electrospun fibers for anti-infection and osteoinduction. J. Adv. Res. 21, 91–102.
M. F. H. Abd El-Kader, M. K. Ahmed, M. T. Elabbasy, M. Afifi, and A. A. Menazea (2021). Morphological, ultrasonic mechanical and biological properties of hydroxyapatite layers deposited by pulsed laser deposition on alumina substrates. Surf. Coatings Technol. 409, 126861.
H. Shi, Z. Zhou, W. Li, Y. Fan, Z. Li, and J. Wei (2021). Hydroxyapatite based materials for bone tissue engineering: a brief and comprehensive introduction. Crystals. 11, 149.
T. E. Paterson, R. Shi, J. Tian, C. J. Harrison, M. De Sousa Mendes, P. V. Hatton, Z. Li, and I. Ortega (2020). Electrospun scaffolds containing silver-doped hydroxyapatite with antimicrobial properties for applications in orthopedic and dental bone surgery. J. Funct. Biomater. 11, 58.
Á. de Jesús Ruíz-Baltazar, S. Y. Reyes-López, P. N. Silva-Holguin, D. Larrañaga, M. Estévez, and R. Pérez (2018). Novel biosynthesis of Ag-hydroxyapatite: Structural and spectroscopic characterization. Results Phys. 9, 593–597.
A. Fakharzadeh, R. Ebrahimi-Kahrizsangi, B. Nasiri-Tabrizi, and W. J. Basirun (2017). Effect of dopant loading on the structural features of silver-doped hydroxyapatite obtained by mechanochemical method. Ceram. Int. 43, 12588–12598.
B. Yilmaz, A. Z. Alshemary, and Z. Evis (2019). Co-doped hydroxyapatites as potential materials for biomedical applications. Microchem. J. 144, 443–453.
R. B. Bostancioglu, M. Gurbuz, A. G. Akyurekli, A. Dogan, A. S. Koparal, and A. T. Koparal (2017). Adhesion profile and differentiation capacity of human adipose tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells grown on metal ion (Zn, Ag and Cu) doped hydroxyapatite nano-coated surfaces. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces. 155, 415–428.
M. H. Teaima, F. A. Abdelnaby, M. Fadel, M. A. El-Nabarawi, and K. R. Shoueir (2020). Synthesis of biocompatible and environmentally nanofibrous mats loaded with moxifloxacin as a model drug for biomedical applications. Pharmaceutics. 12, 1029.
M. F. Abdelbar, R. S. Shams, O. M. Morsy, M. A. Hady, K. Shoueir, and R. Abdelmonem (2020). Highly ordered functionalized mesoporous silicate nanoparticles reinforced poly (lactic acid) gatekeeper surface for infection treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 156, 858–868.
Q. Wang, P. Tang, X. Ge, P. Li, C. Lv, M. Wang, K. Wang, L. Fang, and X. Lu (2018). Experimental and simulation studies of strontium/zinc-codoped hydroxyapatite porous scaffolds with excellent osteoinductivity and antibacterial activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 462, 118–126.
Y.-C. Liu, Y.-T. Lee, T.-C. Huang, G.-S. Lin, Y.-W. Chen, B.-S. Lee, and K.-L. Tung (2021). In vitro bioactivity and antibacterial activity of strontium-, magnesium-, and zinc-multidoped hydroxyapatite porous coatings applied via atmospheric plasma spraying. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 4 (3), 2523–2533.
B. Singh, A. K. Dubey, S. Kumar, N. Saha, B. Basu, and R. Gupta (2011). In vitro biocompatibility and antimicrobial activity of wet chemically prepared Ca10− xAgx (PO4) 6 (OH) 2 (0.0≤ x≤ 0.5) hydroxyapatites. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 31, 1320–1329.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mosaad, K.E., Shoueir, K.R. & Dewidar, M.M. Fabrication of Multifunctional Wound Dressing Composite Biomaterials Composed of Ag/Mg-Hydroxyapatite Doped Electrospun Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) Nanofibers for Skin Tissue Regeneration. J Clust Sci 34, 135–146 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02195-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02195-1