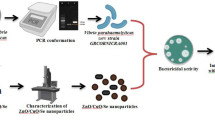
Abstract
Marine biofouling cause huge economic losses in the aquaculture industries as well as in the marine installation. Biofilm formation is an initial stage of biofouling. Conventional antifoulants including biocides and heavy metal induce toxicity to the aquatic organisms. Marine microorganisms provide a wide range of non-toxic biologically active molecules that helps in synthesis of antimicrobial compounds. The present study was aimed to synthesize zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) using cell free supernatant of Bacillus paramycoides. UV–visible spectrum showed the characteristic surface plasmon resonance absorption band for ZnO NPs at 372 nm. X-ray diffraction shows planes of hexagonal wurtzite structure of ZnO NPs and narrow peaks confirm the crystalline nature of ZnO NPs. Field emission scanning electron microscopic image shows spherical shaped particles in the range of 35–90 nm. Biosynthesized ZnO NPs cause membrane damage in bacterial cells and subsequent protein leakage. ZnO NPs showed remarkable antimicrobial activity against four marine biofilm forming bacteria i.e., Aeromonas hydrophila, Halomonas aquamarina, Escherichia coli and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Minimum inhibitory concentration value was observed as 10 μg ml−1 with all the bacterial strains. This study also highlights the rapid biosynthesis of ZnO NPs using cell free supernatant of B. paramycoides.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Inbakandan, C. Kumar, L. S. Abraham, R. Kirubagaran, R. Venkatesan, and S. A. Khan (2013). Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 111, 636–643.
N. P. Gule, N. M. Begum, and B. Klumperman (2016). Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 46, 535–555.
Y. Xiong and Y. Liu (2010). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86, 825–837.
N. P. Gule, M. de Kwaadsteniet, T. E. Cloete, and B. Klumperman (2013). Water Res 47, 1049–1059.
K. Mochida, K. Ito, H. Harino, A. Kakuno, and K. Fujii (2006). Environ Toxicol Chem 25, 3058–3064.
M. A. Champ (2003). Mar Pollut Bull 46, 935–940.
R. J. Huggett, M. A. Unger, P. F. Seligman, and A. O. Valkirs (1992). Environ Sci Technol 26, 232–237.
J. Atalah, G. A. Hopkins, and B. M. Forrest (2013). PLoS One 8, e80365.
J. Atalah, E. M. Newcombe, G. A. Hopkins, and B. M. Forrest (2014). Biofouling 30, 999–1010.
M. Y. Zhang, R. W. Field, and K. S. Zhang (2014). J Membrane Sci 471, 274–284.
Y. Ma, J. W. Metch, Y. Yang, A. Pruden, and T. Zhang (2016). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 92, fiw002.
H.C. Flemming. Microbial Biofouling: Unsolved Problems, Insufficient Approaches, and Possible Solutions. In: F. HC, W. J, S. U (Eds.), Biofilm Highlights, vol 5, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2011, pp. 81-109.
K. M. Reddy, K. Feris, J. Bell, D. G. Wingett, C. Hanley, and A. Punnoose (2007). Appl Phys Lett 90, 2139021–2139023.
H. F. Hassan, A. M. Mansour, A. M. Abo-Youssef, B. E. Elsadek, and B. A. Messiha (2017). Clin Exp Pharmacol 44, 235–243.
P. J. Lu, S. W. Fang, W. L. Cheng, S. C. Huang, M. C. Huang, and H. F. Cheng (2018). J Food Drug Anal 26, 1192–1200.
X. Q. Hou, X. L. Ren, F. Q. Tang, D. Chen, and Z. P. Wang (2006). Chinese J Anal Chem 34, 303–306.
F. T. Muniz, M. A. Miranda, C. Morilla Dos Santos, and J. M. Sasaki (2016). Acta Crystallogr A Found Adv 72, 385–390.
U. Holzwarth and N. Gibson (2011). Nat Nanotechnol 6, 534.
P. Basnet, T. I. Chanu, D. Samanta, and S. Chatterjee (2018). J Photoch Photobio B 183, 201–221.
V. N. Kalpana and V. D. Rajeswari (2018). Bioinorg Chem Appl. 2018, 3569758.
B. Malaikozhundan, B. Vaseeharan, S. Vijayakumar, and M. P. Thangaraj (2017). J Photochem Photobiol B 174, 306–314.
B. Balraj, N. Senthilkumar, C. Siva, R. Krithikadevi, A. Julie, I. V. Potheher, and M. Arulmozhi (2017). Res Chem Intermediat 43, 2367–2376.
E. Selvarajan and V. Mohanasrinivasan (2013). Mater Lett 112, 180–182.
D. Kundu, C. Hazra, A. Chatterjee, A. Chaudhari, and S. Mishra (2014). J Photoch Photobio B 140, 194–204.
G. Rajivgandhi, M. Maruthupandy, T. Muneeswaran, M. Anand, and N. Manoharan (2018). Process Biochem 67, 8–18.
V. V. Kadam, J. P. Ettiyappan, and R. M. Balakrishnan (2019). Mater Sci Eng B-Adv 243, 214–221.
N. Rajabairavi, C. Raju, C. Karthikeyan, K. Varutharaju, S. Nethaji, A. Hameed, and A. Shajahan Biosynthesis of novel zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) using endophytic bacteria Sphingobacterium thalpophilum. in J. Ebenezar (ed.), Recent trends in materials science and applications, vol. 189 (Springer International Publishing, Switzerland, 2017), pp. 245–254.
S. Rehman, B. R. Jermy, S. Akhtar, J. F. Borgio, S. A. Azeez, V. Ravinayagam, R. Alindan, Z. H. Al Asalem, A. Buhameid, and A. Gani (2019). Artif. Cell Nanomed. B 47, 2072–2082.
P. Eaton, P. Quaresma, C. Soares, C. Neves, M. P. de Almeida, E. Pereira, and P. West (2017). Ultramicroscopy 182, 179–190.
M. Abinaya, B. Vaseeharan, M. Divya, A. Sharmili, M. Govindarajan, N. S. Alharbi, S. Kadaikunnan, J. M. Khaled, and G. Benelli (2018). J Trace Elem Med Bio 45, 93–103.
A. Sirelkhatim, S. Mahmud, A. Seeni, N. H. M. Kaus, L. C. Ann, S. K. M. Bakhori, H. Hasan, and D. Mohamad (2015). Nanomicro Lett 7, 219–242.
N. Jones, B. Ray, K. T. Ranjit, and A. C. Manna (2008). FEMS Microbiol Lett 279, 71–76.
O. Yamamoto (2001). International Journal of Inorganic Materials 3, 643–646.
K. Nithya and S. Kalyanasundharam (2019). OpenNano 4, 100024.
C. Hanley, J. Layne, A. Punnoose, K. M. Reddy, I. Coombs, A. Coombs, K. Feris, and D. Wingett (2008). Nanotechnology 19, 295103.
A. S. H. Hameed, C. Karthikeyan, A. P. Ahamed, N. Thajuddin, N. S. Alharbi, S. A. Alharbi, and G. Ravi (2016). Sci Rep 6, 24312.
R. Brayner, R. Ferrari-Iliou, N. Brivois, S. Djediat, M. F. Benedetti, and F. Fievet (2006). Nano Lett 6, 866–870.
Z. B. Huang, X. Zheng, D. H. Yan, G. F. Yin, X. M. Liao, Y. Q. Kang, Y. D. Yao, D. Huang, and B. Q. Hao (2008). Langmuir 24, 4140–4144.
R. Pati, R. K. Mehta, S. Mohanty, A. Padhi, M. Sengupta, B. Vaseeharan, C. Goswami, and A. Sonawane (2014). Nanomedicine 10, 1195–1208.
J. Sawai (2003). J Microbiol Meth 54, 177–182.
P. Bhattacharyya, B. Agarwal, M. Goswami, D. Maiti, S. Baruah, and P. Tribedi (2018). Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 111, 89–99.
A. Iswarya, B. Vaseeharan, M. Anjugam, B. Ashokkumar, M. Govindarajan, N. S. Alharbi, S. Kadaikunnan, J. M. Khaled, and G. Benelli (2017). Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 158, 257–269.
M. A. Champ (2000). Sci Total Environ 258, 21–71.
J. E. Eckman, D. Thistle, W. C. Burnett, G. L. J. Paterson, C. Y. Robertson, and P. J. D. Lambshead (2001). J Mar Res 59, 79–95.
I. Amara, W. Miled, R. Slama, and N. Ladhari (2018). Environ Toxicol Phar 57, 115–130.
T. Marudhupandi, T. T. A. Kumar, S. Prakash, J. Balamurugan, and N. B. Dhayanithi (2017). Aquacult Rep 8, 39–44.
Acknowledgement
The authors are thankful for the RUSA Scheme Phase 2.0 grant [F-24-51/2014–U, Policy (TNMulti-Gen), Department of Education, Govt. of India. Dt.09.10.2018]. Authors thank the authorities of Alagappa University, Karaikudi and Head, Department of Animal Health and Management for their kind encouragement and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dharmaraj, D., Krishnamoorthy, M., Rajendran, K. et al. Protein Leakage Induced Marine Antibiofouling Activity of Biosynthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. J Clust Sci 32, 643–650 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01827-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01827-2