Abstract
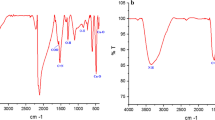
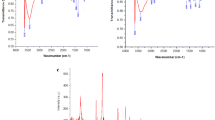
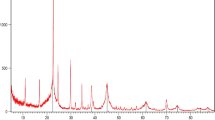
The present study, evaluate the anti-cancer properties of nickel oxide nanoparticles functionalized by glutamic acid and conjugated with thiosemicarbazide (NiO@Glu/TSC). First, the NiO@Glu/TSC nanoparticles were prepared using co-condensation reaction. Different techniques were achieved for confirming the synthesized nanoparticles such as Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), DLS (dynamic light scattering) and ZP (zeta potential) analysis. Interestingly, the transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) results indicated that the structure and size of NiO@Glu/TSC nanoparticles were spherical ranging from 20 to 80 nm. NiO@Glu/TSC nanoparticles revealed significant growth inhibition of MCF-7 (human breast cancer) cells with IC50 values of 298.33 μg/mL, while no significant toxicity was evaluated in HEK293 (normal human embryonic kidney) cells after using in vitro toxicity method. Compared with HEK293 cells, MCF-7 cells elucidated a higher sensitivity to NiO@Glu/TSC nanoparticles. To determine the induction of apoptosis or necrosis, cells were double stained with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-Annexin V and Propidium Iodide (PI) and assessed by flow cytometry. Moreover, to elucidate the nuclear change through apoptosis, Hoechst 33258 staining was examined to investigate morphological features in the nuclei of MCF-7 cells. The results firmly suggest that NiO@Glu/TSC nanoparticles can be as a potential therapeutic agent for cancer treatment.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Bray, J. Ferlay, I. Soerjomataram, R. L. Siegel, L. A. Torre, and A. Jemal (2018). CA Cancer J. Clin. 68, 394.
I. Baldea, A. Florea, D. Olteanu, S. Clichici, L. David, B. Moldovan, et al. (2020). Nanomedicine 15, 55.
P. Navya, A. Kaphle, S. Srinivas, S. K. Bhargava, V. M. Rotello, and H. K. Daima (2019). Nano Converg 6, 23.
G. Gahlawat and A. R. Choudhury (2019). RSC Adv. 9, 12944.
Z. Amani-Beni and A. Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh (2018). Anal. Chim. Acta 1031, 47.
K. Lingaraju, H. R. Naika, H. Nagabhushana, K. Jayanna, S. Devaraja, and G. Nagaraju (2020). Arab. J. Chem. 13, 4712.
G. Pelosi (2010). Open Crystallogr. J. 3, 16.
N. P. Prajapati and H. D. Patel (2019). Synth. Commun. 49, 2767.
S. A. S. Shandiz, A. Montazeri, M. Abdolhosseini, S. H. Shahrestani, M. Hedayati, Z. Moradi-Shoeili, et al. (2018). J. Clust. Sci. 29, 1107.
J. L. Navarrete, V. Hernandez, and F. Ramirez (1995). J. Mol. Struct. 348, 249.
K. Barick, A. Sharma, N. G. Shetake, R. Ningthoujam, R. Vatsa, P. Babu, et al. (2015). Dalton Trans. 44, 14686.
P. Bindu and M. R. P. Kurup (1997). Transit. Met. Chem. 22, 578.
A. Kumar, A. Saxena, A. De, R. Shankar, and S. Mozumdar (2013). Adv. Nat. Sci: Nanosci. 4, 025009.
C. Bonaccorso, T. Marzo, and D. La Mendola (2020). Pharmaceuticals 13, 4.
P. J. Jansson, D. S. Kalinowski, D. J. Lane, Z. Kovacevic, N. A. Seebacher, L. Fouani, et al. (2015). Pharmacol. Res. 100, 255.
N. R. Jyothi, N. M. Farook, M. Cho, and J. Shim (2013). Asian J. Chem. 25, 5841.
M. Muralisankar, S. M. Basheer, J. Haribabu, N. S. Bhuvanesh, R. Karvembu, and A. Sreekanth (2017). Inorg. Chim. Acta 466, 61.
M. Jarestan, K. Khalatbari, A. Pouraei, S. A. Sadat Shandiz, S. Beigi, M. Hedayati, et al. (2020). 3 Biotech. 10, 1.
J. L. Fox and M. MacFarlane (2016). Br. J. Cancer. 115, 5.
B. A. Carneiro and W. S. El-Deiry (2020). Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 17, 395–417.
S. Elmore (2007). Toxicol. Pathol. 35, 495.
J. Wang, X. Deng, and F. Zhang (2014). Nanoscale Res. Lett. 9, 117.
M. A. Siddiqui, M. Ahamed, J. Ahmad, M. A. Majeed Khan, J. Musarrat, A. A. Al-Khedhairy, et al. (2012). Food Chem. Toxicol. 50, 641.
S. Khan, A. A. Ansari, A. Malik, A. A. Chaudhary, J. B. Syed, and A. A. Khan (2019). J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 52, 12–17.
P. Kalaivani, S. Saranya, P. Poornima, R. Prabhakaran, F. Dallemer, V. V. Padma, and K. Natarajan (2014). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 82, 584.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbaszadeh, N., Jaahbin, N., Pouraei, A. et al. Preparation of Novel Nickel Oxide@ Glutamic/Thiosemicarbazide Nanoparticles: Implications for Cytotoxic and Anti-cancer Studies in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. J Clust Sci 33, 457–465 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-01995-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-01995-9